Sekoia Operating Language (SOL)
Power and Simplicity in Security Analytics
Sekoia Operating Language (SOL) is a powerful, pipe-based query language designed specifically for modern security operations. Built with similarities to KQL (Kusto Query Language) and SQL, SOL combines familiar syntax with advanced security-focused capabilities to deliver exceptional performance when analyzing massive security datasets.
Datasources
SOL provides seamless access to all critical security data within Sekoia SOC platform:
| Data Source | Description | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
events |
Security events | Threat hunting, incident investigation, SOC reporting. You will receive events that are retained for the duration of your hot storage |
event_telemetry |
Telemetry on events | Analytics on your ingestion pipelines |
eternal_events |
Security events related to alerts or cases | Extract metrics from events related to alerts/cases. Access events related to an alert that are beyond your hot storage retention period |
alerts |
Security alerts and detections | SOC monitoring, alert pattern analysis |
cases |
Security incidents and cases | Case management, incident correlation |
custom_statuses |
Alerts and cases custom statuses | Reporting |
custom_priorities |
Cases custom priorities | Reporting |
cases |
Security incidents and cases | Case management, incident correlation |
communities |
Communities (for multi-tenant only) | Multi-tenant reporting |
intakes |
Data sources | Data source management, volume monitoring |
entities |
Company entities | Entity tracking, detailed reporting |
assets |
Known Assets | Asset Investigations |
asset_properties |
Listing known properties related to the Asset | Asset Investigations |
asset_partitions |
Partitions on a per Asset basis and Hygiene related to these | Understand and improve Hygiene state Note: Part of the Reveal plan |
asset_accounts |
Listing local users accounts related to the Asset | Impact analysis and incident correlation Note: Part of the Reveal plan |
Alerts properties
| Alert Property | Description |
|---|---|
| uuid | A unique identifier for the alert. |
| short_ID | A concise identifier for quick reference to the alert. |
| community_uuid | A unique identifier for the community the alert belongs to. |
| entity_uuid | A unique identifier representing the entity associated with the alert. |
| entity_name | The name of the entity linked to the alert. |
| rule_name | The name assigned to the rule that triggered the alert. |
| rule_pattern | The detection pattern of the alert. |
| detection_type | The method by which the alert was detected. |
| alert_type_category | The category of the alert. |
| alert_type_value | The type of the alert. |
| status | The current state of the alert (e.g., open, acknowledged, resolved). |
| urgency | The level of urgency assigned to the alert. |
| created_at | The date and time when the alert was initially created. |
| update_at | The date and time when the alert was last updated. |
| first_seen_at | The date and time of the first alert occurrence. |
| last_seen_at | The date and time of the last alert occurrence. |
| time_to_detect | Duration taken to identify the alert from its occurrence in seconds. |
| time_to_acknowledge | Time elapsed from detection to official acknowledgment of the alert in seconds. |
| time_to_respond | Duration taken to take action after acknowledgment in seconds. |
| time_to_resolve | The total time taken to completely resolve the alert in seconds. |
| time_to_ingest | The duration from alert generation to its final ingestion into the system in seconds. |
| occurrences | The number of alert occurrences |
| rule_instance_uuid | A unique identifier for the rule that generated the alert. |
| cases | List of cases associated to the alert. |
| assets | List of assets associated to the alert. |
| threats | List of threats associated the alert. |
Cases properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| uuid | A unique identifier for the case. |
| short_id | A concise identifier for quick reference to the case. |
| community_uuid | A unique identifier for the community related to the case. |
| title | The title or subject line of the case. |
| description | A detailed description outlining the case's context or issues. |
| priority | The importance level assigned to the case, indicating its urgency. |
| created_at | The date and time when the case was created. |
| created_by | The user or system that created the case. |
| created_by_type | The type of entity that created the case (e.g., user, automated system). |
| updated_at | The date and time when the case was last updated. |
| updated_by | The user or system that last updated the case. |
| updated_by_type | The type of user that last updated the case. |
| first_seen_at | The date and time when the case was first detected. |
| last_seen_at | The date and time when the case was last observed or updated. |
Custom statuses
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| uuid | A unique identifier for the custom status. |
| community_uuid | A unique identifier for the community related to the custom status. |
| level | The numeric level of the status. |
| created_at | The date and time when the custom status was created. |
| created_by | The user or system that created the custom status. |
| created_by_type | The type of entity that created the custom status (e.g., avatar, apikey). |
| updated_at | The date and time when the custom status was last updated. |
| updated_by | The user or system that last updated the custom status. |
| updated_by_type | The type of entity that last updated the custom status. |
| stage | The workflow stage of the status (e.g., New, In progress, Closed). |
| label | The display label for the status. |
| description | A text description of the status. |
| type | The type(s) this status applies to (e.g., case, alert). |
Custom priorities
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| uuid | A unique identifier for the custom priority. |
| community_uuid | A unique identifier for the community related to the custom priority. |
| level | The numeric level of the priority. |
| created_at | The date and time when the custom priority was created. |
| created_by | The user or system that created the custom priority. |
| created_by_type | The type of entity that created the custom priority (e.g., avatar, apikey). |
| updated_at | The date and time when the custom priority was last updated. |
| updated_by | The user or system that last updated the custom priority. |
| updated_by_type | The type of entity that last updated the custom priority. |
| color | The color associated with the priority (CSS variable or color name). |
| label | The display label for the priority. |
| description | A text description of the priority. |
Entities properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| uuid | A unique identifier for the entity. |
| name | The name of the entity. |
| alerts_generation | The alert generation mode of the entity. |
| description | The description of the entity. |
| entity_id | The ID of the entity. |
| community_uuid | A unique identifier for the community related to the entity. |
| created_at | The date and time when the entity was created. |
| updated_at | The date and time when the entity was last updated. |
Intakes properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| uuid | A unique identifier for the intake. |
| name | The name of the intake. |
| community_uuid | A unique identifier for the community related to the intake. |
| entity_uuid | A unique identifier for the entity related to the intake. |
| format_uuid | A unique identifier for the format related to the intake. |
| intake_key | The intake key of the intake. |
| created_at | The date and time when the intake was created. |
| created_by | The user or system that created the intake. |
| created_by_type | The type of entity that created the intake (e.g., avatar, apikey). |
| updated_at | The date and time when the intake was last updated. |
| updated_by | The user or system that last updated the intake. |
| updated_by_type | The type of user that last updated the intake. |
| is_custom_format | Indicate if the intake uses a custom format. |
| connector_configuration_uuid | A unique identifier for the connector configuration related to the intake. |
Communities properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| uuid | A unique identifier for the community. |
| name | The name of the community. |
| description | The description of the community. |
| homepage_url | The homepage url of the community. |
| picture_mode | The picture mode of the community. |
| created_at | The date and time when the community was created. |
| created_by | The user or system that created the community. |
| created_by_type | The type of entity that created the community (e.g., avatar, apikey). |
| updated_at | The date and time when the community was last updated. |
| company_size | The size of the company. |
| company_security_team_size | The size of the security team. |
| company_sector | The sector of the company. |
| company_location | The location of the company. |
| is_parent | Indicate if the community is a parent community. |
| parent_uuid | A unique identifier of the parent community. |
| subcommunities | Indicate if the community has subcommunities. |
| is_mfa_enforced | Indicate if MFA is enforced at the community level. |
| session_timeout | The duration before users are automatically logged after inactivity. |
| disable_inactive_avatars | Indicate if users are disabled after 90 days of inactivity. |
| disabled | Indicate if the community is disabled. |
Assets
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| uuid | A unique identifier for the asset. |
| community_uuid | A unique identifier for the community related to the asset. |
| name | The name of the Asset |
| type | Type of asset (host, account or network.) |
| category | Category of the asset |
| criticality | Criticality of the asset |
| created_at | The date and time when the asset was created. |
| updated_at | The date and time when the asset was last updated. |
| revoked | Indicates whether the asset is revoked |
| reviewed | Indicates if the asset has been reviewed |
| atoms | List of related names/identifiers (e.g., hostname, IPs, etc.) |
Asset Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| asset_uuid | UUID of the asset to which the property is associated |
| value | The value of the property (e.g., darwin) |
| name | The name of the property (e.g., os) |
Asset Partitions
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| asset_uuid | UUID of the asset to which the partitions is associated |
| community_uuid | UUID of the community the asset belongs to |
| asset_name | The name of the asset that the partitions is associated with |
| last_seen | Last time the asset was seen |
| mountpoint | Partition mount point (e.g., C:) |
| encrypted | Whether the partition is encrypted (true/false) |
Asset Accounts
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| asset_uuid | UUID of the asset to which the accounts is associated |
| community_uuid | UUID of the community the asset belongs to |
| asset_name | The name of the asset that the partitions is associated with |
| last_seen | Last time the asset was seen |
| username | Name of the local user account |
| is_enabled | Whether the account is enabled |
| is_admin | Whether the account has administrative privileges |
| last_logon | Last time the account was used to log in |
| bad_password_count | Number of failed logon attempts |
| number_of_logons | Total number of logons recorded |
| account_type | Type of account (LocalUser, MicrosoftAccount, …) |
Event Telemetry
The event_telemetry data source provides aggregated metrics about the events processed by your intakes. It allows you to monitor, report, and troubleshoot data ingestion across your Sekoia.io tenant.
Each record in event_telemetry represents a time-bucketed summary of event activity for a given intake, including the number of events, total data volume, event sizes, and processing lags. This makes it easy to:
- Analyze your data usage over time, per intake
- Identify anomalies such as sudden spikes in data volume or processing delays
- Detect potential misconfigurations that could lead to unexpected data costs or ingestion issues
Typical Use Cases:
- Usage reporting: Track how much data each intake is sending over specific timeframes.
- Performance monitoring: Observe event size distributions and processing lags to ensure optimal pipeline performance.
- Root cause analysis: Investigate policy violations or overages by drilling down into intake-level telemetry.
You can query event_telemetry in the SOL query builder and combine it with other sources (e.g., intakes) to enrich your reports with intake names and configurations.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| community_uuid | UUID of the community the events belongs to |
| intake_uuid | UUID of the intake source generating the events |
| intake_dialect_uuid | UUID representing the dialect used for the intake |
| bucket_start_date | UTC timestamp representing the beginning of the aggregation window |
| bucket_end_date | UTC timestamp representing the end of the aggregation windows |
| occurrences | Number of events in the aggregation |
| total_message_size | Total size (in bytes) of raw events in the bucket |
| max_message_size | Size (in bytes) of the largest raw event in the bucket |
| min_message_size | Size (in bytes) of the smallest raw event in the bucket |
| total_event_size | Total size (in bytes) of all events in the bucket |
| max_event_size | Size (in bytes) of the largest event in the bucket |
| min_event_size | Size (in bytes) of the smallest event in the bucket |
| max_lag | Maximum observed delay (in seconds) between the event's timestamp and its reception date. |
| min_lag | Minimum observed delay (in seconds) between the event's timestamp and its reception date. |
| total_lag | Total accumulated lag (in seconds) across all events in the bucket. |
| max_processing_lag | Maximum processing time (in seconds) taken by Sekoia.io to process an event. |
| min_processing_lag | Minimum processing time (in seconds) taken by Sekoia.io to process an event. |
| total_processing_lag | Total accumulated processing time (in seconds) for all events in the bucket. |
Filters
Note
Filters are currently released under the Early Access Program.
Filters make SOL queries dynamic and interactive. They let you reuse the same query across dashboards and contexts by substituting values dynamically — without modifying the query itself.
Filters are referenced using the ?filter_name syntax.
When a query uses one or more filters, the Query Builder and Dashboards:
- Automatically detect them,
- Display user input fields (text, date, select, etc.),
- Re-execute the query whenever a filter value changes.
Syntax
Use the ?filter_name notation anywhere you would normally write a static value:
<table name>
| where <column> == ?filter_name
Example with a time range filter
events
| where timestamp between (?time.start .. ?time.end)
Built-in Filters
Certain filters are predefined and automatically available across all queries and dashboards.
| Filter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
?time.start |
datetime | Start of the time range to analyze |
?time.end |
datetime | End of the time range to analyze |
?communities |
string[] | UUID of all the communities of the workspace |
?intakes |
string[] | UUID of all the intakes of the workspace |
Custom Filters
You can create additional filters for values that depend on your investigation context (e.g., hostname, domain, community, entity, etc.).
Example
events
| where timestamp between (?time.start .. ?time.end)
| where process.name == ?process_name
| select timestamp, host.name, user.name, process.name, process.command_line
| order by timestamp desc
| limit 100
Filters in SOL are created and managed in the Query Builder or Dashboard editor.
Each filter defines how a variable (referenced as ?filter_name) behaves in queries — its input type, allowed values, and how it is displayed to end users.
When creating or editing a filter, you can:
- Select its type (Text, Boolean, Time, etc.)
- Add a description to clarify its purpose
- Optionally define authorized values — either statically or dynamically
- Preview how the filter will appear to users
- Copy the syntax (
?filter_name) to reuse in SOL queries
Supported Types
SOL filters support the following types:
| Type | Example usage | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Text | where user.name == ?username |
Free text input |
| Boolean | where event.success == ?is_success |
Displayed as toggle |
| Time | where timestamp between (?time.start .. ?time.end) |
Common in dashboards |
| Single Selection | where timestamp == ?alert_uuid |
One value among the accepted ones |
| Multiple Selection | where host.name in ?hostnames |
Multiple values are allowed |
Authorized Values
For Single or Multiple selection filters, you can define authorized values in two ways:
Static List
Enter comma-separated values directly in the configuration panel.
Example:
powershell.exe, cmd.exe, rundll32.exe, chrome.exe
Dynamic List
Generate authorized values automatically using a SOL query.
Example:
events
| distinct process.name
| limit 100
Note
You can dissociate the technical value from its display label by using the syntax value:Label.
The value (left side) is used in the SOL query, while the label (right side) is what the user sees in the interface.
For example:
powershell.exe:PowerShell, cmd.exe:Command Prompt, bash:Bash
- The user sees PowerShell, Command Prompt, and Bash in the dropdown
- The query receives
powershell.exe,cmd.exe, orbashas the actual filter value
Behavior
- Values are separated by commas
- Labels after the colon (:) are optional
- Whitespace is trimmed automatically
- Duplicate values are silently ignored
- To include a comma inside a value, escape it with a backslash (
\)
Filter Preview
The Preview panel (right side of the editor) shows how the filter will appear to users in dashboards or query widgets.
Examples:
- Boolean filter → toggle with labels “On” / “Off”
- Text filter → input field
- Selection filters → dropdown menus
- Time filter → unified date range picker
How to Use Filters in Queries
To use a filter in a SOL query, reference its name prefixed by ?.
events
| where timestamp between (?time.start .. ?time.end)
| where process.name == ?process_name
| select timestamp, host.name, process.command_line
| order by timestamp desc
| limit 100
In this example:
?time.startand?time.endare predefined time filters.?process_nameis a custom filter (e.g., single selection).
When added to a dashboard, users can adjust these filters without modifying the query itself.
Best Practices
- ✅ Use descriptive names like
process_name,user_email,community_uuid. - ✅ Reuse filter names across queries to enable dashboard-level synchronization.
- ✅ Prefer dynamic lists when values depend on live data (e.g., entities, hosts).
- ✅ Use
?time.startand?time.endfor all time-based filtering. - ❌ Avoid numeric filters — they are not fully supported.
- ❌ Avoid hard-coded customer identifiers.
Operators
The next sections describe the different operators supported by Sekoia Operating Language (SOL).
Count rows
Description
Use the count operator to count the number of rows returned by the statement.
<table name>
| count
Example
Count the number of rows in the events table
events
| where timestamp > ago(30m)
| count
Select columns
Description
Use the select operator to define the columns to retrieve from the table. The order of the columns defined in the query will define the order of the columns in the results.
<table name>
| select <column name 1>, <column name 2>
Example
Select the columns host.name and source.ip from the events table
events
| select host.name, source.ip
| limit 100
Distinct
Description
Use the distinct operator to list all the unique values of a column.
<table name>
| distinct <column name>
Example
List the unique values of client.ip from the events table
events
| where timestamp > ago(24h)
| distinct client.ip
| limit 100
Where
Description
Use the where operator to filter rows by a list of conditions. Use parenthesis and keywords and, or to define complex conditions.
<table name>
| where <conditions>
Example 1
Filter the query by excluding events older than 5 days and retrieving only user agent from Mac
events
| where timestamp > ago(5d) and user_agent.device.name == 'Mac'
| limit 100
Example 2
Filter the query by excluding events older than 5 days and retrieving only user agent from Mac or Android
events
| where timestamp > ago(5d) and (user_agent.device.name == 'Mac' or user_agent.device.name == 'Android')
| limit 100
Example 3
Same as example 2 but with multiple where statements
events
| where timestamp > ago(5d)
| where user_agent.device.name == 'Mac' or user_agent.device.name == 'Android'
| limit 100
Nested query
Description
Use the in operator to use the results of a previous query.
let query = <table name> | select <column name>;
<table name>
| where <column name> in query
Example
let chromium_browsers = events
| where timestamp > ago(30d)
| where process.command_line contains " --type=renderer " and process.command_line contains " --extension-process "
| distinct process.command_line;
events
| where process.command_line in chromium_browsers
| aggregate count_agents=count_distinct(agent.id), executables=make_set(process.executable) by process.name
| order by count_agents
Sort results
Description
Use the order by operator to sort rows by a column. The default sort order is descending.
<table name>
| order by <column name> <desc | asc>
Example 1
Order the rows by the timestamp column in ascending order
events
| order by timestamp asc
| limit 100
Example 2
Order alerts by descending urgency and ascending first_seen_at
alerts
| order by urgency desc, first_seen_at asc
| select short_id, rule_name, urgency, first_seen_at
| limit 100
Limit results
Description
Use the limit operator to retrieve the last n number of rows based on the current sort order.
<table name>
| limit <integer>
Example
Get 1000 events from events table
events
| limit 1000
Get the Top n rows
Description
Use the top operator to returns the first n rows sorted by the specified column.
<table name>
| top <integer> by <column name> [asc | desc]
Example
Get the top 5 alerts with the most occurrences from alerts table in the last 7 days
alerts
| where created_at > ago(7d)
| top 5 by occurrences
Note that the query below is equivalent.
alerts
| order by occurrences desc
| limit 5
Create calculated columns
Description
You can use select or extend operators to create calculated columns.
Use select to specify the columns to display. When using extend, the calculated column is appended to the end of the table.
<table name>
| select <new column name> = <column name 1> + <column name 2>
Example
Create a calculated column named total that sums the time_to_detect, time_to_respond and time_to_resolve values
alerts
| select total = time_to_detect + time_to_respond + time_to_resolve
| limit 100
Aggregate rows
Description
Use the aggregate operator to group rows by a column and perform aggregations with a chosen function: count, sum, min, max, avg, count_distinct, make_set, countif.
<table name>
| aggregate <function> by <column name>
Example 1
Count the number of events per asset in the events table
events
| aggregate count() by sekoiaio.any_asset.name
| limit 100
Note that you can specify a column name for the aggregation. In the example below, the column name is defined as total.
events
| aggregate total = count() by sekoiaio.any_asset.name
| limit 100
Example 2
Count the number of events per source.ip and per action.outcome in the events table
events
| where timestamp >= ago(24h) and event.category == 'authentication'
| aggregate count() by source.ip, action.outcome
Example 3
Sum the values of 'time_to_detect' column in the alerts table
alerts
| aggregate sum(time_to_detect)
| limit 100
Example 4
Retrieve the minimum value of 'time_to_detect' column in the alerts table
alerts
| aggregate min(time_to_detect)
| limit 100
Example 5
Retrieve the maximum value of 'time_to_detect' column in the alerts table
alerts
| aggregate max(time_to_detect)
| limit 100
Example 6
Calculate the average value of 'time_to_detect' column in the alerts table
alerts
| aggregate avg(time_to_detect)
| limit 100
Example 7
Count unique values of 'source.ip' column in the events table
events
| aggregate count_distinct(source.ip)
| limit 100
Example 8
Create an array of the set of distinct values of 'source.ip' column in the events table.
Note that null values are ignored.
events
| aggregate make_set(source.ip)
| limit 100
Example 9
Count allowed and denied network events per destination port using countif
events
| where timestamp >= ago(24h) and event.category == 'network'
| aggregate allowed = countif(action.outcome == 'success'), denied = countif(action.outcome == 'failure') by destination.port
| order by denied desc
| limit 100
Render results in chart
Description
Use the render operator to display results in a chart to identify more easily anomalies or outliers. Supported charts are:
numberpiechartcolumnchartbarchartlinechart
<table name>
| aggregate <function> by <column name>
| render <chart_type> with (x=<column name>, y=<column name>, breakdown_by=<column name>, mode=<grouped | stacked>)
Example
Count the number of events per asset in the events table and render it in a bar chart.
events
| aggregate count() by sekoiaio.any_asset.name
| render barchart with (y=sekoiaio.any_asset.name)
| limit 100
Join tables
Description
Use the join operator to combine data from multiple tables, enriching the data context, filtering more accurately data.
Available join types are:
- inner join: Returns records that have matching values in both tables (default)
- left join: Returns all records from the left table, and the matched records from the right table
<left table name>
| inner join <right table name> on <left column name> == <right column name>
| select <model object>.<right column name>, <left column name>
When performing join, the right table is injected into a model object.
This model object (similar to a class Object in code development) contains a set properties. Each property represents a column of the original table.
Info
By convention, we consider that when using join, the left part of the statement represents the column of the left table and the right part of the statement represents the column of the right table.
Example 1
Join the tables events and intakes
events
| where timestamp > ago(24h)
| limit 100
| inner join intakes on sekoiaio.intake.uuid == uuid // sekoiaio.intake.uuid belongs to events table and uuid belongs to intakes table
| distinct intake.name
The model object default name is related to the table name it is originating from. In this case, the model name is intake since the join was performed on the intakes table.
Example 2
Join the tables alerts and entities
alerts
| where created_at > ago(24h)
| limit 100
| inner join entities on entity_uuid == uuid // entity_uuid belongs to alerts table and uuid belongs to entities table
| distinct entity.name
The model object default name is related to the table name it is originating from. In this case, the model name is entity since the join was performed on the entities table.
Define model object name
In this example, we define a specific name for the model object with the into operator.
alerts
| where created_at > ago(24h)
| inner join entities on entity_uuid == uuid into my_entity
| select my_entity.name
Lookup
Description
Use the lookup operator to extend a table. Extends the current table with values looked-up in another table.
Prefer the lookup operator over join when the right table is small enough to fit into memory to improve query performance.
Info
The result doesn't repeat columns from the right table that are the basis for the join operation.
The lookup operator only supports left join.
<left table name>
| lookup <right table name> on <left column name> == <right column name>
| aggregate <function> by <column name>
| order by <column name>
Similarly to join operator, lookup will inject the right table into a model object.
Compare
Description
Use the following operators to compare values.
| Comparator | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| == | Equals | 1 == 1 |
| =~ | Equals (case insensitive) | '.exe' == '.EXE' |
| != | Not equals | 1 != 0 |
| < | Less | 1 < 10 |
| <= | Less or equals | 4 <= 5 |
| > | Greater | 20 > 10 |
| >= | Greater or equals | 5 >= 4 |
In
Description
Use the in operator to filter the rows based on a set of case-sensitive strings.
Use in~ to filter on a set of case-insensitive strings.
<table name>
| where <column name> in [<value 1>, <value 2>]
Example 1
Find events where client.ip equals to theses values: 192.168.0.1, 192.168.0.2.
events
| where client.ip in ['192.168.0.1', '192.168.0.2']
| limit 100
Example 2
Find events where process.name equals to theses values ignoring case-sensitivity: powershell.exe, powershell_ise.exe.
events
| where process.name in~ ['powershell.exe', 'powershell_ise.exe']
| limit 100
Contains
Description
Use the contains operator to filter the rows that contains a case-sensitive string.
Use contains~ to switch to case-insensitive strings.
<table name>
| where <column name> contains <value 1>
Example 1
Find events where user.full_name contains the string Admin (case sensitive).
events
| where user.full_name contains 'Admin'
| limit 100
Example 2
Find events where user.full_name contains the string ADMIN (case insensitive).
events
| where user.full_name contains~ 'ADMIN'
| limit 100
Starts with
Description
Use the startswith operator to filter rows that starts with a case-sensitive string.
Use startswith~ to switch to case-insensitive strings.
<table name>
| where <column name> startswith <pattern>
Example 1
Find events where url.domain starts with the string api.prod.
events
| where url.domain startswith 'api.prod'
| limit 100
Example 2
Find events where process.command_line starts with the string Invoke ignoring case-sensitivity.
events
| where process.command_line startswith~ 'Invoke'
| limit 100
Ends with
Description
Use the endswith operator to filter rows that ends with a case-sensitive string.
Use endswith~ to switch to case-insensitive strings.
<table name>
| where <column name> endswith <pattern>
Example 1
Find events where url.path ends with the string /admin.
events
| where url.path endswith '/admin'
| limit 100
Example 2
Find events where process.command_line ends with the string .DLl ignoring case-sensitivity.
events
| where process.command_line endswith~ '.DLl'
| limit 100
Not
Description
Use the not operator to negate any comparison.
<table name>
| where not <column name> <comparison operator> <pattern>
Example 1
Find events where client.ip does not equal to theses values: 192.168.0.1, 192.168.0.2.
events
| where not client.ip in ['192.168.0.1', '192.168.0.2']
| limit 100
Example 2
Find events where user.full_name does not contain the string Admin (case sensitive).
events
| where not user.full_name contains 'Admin'
| limit 100
Example 3
Find events where process.command_line does not start with the string Invoke ignoring case-sensitivity.
events
| where not process.command_line startswith~ 'Invoke'
| limit 100
Example 4
Find events where process.command_line does not end with the string .DLl ignoring case-sensitivity.
events
| where not process.command_line endswith~ '.DLl'
| limit 100
Regex
Description
Use the matches regex operator to filter the rows based on a regex pattern.
<table name>
| where <column name> matches regex <pattern>
| Pattern | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
. |
Matches any character | ab. matches 'aba', 'abb', 'abz' |
? |
Repeat the preceding character zero or one times | abc? matches 'ab' and 'abc' |
+ |
Repeat the preceding character one or more times | ab+ matches 'ab', 'abb', 'abbb' |
* |
Repeat the preceding character zero or more times | ab* matches 'a', 'ab', 'abb', 'abbb' |
{} |
Minimum and maximum number of times the preceding character can repeat | a{2} matches 'aa'a{2,5} matches 'aa', 'aaa' and 'aaaa'a{2,} matches 'a' repeated two or more times |
| |
OR operator. The match will succeed if the longest pattern on either the left side OR the right side matches | abc|xyz matches 'abc' and 'xyz' |
(...) |
Forms a group. You can use a group to treat part of the expression as a single character | abc(def)? matches 'abc' and 'abcdef' but not 'abcd' |
[...] |
Match one of the character in the brackets Inside the brackets, - indicates a range unless - is the first character or escapedA ^ before a character in the brackets negates the character or range |
[abc] matches 'a', 'b', 'c'[-abc] matches '-', 'a', 'b', 'c'[^abc] matches any character except 'a', 'b', or 'c' |
Info
Some characters are reserved as operators: . ? + * | { } [ ] ( ) " \ .
Escape reserved operators with a preceding backslash \ or surround them with double quotes "".\@ renders as a literal '@'.\\ renders as a literal '\'."john@smith.com" renders as 'john@smith.com'.
Example
Find events where file.name contains '.sh'.
let StartTime = ago(1h);
let EndTime = now();
events
| where timestamp between (StartTime .. EndTime)
| where file.name matches regex '.*\.sh'
| limit 100
Variables
Description
Use the let operator to define variables.
let <variable name> = <string | integer>;
<table name>
| where <column name> == <variable name>
Example
Count the number of events in the last 24 hours.
let StartTime = ago(24h);
let EndTime = now();
events
| where event.created > StartTime and event.created <= EndTime
| count
Comments
Description
Use // to add comments in the query.
Example
// Comment the filtering condition
<table name>
//| where <column name> = <variable name>
| limit 100
Functions
Datetime: now()
Description
Returns the current UTC time, optionally offset by a given timespan.
Example
let time = now();
let time_earlier = now(-2d);
Datetime: ago()
Description
Returns a datetime value equal to the current UTC time minus the timespan.
| Syntax | Description | Example | Length of time |
|---|---|---|---|
| d | day time interval | 2d |
2 days |
| h | hour time interval | 1h |
1 hour |
| m | minute time interval | 30m |
30 minutes |
| s | second time interval | 10s |
10 seconds |
Example
let time = ago(1h);
Timestamp: bin()
Description
Rounds values down to an integer multiple of a given bin size.
Example
events
| aggregate count() by bin(timestamp, 1d)
Year
Description
Returns the year by a given date in the following format: YYYY.
Example
let time = year(now());
Month
Description
Returns the year and month by a given date in the following format: YYYY-MM.
Example
let time = month(now());
Week
Description
Returns the year and month by a given date in the following format: YYYY - Week {week number}.
Example
let time = week(now());
To scalar
Description
Use the toscalar function to return a constant value of a statement.
Example
let total = toscalar(alerts | where created_at >= ago(7d) | count);
alerts
| where created_at >= ago(7d)
| aggregate count() by detection_type
| extend percentage = (count / total) * 100
String: tolower()
Description
Converts a string to lowercase. This function is useful for normalizing text data for case-insensitive comparisons and analysis.
Syntax
tolower(<string>)
Parameters
string: A string value to be converted to lowercase
Return Value
Returns the lowercase version of the input string.
Example
Normalize user names to lowercase for consistent analysis:
events
| where timestamp > ago(24h) and user.name != null
| aggregate count_by_user = count() by user.name
| aggregate sum(count_by_user) by normalized_user = tolower(user.name)
| limit 100
String: toupper()
Description
Converts a string to uppercase. This function is useful for normalizing text data for case-insensitive comparisons and analysis.
Syntax
toupper(<string>)
Parameters
string: A string value to be converted to uppercase
Return Value
Returns the uppercase version of the input string.
Example
Normalize command lines to uppercase for consistent analysis:
events
| where timestamp > ago(24h) and process.command_line != null
| aggregate count_by_cmd = count() by process.command_line
| aggregate sum(count_by_cmd) by normalized_cmd = toupper(process.command_line)
| limit 100
String: extract()
Description
Extracts a match for a regular expression from a string. Optionally targets a specific capture group. This function is useful for parsing structured data from free-text fields such as URLs, log messages, or command lines.
Syntax
extract(<regex>, <capture_group>, <source>)
Parameters
regex: A regular expression pattern to match against the source string (required). Use the@prefix for raw string literals to avoid double-escaping backslashes (e.g.,@'https?://([^/]+)').capture_group: The capture group index to extract (required).0returns the entire match;1returns the first parenthesized group;2+for subsequent groups.source: The string to search (required)
Return Value
Returns the matched substring for the specified capture group. Returns null if the regex finds no match.
Example 1
Extract the domain from a URL:
events
| where timestamp > ago(24h) and url.original != null
| select timestamp, domain = extract(@'https?://([^/]+)', 1, url.original)
| limit 100
Example 2
Extract user identifiers from log messages:
events
| where timestamp > ago(24h) and message != null
| select timestamp, user_id = extract(@'user_(\d+)', 1, message)
| where user_id != null
| limit 100
String: replace_regex()
Description
Replaces all matches of a regular expression in a string with a specified replacement pattern. This function is useful for sanitizing, normalizing, or transforming string data in security investigations.
Syntax
replace_regex(<source>, <lookup_regex>, <rewrite_pattern>)
Parameters
source: The source string to search and replace within (required)lookup_regex: The regular expression to search for (required). Can contain capture groups in parentheses. Use the@prefix for raw string literals to avoid double-escaping backslashes.rewrite_pattern: The replacement pattern (required). Use$0for the whole match,$1for the first capture group,$2for the second, etc.
Return Value
Returns the modified string with all non-overlapping matches replaced. If no matches are found, the original string is returned unchanged.
Example 1
Strip the protocol from URLs:
events
| where timestamp > ago(24h) and url.original != null
| select timestamp, cleaned_url = replace_regex(url.original, @'https?://', '')
| limit 100
Example 2
Sanitize email addresses in logs:
events
| where timestamp > ago(24h) and user.email != null
| select timestamp, sanitized_email = replace_regex(user.email, @'(\w+)@.*', '$1@example.com')
| limit 100
Math: round()
Description
Rounds a number to a specified precision (number of decimal places). This function is useful for formatting numerical results and creating cleaner reports with rounded values.
Syntax
round(<number> [, <precision>])
Parameters
number: The number to round (required)precision: Number of decimal places to round to (optional, defaults to 0)
Return Value
Returns the rounded number to the specified precision.
Example
Round time_to_detect values to 2 decimal places for cleaner reporting:
alerts
| where created_at > ago(7d)
| select ttd_minutes = round(time_to_detect / 60.0, 2)
| limit 100
Type conversion: toint()
Description
Converts a value to a signed 32-bit integer representation. This function is useful for converting string fields to numeric values for comparisons, calculations, or filtering.
Syntax
toint(<value>)
Parameters
value: The value to convert to an integer (required). Can be a string, float, or other scalar type.
Return Value
Returns the integer representation of the value. Returns null if the conversion fails (e.g., non-numeric string).
If the input is a decimal number, the value is truncated to the integer portion (e.g., toint(2.9) returns 2).
Example 1
Convert a string field to integer for numeric comparison:
events
| where timestamp > ago(24h)
| select port_number = toint(destination.port)
| where port_number > 1024
| limit 100
Example 2
Convert and aggregate by numeric field:
events
| where timestamp > ago(24h)
| extend severity_int = toint(event.severity)
| aggregate count() by severity_int
| order by severity_int desc
Conditional: iff()
Description
Returns a value based on a conditional expression. Evaluates a boolean condition and returns one value if the condition is true, another value if the condition is false. This function is useful for data categorization and conditional transformations.
Syntax
iff(<condition>, <then_value>, <else_value>)
Parameters
condition: A boolean expression to evaluate (required)then_value: Value returned if condition is true (required)else_value: Value returned if condition is false (required)
Return Value
Returns the then_value when condition is true, otherwise returns else_value.
Example
Categorize alerts based on urgency and time to detect:
alerts
| where created_at > ago(7d)
| aggregate count() by severity_category = iff(urgency >= 80, "Critical",
iff(urgency >= 50, "High", "Medium"))
| limit 100
Null handling: coalesce()
Description
Returns the first non-null value from a list of expressions. This function is useful for providing fallback values when dealing with potentially null data, ensuring queries can handle missing or incomplete information gracefully.
Syntax
coalesce(<arg1>, <arg2>, [<arg3>, ...])
Parameters
arg1, arg2, ...: A list of expressions of the same type to evaluate (at least 2 arguments required)
Return Value
Returns the first non-null value from the argument list, or null if all arguments are null.
Example
Provide fallback values for user identification when some fields might be null:
events
| where timestamp > ago(24h)
| aggregate count() by user_identifier = coalesce(user.name, user.email, "Unknown")
| limit 100
Datetime: format_datetime()
Description
Formats datetime values using Python strftime format specifiers, enabling flexible datetime representation in SOL queries. Supports both datetime objects and ISO format datetime strings.
Syntax
format_datetime(<datetime>, <format>)
Parameters
datetime: Datetime object (from functions likenow()) or ISO format string to format (required)format: String specifying the output format using Python strftime specifiers (required)
Return Value
Returns a formatted string representation of the datetime.
Common Format Specifiers
| Specifier | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
%Y |
4-digit year | 2025 |
%m |
Month (01-12) | 12 |
%d |
Day of month (01-31) | 25 |
%H |
Hour (00-23) | 14 |
%M |
Minutes (00-59) | 30 |
%S |
Seconds (00-59) | 45 |
%B |
Full month name | December |
%b |
Abbreviated month | Dec |
%A |
Full weekday name | Monday |
Example
Format timestamps for cleaner reporting:
alerts
| where created_at > ago(24h)
| extend date_only = format_datetime(created_at, '%Y-%m-%d')
| extend readable_time = format_datetime(created_at, '%B %d, %Y at %H:%M')
| extend eu_format = format_datetime(created_at, '%d-%m-%Y')
| aggregate count() by date_only, readable_time, eu_format, detection_type
| limit 100
Aggregation: countif()
Description
Counts the number of rows for which a predicate evaluates to true. This function is used within the aggregate operator and is useful for computing conditional counts in a single query, such as counting successes and failures side by side.
Syntax
countif(<predicate>)
Parameters
predicate: A boolean expression to evaluate for each row (required). Rows where this evaluates totrueare counted; rows where it evaluates tofalseornullare not counted.
Return Value
Returns the count of rows for which the predicate is true. Returns 0 if no rows match.
Example 1
Count successful and failed login attempts per source IP:
events
| where timestamp > ago(24h) and event.category == 'authentication'
| aggregate success_count = countif(event.code == '4624'), failed_count = countif(event.code == '4625') by source.ip
| order by failed_count desc
| limit 100
Example 2
Count high-urgency vs. low-urgency alerts per detection type:
alerts
| where created_at > ago(7d)
| aggregate high = countif(urgency >= 80), low = countif(urgency < 80) by detection_type
SOL Datasets
SOL Datasets is a powerful CSV import feature that enables SOC analysts to enrich security investigations by importing external data sources directly into the SOL query environment. This capability transforms static data lookups into dynamic, queryable datasets that can be seamlessly integrated with security events, alerts, and other platform data.
Feature benefits
SOL Datasets addresses critical challenges in security operations:
- Enhanced Investigation Context: Import custom threat intelligence, critical security context, list of approved software and other contextual data
- Eliminates Manual Lookups: Replace time-consuming manual data correlation with automated joins
- Flexible Data Integration: Combine external data with events, alerts, and cases using SOL's powerful query language
Accessing SOL Datasets
SOL Datasets can be accessed from the Queries page in the SOL query builder interface:
- Navigate to Investigate > Queries in the main navigation
- Click the SOL Datasets button in the interface toolbar
- The SOL Datasets panel opens laterally, displaying available datasets

The datasets panel provides:
- Search functionality for finding specific datasets by their name
- Dataset cards displaying key metadata
- New dataset creation button
- Management controls for existing datasets
Dataset management interface
Each dataset is displayed as an information card containing:
- Dataset Name: Table name used in SOL queries
- Upload Date: When the dataset was imported (e.g., "09/30/2025 12:07:56")
- Author: User who uploaded the dataset (e.g., "John Doe")
- File Size: Dataset size in MB (e.g., "10MB")
- Actions: Delete option
The interface supports:
- Sorting: Datasets ordered by upload date (most recent first)
- Search: Filter datasets by name using the search bar
- Pagination: Navigate through large dataset collections
CSV import process
File requirements
CSV Import Requirements
Before importing your CSV file, ensure it meets these requirements:
- Column names follow snake_case format and are unique
- Column names are no longer than 128 characters
- The file is encoded in UTF-8 or ASCII
- The file size does not exceed 100 MB
Import workflow
Step 1: Initiate import
- Click + New dataset in the SOL Datasets panel
- The import modal opens with file selection interface
Step 2: File selection
- Drag and drop your CSV file or click Upload a file
- Browse and select your CSV file from the file system
- The system validates file format and requirements
Step 3: File preview and validation
- After selection, the system displays file details and any validation errors
- Preview shows first 100 rows of data for verification
- Column names are automatically detected
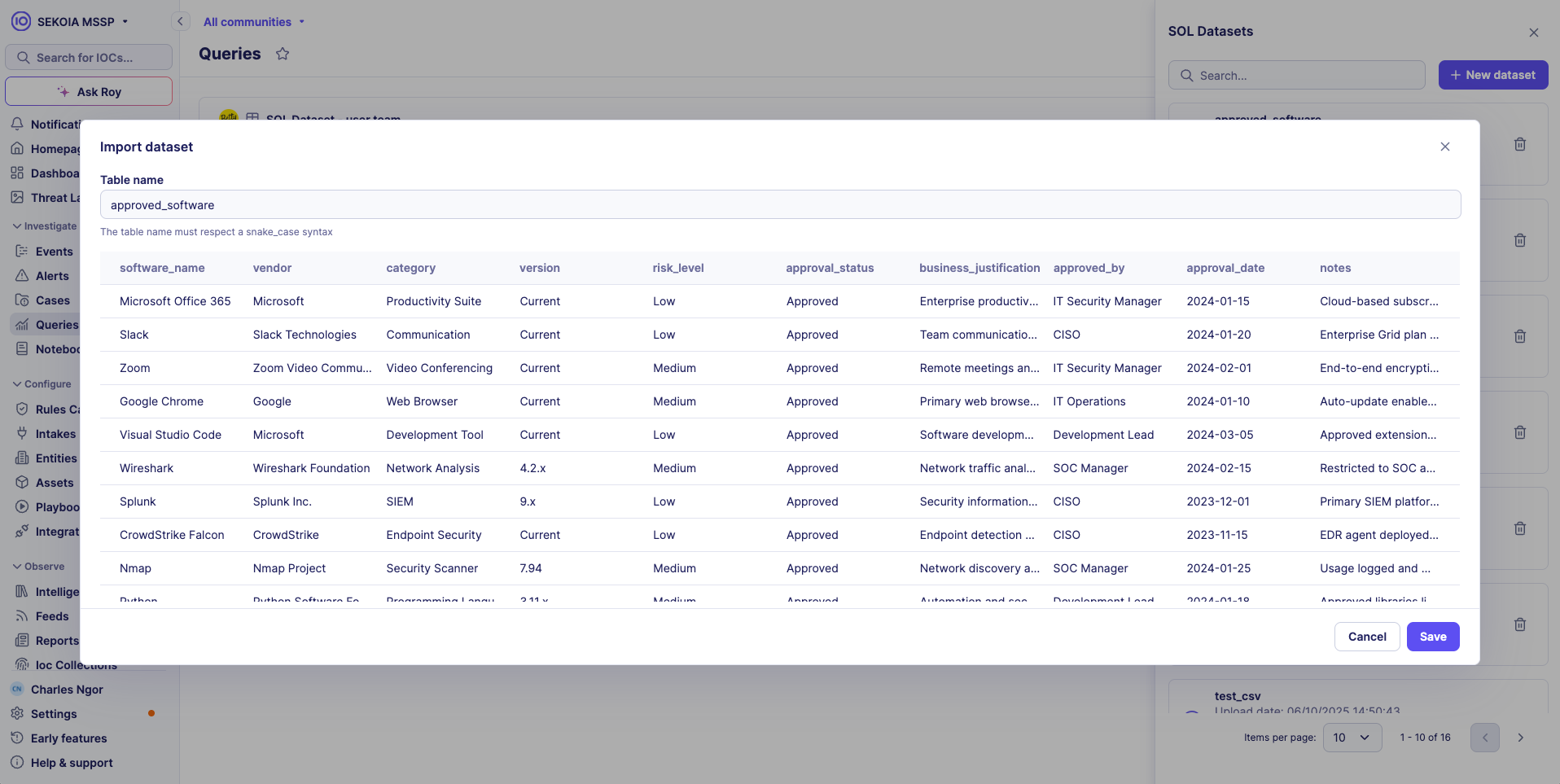
Step 4: Dataset configuration
- Dataset Name: Defaults to filename
- Community: Select target community (for multi-tenancy)
- Review settings and click Import
Step 5: Import completion
- The system processes the CSV file
- Dataset appears in the SOL Datasets panel
- Dataset is immediately available for use in SOL queries
Multi-tenancy and access control
SOL Datasets support multi-tenant environments with the following access patterns:
Shared access within community
- All datasets uploaded to a community are shared among all users within that community
- Any user can query any dataset within their community
- Dataset visibility is automatically scoped to the user's community
Sub-community limitations
- Sub-community users can only access datasets uploaded within their specific sub-community
- Sub-community users cannot access parent datasets
- This ensures data isolation and security between different organizational units
Parent community privileges
- Parent community users have access to their own datasets
- Parent tenant users can also access datasets from all sub-communities under their management
- This enables centralized oversight and cross-tenant analysis
Using datasets in SOL queries
Dataset discovery
SOL provides autocomplete functionality for imported datasets:
- Start typing in the SOL query editor
- Imported datasets appear in autocomplete suggestions
- Select the dataset name to include it in your query
Query integration
Imported datasets can be used like any other SOL data source:
Basic dataset query
authorized_domains
| limit 100
Detect unauthorized domains instantly:
events
| where timestamp > ago(24h) and url.domain != null
| where not url.domain in (authorized_domains | select url_domain)
| select timestamp, source.ip, url.domain
| limit 100
Correlate user activities with business roles:
events
| where timestamp > ago(24h)
| lookup user_roles on user.full_name == full_name into roles_list
| distinct user.full_name, roles_list.role
| limit 100
Best practices for dataset queries
Performance optimization
- Use
lookupinstead ofjoinwhen the imported dataset is small (< 10,000 rows) - Apply filters to main tables before joining with datasets
- Limit result sets using
limitoperator
Data quality
- Validate data consistency before importing
- Use consistent naming conventions across datasets
- Handle null values appropriately in join conditions
Query structure
// Filter main data source first
events
| where timestamp > ago(1h) and user.name != null
// Then join with SOL dataset. The modal object name is defined as 'dataset' here
| lookup user_roles_dataset on user.name == username into dataset
// Select relevant columns
| select timestamp, user.name, dataset.role, event.action
| limit 1000
Common use cases
Automatically identify and prioritize alerts from known malicious sources
Instantly correlate your alerts with external threat intelligence feeds to distinguish between noise and genuine threats. This query enriches recent alerts with threat context, helping analysts focus on the most critical security events first.
alerts
| where created_at > ago(24h)
| lookup threat_intel_dataset on source.ip == indicator_value into dataset
| where dataset.threat_type != null
| select rule_name, source.ip, dataset.threat_type, dataset.confidence
Understand event patterns across business units and system criticality
Transform raw security events into business-aware insights by correlating them with your asset inventory. Quickly identify which departments or critical systems are generating the most security events, enabling targeted investigation and resource allocation.
events
| where timestamp > ago(1h)
| lookup asset_inventory on host.name == hostname into dataset
| aggregate event_count = count() by dataset.department, dataset.criticality
| order by event_count desc
Detect privileged account activity and potential privilege escalation
Monitor administrative activities by correlating authentication events with your user directory. This helps identify unusual admin access patterns, shared accounts, or potential insider threats by tracking who is accessing what systems with elevated privileges.
events
| where event.category == 'authentication' and action.outcome == 'success'
| lookup user_directory on user.name == username into dataset
| where dataset.role == 'admin'
| aggregate count() by user.name, host.name
Troubleshooting common issues
Import failures
File format errors
- Issue: Column names contain spaces or special characters
- Solution: Convert to snake_case format (e.g., "User Name" → "user_name")
Encoding problems
- Issue: Special characters appear corrupted
- Solution: Save CSV file with UTF-8 encoding
Size limitations
- Issue: File exceeds 100 MB limit
- Solution: Split large files or filter to essential columns only
Query performance issues
Slow join operations
- Issue: Queries timeout or perform slowly
- Solution: Use
lookupinstead ofjoinfor smaller datasets
Memory limitations
- Issue: Large dataset queries fail
- Solution: Apply filters before joins, use
limitoperators
Data access problems
Dataset not found
- Issue: Dataset doesn't appear in autocomplete
- Solution: Verify dataset import completed successfully
Join mismatches
- Issue: Join operations return no results
- Solution: Check column names and data formats match exactly
Join examples
Join between events and communities tables (for Multi-tenant)
events
| where timestamp > ago(5m)
| limit 100
| join communities on sekoiaio.customer.community_uuid == uuid
| select timestamp, sekoiaio.customer.community_uuid, community.name
Join between events and entities tables
events
| limit 100
| lookup entities on sekoiaio.entity.uuid == uuid
| aggregate count=count() by entity.name
| select entity.name, count
Join between alerts and communities tables (for Multi-tenant)
alerts
| aggregate count=count() by community_uuid
| join communities on community_uuid == uuid
| select community.name, community_uuid, count
| limit 100
Alerts query examples
Detection rules ranked by number of alerts
alerts
| where created_at > ago(30d)
| order by occurrences desc
| select rule_name, occurrences
Assets ranked by number of alerts
alerts
| where created_at > ago(30d)
| aggregate count=count() by assets.uuid
| order by count desc
| limit 100
Threats ranked by number of alerts
alerts
| where created_at > ago(30d)
| aggregate count=count() by threats.name
| order by count desc
| limit 100
Alerts per detection type
alerts
| where created_at > ago(30d)
| aggregate count() by detection_type
Average time to detect in last 30 days
alerts
| where created_at > ago(30d)
| aggregate avg(time_to_detect)
Rename columns and convert time_to_detect in minutes
alerts
| where time_to_detect != null
| select entity = entity_name, rule = rule_name, ttd = time_to_detect/60
| limit 10
Ranking of communities by alerts
alerts
| aggregate AlertCount = count() by community_uuid
| left join communities on community_uuid == uuid
| order by AlertCount desc
| select community.name, AlertCount
Ranking of communities by intakes
alerts
| aggregate AlertCount = count() by community_uuid
| left join communities on community_uuid == uuid
| order by AlertCount desc
| select community.name, AlertCount
Events query examples
Number of unique command lines per host.name
events
| where timestamp > ago(24h)
| aggregate count=count_distinct(process.command_line) by host.name
| order by count desc
Number of unique hostname per month
events
| where timestamp > ago(90d)
| aggregate count=count_distinct(log.hostname) by month(timestamp)
Top 10 visited URL
events
| where timestamp >= ago(24h)
| aggregate count() by url.domain
| top 10 by count
Top 10 blocked URL
events
| where timestamp >= ago(24h) and event.action == 'blocked' and user.name != null and url.domain != null
| aggregate count() by url.domain
| top 10 by count
Top 10 login failures on Windows
events
| where timestamp > ago(24h) and event.code == 4625
| aggregate failed_login_count=count() by user.target.name
| top 10 by failed_login_count
Sekoia.io endpoint agents per version
events
| where timestamp >= ago(24h)
| where sekoiaio.intake.dialect == 'sekoia.io endpoint agent'
| where event.action == 'stats'
| aggregate count_distinct(agent.id) by agent.version
List unique user.name
events
| where timestamp >= ago(24h)
| distinct(user.name)
Number of events per IP address
events
| where timestamp > ago(30d)
| aggregate count=count() by client.ip
| order by count desc
Aggregate events by source.ip and action.outcome
events
| where timestamp >= ago(24h) and event.category == 'authentication'
| aggregate count() by source.ip, action.outcome
Events where process.name starts with 'chrome'
events
| where timestamp > ago(24h) and process.name startswith('chrome')
| limit 100
Events of specific intake
events
| left join intakes on sekoiaio.intake.uuid == uuid
| where timestamp >= ago(24h) and intake.name == '<intake name>'
| limit 100
Number of defended assets: unique host.name with more than 10 events during 2 weeks in the last 30 days
events
| where timestamp > ago(30d)
| aggregate events_count = count() by host.name, week = week(timestamp)
| where events_count > 10
| aggregate week_count = count(), total_count = sum(events_count) by host.name
| where week_count >= 2
| order by total_count
| project host.name, total_count
select command can also be used. select and project are aliases and both return the same results.
host.os.type per Sekoia endpoint agent
events
| where sekoiaio.intake.dialect == 'sekoia.io endpoint agent'
| aggregate count() by host.os.type
| limit 100
Received Kbytes per month per intake
event_telemetry
| where bucket_start_date >= ago(30d)
| summarize sum_bytes = sum(total_message_size) by intake_uuid
| lookup intakes on intake_uuid == uuid
| select sum_gb = sum_bytes / (1000*1000*1000), intake.name
| order by sum_gb desc