Kaspersky Endpoint Security
Overview
Kaspersky Endpoint Security is an advanced security solution designed to safeguard businesses, their networks, and data against a wide array of cyber threats. Employing a multi-layered approach, it integrates various protection technologies including signature-based detection, heuristic analysis, machine learning, and real-time monitoring to detect and thwart malware, ransomware, zero-day attacks, and other threats effectively.
- Vendor: Kaspersky
- Supported environment: On Premise, Saas
- Version compatibility, if applicable:
- Detection based on: Endpoint Telemetry
- Supported application or feature: Endpoint Security
High-Level Architecture Diagram
- Type of integration: Outbound (PUSH to Sekoia.io)
Specification
Prerequisites
- Licence level:
- Proprietary
- Resource:
- Self-managed syslog forwarder
- Network:
- Outbound traffic allowed
- Permissions:
- Administrator rights on the Kaspersky Security Center Cloud
- Root access to the Linux server with the syslog forwarder
Transport Protocol/Method
- Indirect Syslog
Logs details
- Supported functionalities: See section Overview
- Supported type(s) of structure: syslog
- Supported verbosity level: Emergency / Alert / Critical / Error / Warning / Notice / Informational / Debug
Note
- Log levels are based on the taxonomy of RFC5424. Adapt according to the terminology used by the editor.
Warning
- Please ensure your logs are sent in English. Otherwise, duplicate the official parser to customize it.
Step-by-Step Configuration Procedure
Instructions on the 3rd Party Solution
Forward Kaspersky Endpoint Security Logs to Sekoia.io
This setup guide describes how to forward events produced by Kaspersky Endpoint Security to Sekoia.io by means of a syslog transport channel.
Detailed Procedure:
- Login to Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Center:
-
Log in to the Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Center available at
https://ksc.kaspersky.com -
Enable SIEM Configuration:
-
In the console, on the left panel, click on the spanner at the right of Administration server:
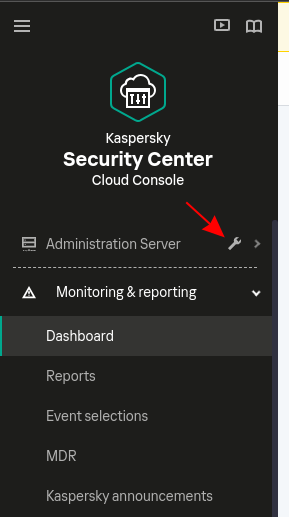
-
In the General tab, click on SIEM on the menu:
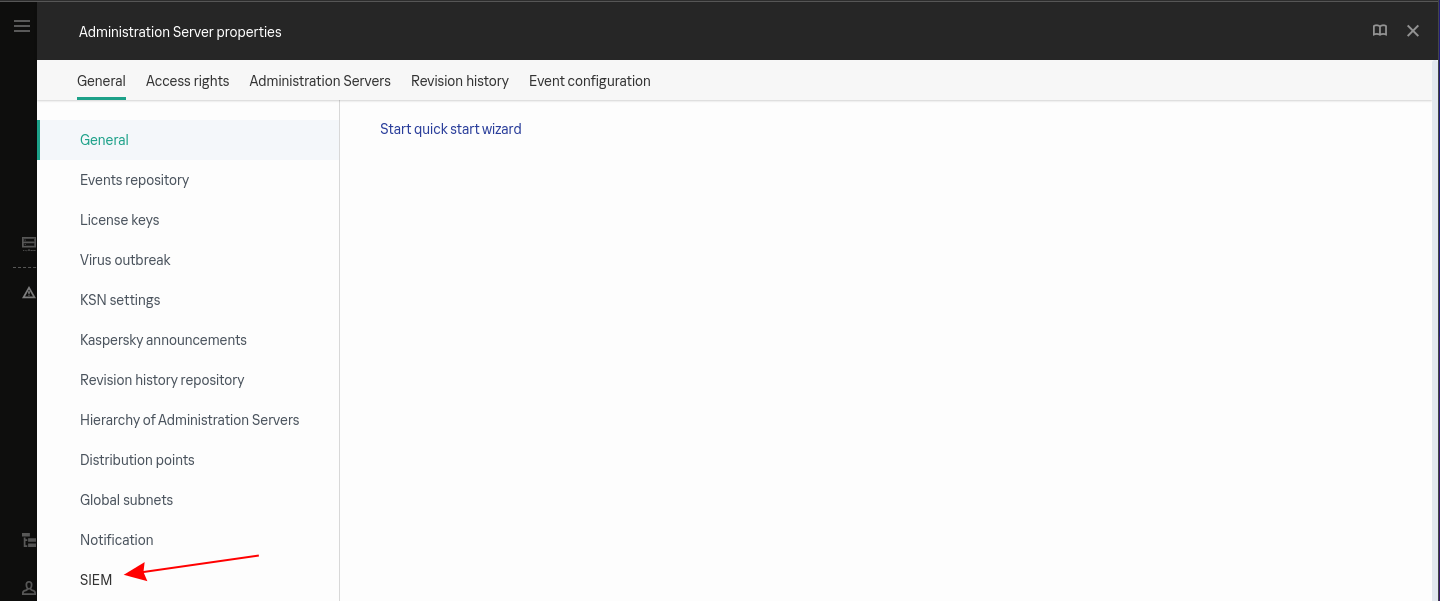
-
Click on settings to configure the forwarding (point 1):
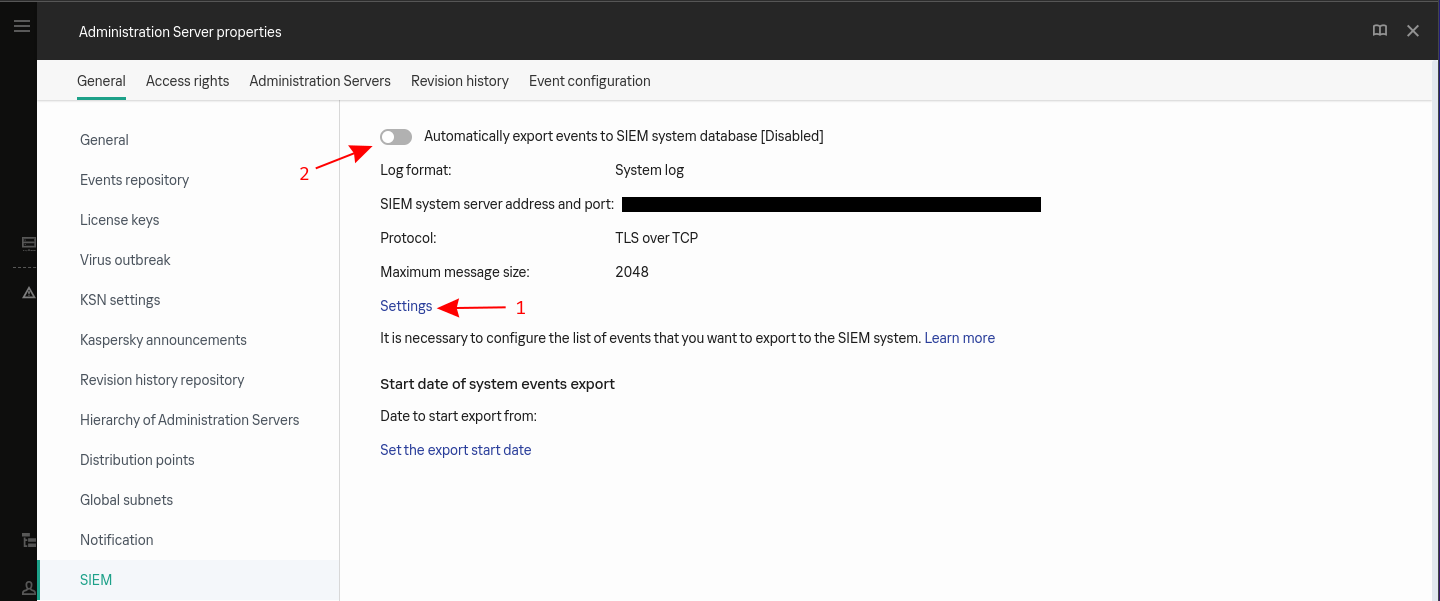
-
Configure the forwarding: a. Type the address of your log concentrator in the SIEM system server address b. Type the port in SIEM system port c. Select TLS over TCP as the protocol d. Select the way to authenticate the concentrator’s certificate e. Click on OK
!!! warning If you need to generate a custom certificate:
```bash $ openssl req -new -x509 -keyout server.key -out server.crt -nodes $ cat server.key server.crt > server.pem $ openssl x509 -in cert.crt -noout -fingerprint # copy the output ```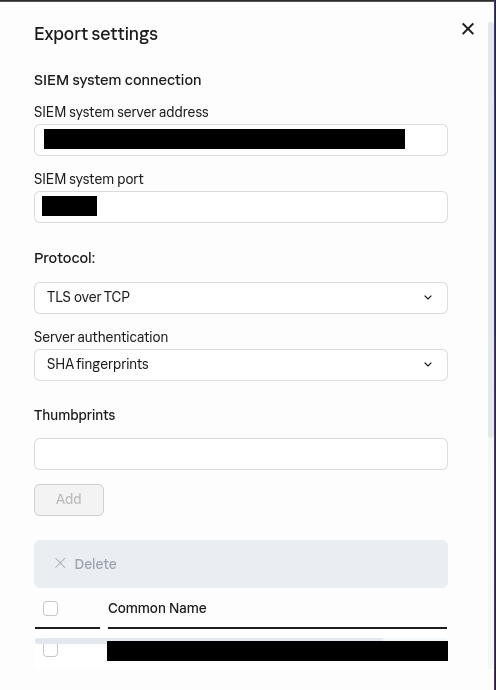
-
Check Automatically export event to SIEM system database (point 2):

-
Apply Log Export Configuration on Devices:
-
In the console, on the left menu, click on Devices > Policies & profiles:
-
For each policy Kaspersky Endpoint Security for X, click on the policy:
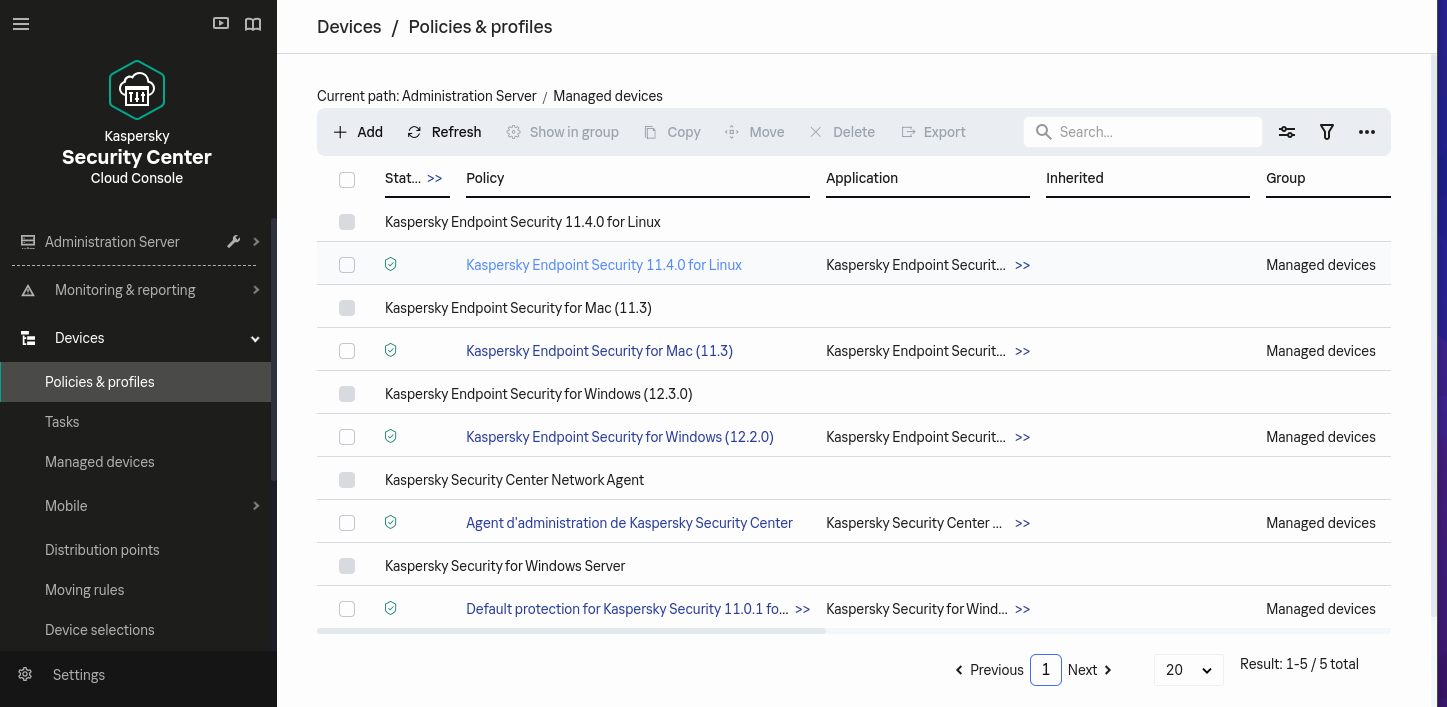
-
In the policy, select the Event configuration tab:
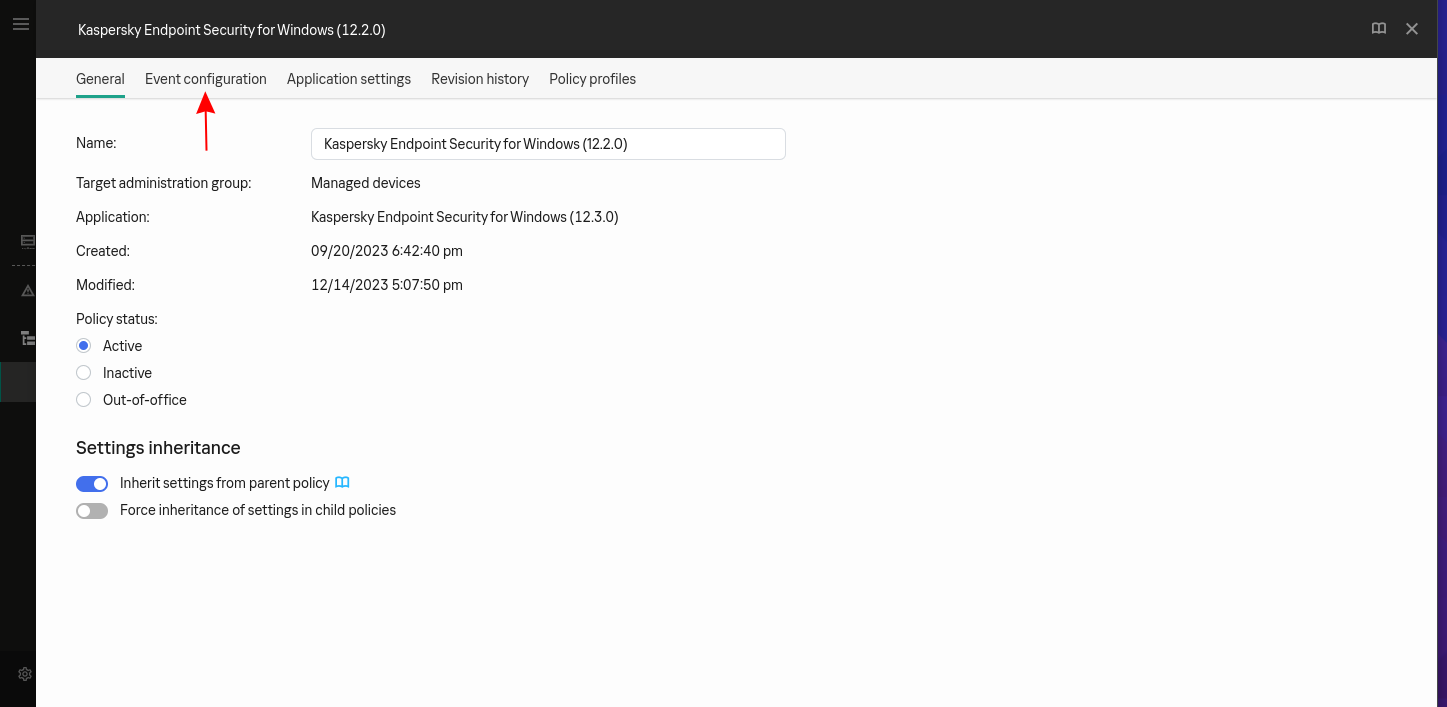
-
On the left panel, select the section Critical. Select all event types and click on Mark for export to SIEM system by using Syslog:
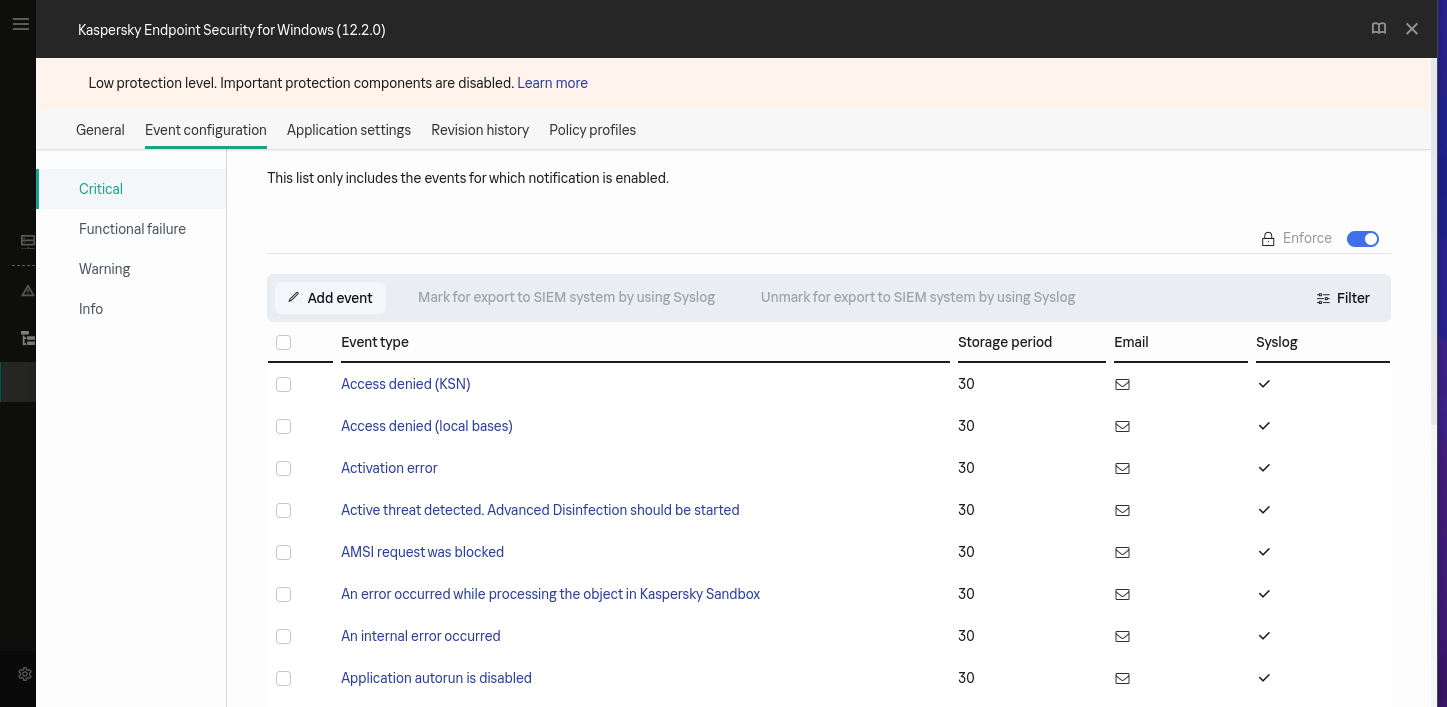
-
Select the section Warning and select all event types and click on Mark for export to SIEM system by using Syslog.
Instruction on Sekoia
Configure Your Intake
This section will guide you through creating the intake object in Sekoia, which provides a unique identifier called the "Intake key." The Intake key is essential for later configuration, as it references the Community, Entity, and Parser (Intake Format) used when receiving raw events on Sekoia.
- Go to the Sekoia Intake page.
- Click on the
+ New Intakebutton at the top right of the page. - Search for your Intake by the product name in the search bar.
- Give it a Name and associate it with an Entity (and a Community if using multi-tenant mode).
- Click on
Create.
Note
For more details on how to use the Intake page and to find the Intake key you just created, refer to this documentation.
Configure a forwarder
To forward events using syslog to Sekoia.io, you need to update the syslog header with the intake key you previously created. Here is an example of your message before the forwarder
<%pri%>1 %timestamp:::date-rfc3339% %hostname% %app-name% %procid% LOG RAW_MESSAGE
<%pri%>1 %timestamp:::date-rfc3339% %hostname% %app-name% %procid% LOG [SEKOIA@53288 intake_key=\"YOUR_INTAKE_KEY\"] RAW_MESSAGE
To achieve this you can:
- Use the Sekoia.io forwarder which is the official supported way to collect data using the syslog protocol in Sekoia.io. In charge of centralizing data coming from many equipments/sources and forwarding them to Sekoia.io with the apporpriated format, it is a prepackaged option. You only have to provide your intake key as parameter.
- Use your own Syslog service instance. Maybe you already have an intance of one of these components on your side and want to reuse it in order to centralize data before forwarding them to Sekoia.io. When using this mode, you have to configure and maintain your component in order to respect the expected Sekoia.io format.
Warning
Only the Sekoia.io forwarder is officially supported. Other options are documented for reference purposes but do not have official support.
Raw Events Samples
In this section, you will find examples of raw logs as generated natively by the source. These examples are provided to help integrators understand the data format before ingestion into Sekoia.io. It is crucial for setting up the correct parsing stages and ensuring that all relevant information is captured.
Event type: Error verifying application databases and modules\r\nResult description: Error\r\nError: Update files are corrupted\r\nObject type: Web page\r\nObject name: updates/kdb/i386/kdb-i386-1901g.xml\r\nUser: MyMachine\jdoe (Active user)\r\nRelease date: 12/14/2023 3:49:00 PM
Event type: Not all components were updated\r\nResult description: Error\r\nError: Not all components were updated\r\nUser: MyMachine\jdoe (Active user)\r\nRelease date: 12/14/2023 3:49:00 PM
Result description: Detected\r\nType: Virus\r\nName: EICAR-Test-File\r\nUser: MyMachine\jdoe (Initiator)\r\nObject: C:\Users\jdoe\Downloads\eicar-com.txt\r\nReason: Expert analysis\r\nDatabase release date: 12/14/2023 8:15:00 AM\r\nSHA256: 275A021BBFB6489E54D471899F7DB9D1663FC695EC2FE2A2C4538AABF651FD0F\r\nMD5: 44D88612FEA8A8F36DE82E1278ABB02F
Result description: Not processed\r\nType: Virus\r\nName: EICAR-Test-File\r\nUser: MyMachine\jdoe (Initiator)\r\nObject: C:\Users\jdoe\Downloads\eicar-com.txt\r\nReason: Already processed\r\nSHA256: 275A021BBFB6489E54D471899F7DB9D1663FC695EC2FE2A2C4538AABF651FD0F\r\nMD5: 44D88612FEA8A8F36DE82E1278ABB02
Result description: Deleted\r\nType: Virus\r\nName: EICAR-Test-File\r\nUser: MyMachine\jdoe (Initiator)\r\nObject: C:\Users\jdoe\Downloads\eicar.com.txt\r\nSHA256: 275A021BBFB6489E54D471899F7DB9D1663FC695EC2FE2A2C4538AABF651FD0F\r\nMD5: 44D88612FEA8A8F36DE82E1278ABB02F
Event type: Object not processed\r\nName: msiexec.exe\r\nApplication path: C:\Windows\System32\r\nProcess ID: 7684\r\nUser: WORKGROUP\MyMachine$ (Initiator)\r\nComponent: File Threat Protection\r\nResult description: Not processed\r\nObject type: File\r\nPath to object: C:\Windows\Installer\r\nObject name: 8056b1f.msi\r\nReason: Size
Detection section
The following section provides information for those who wish to learn more about the detection capabilities enabled by collecting this intake. It includes details about the built-in rule catalog, event categories, and ECS fields extracted from raw events. This is essential for users aiming to create custom detection rules, perform hunting activities, or pivot in the events page.
Related Built-in Rules
The following Sekoia.io built-in rules match the intake Kaspersky Endpoint Security. This documentation is updated automatically and is based solely on the fields used by the intake which are checked against our rules. This means that some rules will be listed but might not be relevant with the intake.
SEKOIA.IO x Kaspersky Endpoint Security on ATT&CK Navigator
Adidnsdump Enumeration
Detects use of the tool adidnsdump for enumeration and discovering DNS records.
- Effort: advanced
Advanced IP Scanner
Detects the use of Advanced IP Scanner. Seems to be a popular tool for ransomware groups.
- Effort: master
Certify Or Certipy
Detects the use of certify and certipy which are two different tools used to enumerate and abuse Active Directory Certificate Services.
- Effort: advanced
Cobalt Strike Default Beacons Names
Detects the default names of Cobalt Strike beacons / payloads.
- Effort: intermediate
Credential Dump Tools Related Files
Detects processes or file names related to credential dumping tools and the dropped files they generate by default.
- Effort: advanced
Discord Suspicious Download
Discord is a messaging application. It allows users to create their own communities to share messages and attachments. Those attachments have little to no overview and can be downloaded by almost anyone, which has been abused by attackers to host malicious payloads.
- Effort: advanced
Formbook File Creation DB1
Detects specific file creation (Users*\AppData\Local\Temp\DB1) to store data to exfiltrate (Formbook behavior). Logging for Sysmon event 11 is usually used for this detection.
- Effort: intermediate
HackTools Suspicious Names
Quick-win rule to detect the default process names or file names of several HackTools.
- Effort: advanced
Koadic MSHTML Command
Detects Koadic payload using MSHTML module
- Effort: intermediate
Linux Masquerading Space After Name
This detection rule identifies a process created from an executable with a space appended to the end of the name.
- Effort: intermediate
NTDS.dit File In Suspicious Directory
The file NTDS.dit is supposed to be located mainly in C:\Windows\NTDS. The rule checks whether the file is in a legitimate directory or not (through file creation events). This is usually really suspicious and could indicate an attacker trying copy the file to then look for users password hashes.
- Effort: advanced
OneNote Embedded File
Detects creation or uses of OneNote embedded files with unusual extensions.
- Effort: intermediate
PasswordDump SecurityXploded Tool
Detects the execution of the PasswordDump SecurityXploded Tool
- Effort: elementary
Phorpiex Process Masquerading
Detects specific process executable path used by the Phorpiex botnet to masquerade its system process network activity. It looks for a pattern of a system process executable name that is not legitimate and running from a folder that is created via a random algorithm 13-15 numbers long.
- Effort: elementary
Potential Azure AD Phishing Page (Adversary-in-the-Middle)
Detects an HTTP request to an URL typical of the Azure AD authentication flow, but towards a domain that is not one the legitimate Microsoft domains used for Azure AD authentication.
- Effort: intermediate
Process Trace Alteration
PTrace syscall provides a means by which one process ("tracer") may observe and control the execution of another process ("tracee") and examine and change the tracee's memory and registers. Attacker might want to abuse ptrace functionnality to analyse memory process. It requires to be admin or set ptrace_scope to 0 to allow all user to trace any process.
- Effort: advanced
RTLO Character
Detects RTLO (Right-To-Left character) in file and process names.
- Effort: elementary
Remote Monitoring and Management Software - AnyDesk
Detect artifacts related to the installation or execution of the Remote Monitoring and Management tool AnyDesk.
- Effort: master
Remote Monitoring and Management Software - Atera
Detect artifacts related to the installation or execution of the Remote Monitoring and Management tool Atera.
- Effort: master
Suspicious ADSI-Cache Usage By Unknown Tool
Detects the usage of ADSI (LDAP) operations by tools. This may also detect tools like LDAPFragger. It needs file monitoring capabilities (Sysmon Event ID 11 with .sch file creation logging).
- Effort: advanced
Suspicious PROCEXP152.sys File Created In Tmp
Detects the creation of the PROCEXP152.sys file in the application-data local temporary folder. This driver is used by Sysinternals Process Explorer but also by KDU (https://github.com/hfiref0x/KDU) or Ghost-In-The-Logs (https://github.com/bats3c/Ghost-In-The-Logs), which uses KDU. Note - Clever attackers may easily bypass this detection by just renaming the driver filename. Therefore just Medium-level and don't rely on it.
- Effort: advanced
Suspicious desktop.ini Action
Detects unusual processes accessing desktop.ini, which can be leveraged to alter how Explorer displays a folder's content (i.e. renaming files) without changing them on disk.
- Effort: advanced
WAF Block Rule
Detects when one of WAF rule blocked an HTTP request. This rule often needs fine tuning according to the environment.
- Effort: master
WCE wceaux.dll Creation
Detects wceaux.dll creation while Windows Credentials Editor (WCE) is executed.
- Effort: intermediate
Webshell Creation
Detects possible webshell file creation. It requires File Creation monitoring, which can be done using Sysmon's Event ID 11. However the recommended SwiftOnSecurity configuration does not fully cover the needs for this rule, it needs to be updated with the proper file names extensions.
- Effort: master
Event Categories
The following table lists the data source offered by this integration.
| Data Source | Description |
|---|---|
Anti-virus |
Kaspersky Endpoint Security prevents from malware infection |
File monitoring |
Kaspersky Endpoint Security analyzes all files and protect machines from malware files |
Web logs |
Kaspersky Endpoint Security logs provides information about the web if there's something strange |
In details, the following table denotes the type of events produced by this integration.
| Name | Values |
|---|---|
| Kind | `` |
| Category | malware, process |
| Type | info |
Transformed Events Samples after Ingestion
This section demonstrates how the raw logs will be transformed by our parsers. It shows the extracted fields that will be available for use in the built-in detection rules and hunting activities in the events page. Understanding these transformations is essential for analysts to create effective detection mechanisms with custom detection rules and to leverage the full potential of the collected data.
{
"message": "Event type: Error verifying application databases and modules\\r\\nResult description: Error\\r\\nError: Update files are corrupted\\r\\nObject type: Web page\\r\\nObject name: updates/kdb/i386/kdb-i386-1901g.xml\\r\\nUser: MyMachine\\jdoe (Active user)\\r\\nRelease date: 12/14/2023 3:49:00 PM",
"event": {
"action": "Error",
"category": [
"process"
],
"reason": "Error verifying application databases and modules",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"@timestamp": "2023-12-14T15:49:00Z",
"error": {
"message": "Update files are corrupted"
},
"observer": {
"product": "Kaspersky Endpoint Security",
"type": "edr",
"vendor": "Kaspersky"
},
"related": {
"user": [
"jdoe"
]
},
"url": {
"path": "updates/kdb/i386/kdb-i386-1901g.xml"
},
"user": {
"domain": "MyMachine",
"name": "jdoe"
}
}
{
"message": "Event type: Not all components were updated\\r\\nResult description: Error\\r\\nError: Not all components were updated\\r\\nUser: MyMachine\\jdoe (Active user)\\r\\nRelease date: 12/14/2023 3:49:00 PM",
"event": {
"action": "Error",
"category": [
"process"
],
"reason": "Not all components were updated",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"@timestamp": "2023-12-14T15:49:00Z",
"error": {
"message": "Not all components were updated"
},
"observer": {
"product": "Kaspersky Endpoint Security",
"type": "edr",
"vendor": "Kaspersky"
},
"related": {
"user": [
"jdoe"
]
},
"user": {
"domain": "MyMachine",
"name": "jdoe"
}
}
{
"message": "Result description: Detected\\r\\nType: Virus\\r\\nName: EICAR-Test-File\\r\\nUser: MyMachine\\jdoe (Initiator)\\r\\nObject: C:\\Users\\jdoe\\Downloads\\eicar-com.txt\\r\\nReason: Expert analysis\\r\\nDatabase release date: 12/14/2023 8:15:00 AM\\r\\nSHA256: 275A021BBFB6489E54D471899F7DB9D1663FC695EC2FE2A2C4538AABF651FD0F\\r\\nMD5: 44D88612FEA8A8F36DE82E1278ABB02F\n",
"event": {
"action": "Detected",
"category": [
"malware"
],
"reason": "Expert analysis",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"file": {
"hash": {
"md5": "44D88612FEA8A8F36DE82E1278ABB02F",
"sha256": "275A021BBFB6489E54D471899F7DB9D1663FC695EC2FE2A2C4538AABF651FD0F"
},
"name": "eicar-com.txt",
"path": "C:\\Users\\jdoe\\Downloads\\eicar-com.txt"
},
"observer": {
"product": "Kaspersky Endpoint Security",
"type": "edr",
"vendor": "Kaspersky"
},
"related": {
"hash": [
"275A021BBFB6489E54D471899F7DB9D1663FC695EC2FE2A2C4538AABF651FD0F",
"44D88612FEA8A8F36DE82E1278ABB02F"
],
"user": [
"jdoe"
]
},
"threat": {
"software": {
"name": "EICAR-Test-File",
"type": "Malware"
}
},
"user": {
"domain": "MyMachine",
"name": "jdoe"
}
}
{
"message": "Result description: Not processed\\r\\nType: Virus\\r\\nName: EICAR-Test-File\\r\\nUser: MyMachine\\jdoe (Initiator)\\r\\nObject: C:\\Users\\jdoe\\Downloads\\eicar-com.txt\\r\\nReason: Already processed\\r\\nSHA256: 275A021BBFB6489E54D471899F7DB9D1663FC695EC2FE2A2C4538AABF651FD0F\\r\\nMD5: 44D88612FEA8A8F36DE82E1278ABB02",
"event": {
"action": "Not processed",
"category": [
"malware"
],
"reason": "Already processed",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"file": {
"hash": {
"md5": "44D88612FEA8A8F36DE82E1278ABB02",
"sha256": "275A021BBFB6489E54D471899F7DB9D1663FC695EC2FE2A2C4538AABF651FD0F"
},
"name": "eicar-com.txt",
"path": "C:\\Users\\jdoe\\Downloads\\eicar-com.txt"
},
"observer": {
"product": "Kaspersky Endpoint Security",
"type": "edr",
"vendor": "Kaspersky"
},
"related": {
"hash": [
"275A021BBFB6489E54D471899F7DB9D1663FC695EC2FE2A2C4538AABF651FD0F",
"44D88612FEA8A8F36DE82E1278ABB02"
],
"user": [
"jdoe"
]
},
"threat": {
"software": {
"name": "EICAR-Test-File",
"type": "Malware"
}
},
"user": {
"domain": "MyMachine",
"name": "jdoe"
}
}
{
"message": "Result description: Deleted\\r\\nType: Virus\\r\\nName: EICAR-Test-File\\r\\nUser: MyMachine\\jdoe (Initiator)\\r\\nObject: C:\\Users\\jdoe\\Downloads\\eicar.com.txt\\r\\nSHA256: 275A021BBFB6489E54D471899F7DB9D1663FC695EC2FE2A2C4538AABF651FD0F\\r\\nMD5: 44D88612FEA8A8F36DE82E1278ABB02F",
"event": {
"action": "Deleted",
"category": [
"malware"
],
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"file": {
"hash": {
"md5": "44D88612FEA8A8F36DE82E1278ABB02F",
"sha256": "275A021BBFB6489E54D471899F7DB9D1663FC695EC2FE2A2C4538AABF651FD0F"
},
"name": "eicar.com.txt",
"path": "C:\\Users\\jdoe\\Downloads\\eicar.com.txt"
},
"observer": {
"product": "Kaspersky Endpoint Security",
"type": "edr",
"vendor": "Kaspersky"
},
"related": {
"hash": [
"275A021BBFB6489E54D471899F7DB9D1663FC695EC2FE2A2C4538AABF651FD0F",
"44D88612FEA8A8F36DE82E1278ABB02F"
],
"user": [
"jdoe"
]
},
"threat": {
"software": {
"name": "EICAR-Test-File",
"type": "Malware"
}
},
"user": {
"domain": "MyMachine",
"name": "jdoe"
}
}
{
"message": "Event type: Object not processed\\r\\nName: msiexec.exe\\r\\nApplication path: C:\\Windows\\System32\\r\\nProcess ID: 7684\\r\\nUser: WORKGROUP\\MyMachine$ (Initiator)\\r\\nComponent: File Threat Protection\\r\\nResult description: Not processed\\r\\nObject type: File\\r\\nPath to object: C:\\Windows\\Installer\\r\\nObject name: 8056b1f.msi\\r\\nReason: Size",
"event": {
"action": "Not processed",
"category": [
"process"
],
"module": "File Threat Protection",
"reason": "Object not processed because of Size",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"file": {
"directory": "C:\\Windows\\Installer",
"name": "8056b1f.msi"
},
"observer": {
"product": "Kaspersky Endpoint Security",
"type": "edr",
"vendor": "Kaspersky"
},
"process": {
"executable": "C:\\Windows\\System32\"\\\"msiexec.exe",
"pid": 7684
},
"related": {
"user": [
"MyMachine"
]
},
"user": {
"domain": "WORKGROUP",
"name": "MyMachine"
}
}
Extracted Fields
The following table lists the fields that are extracted, normalized under the ECS format, analyzed and indexed by the parser. It should be noted that infered fields are not listed.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
@timestamp |
date |
Date/time when the event originated. |
error.message |
match_only_text |
Error message. |
event.action |
keyword |
The action captured by the event. |
event.category |
keyword |
Event category. The second categorization field in the hierarchy. |
event.module |
keyword |
Name of the module this data is coming from. |
event.reason |
keyword |
Reason why this event happened, according to the source |
event.type |
keyword |
Event type. The third categorization field in the hierarchy. |
file.directory |
keyword |
Directory where the file is located. |
file.hash.md5 |
keyword |
MD5 hash. |
file.hash.sha256 |
keyword |
SHA256 hash. |
file.name |
keyword |
Name of the file including the extension, without the directory. |
file.path |
keyword |
Full path to the file, including the file name. |
observer.product |
keyword |
The product name of the observer. |
observer.type |
keyword |
The type of the observer the data is coming from. |
observer.vendor |
keyword |
Vendor name of the observer. |
process.executable |
keyword |
Absolute path to the process executable. |
process.pid |
long |
Process id. |
threat.software.name |
keyword |
Name of the software. |
threat.software.type |
keyword |
Software type. |
url.path |
wildcard |
Path of the request, such as "/search". |
user.domain |
keyword |
Name of the directory the user is a member of. |
user.name |
keyword |
Short name or login of the user. |
For more information on the Intake Format, please find the code of the Parser, Smart Descriptions, and Supported Events here.