Nozomi Central Management Console
Overview
Nozomi Central Management Console is a centralized platform that streamlines the management of cybersecurity across industrial networks. It enables users to monitor, configure, and respond to threats in real-time, ensuring enhanced visibility and control over operational technology environments. With its user-friendly interface and powerful analytics, the console simplifies security operations and strengthens defense against cyber risks.
- Supported environment: On Prem
- Detection based on: Alerts, Telemetry
- Supported application or feature:
- Alerts
- Health
- Audit
Specification
Prerequisites
-
Resource:
- Self-managed syslog forwarder
-
Network:
- On Premise: Outbound traffic allowed
-
Permissions:
- Administrator access to the Central Management Console
- Root access to the Linux server with the syslog forwarder
Transport Protocol/Method
- Indirect Syslog for On Premise
Logs details
- Supported functionalities: See section Overview
- Supported type(s) of structure: CEF
- Supported verbosity level: Alert, Informational
Note
This is a description of the log level based on the taxonomy of the RFC5424 for standardization purpose. Please adapt to the wording used by the editor.
Step-by-Step Configuration Procedure
To Enable the CEF forwarding:
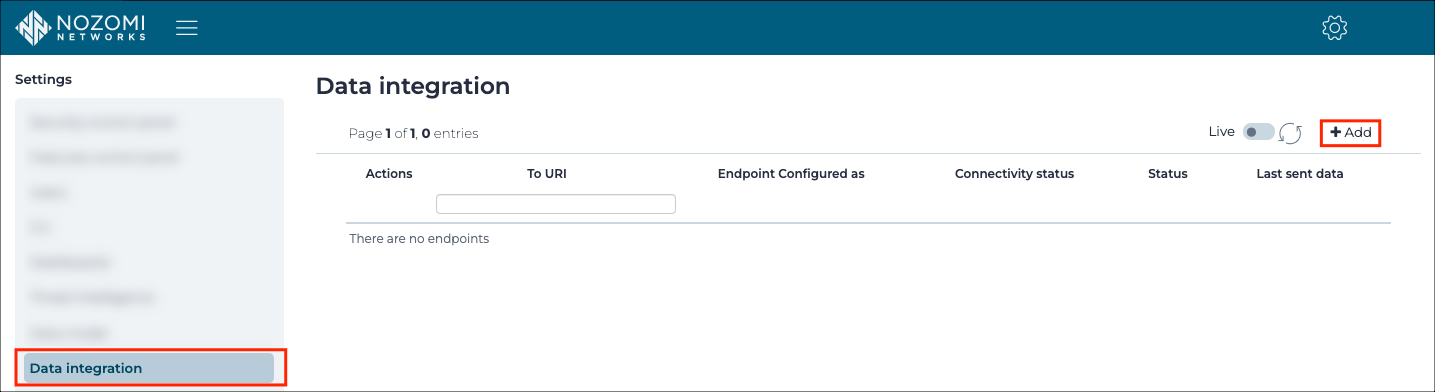
- Log in the Nozomi Central Management Console.
- Click
Administration.

- Go to
Settings>Data integration. - Click
+ Add.
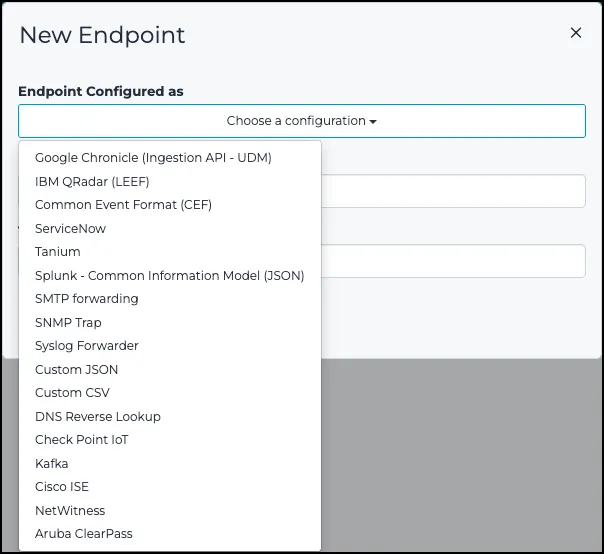
- From the
Choose a configurationdropdown, select CEF.
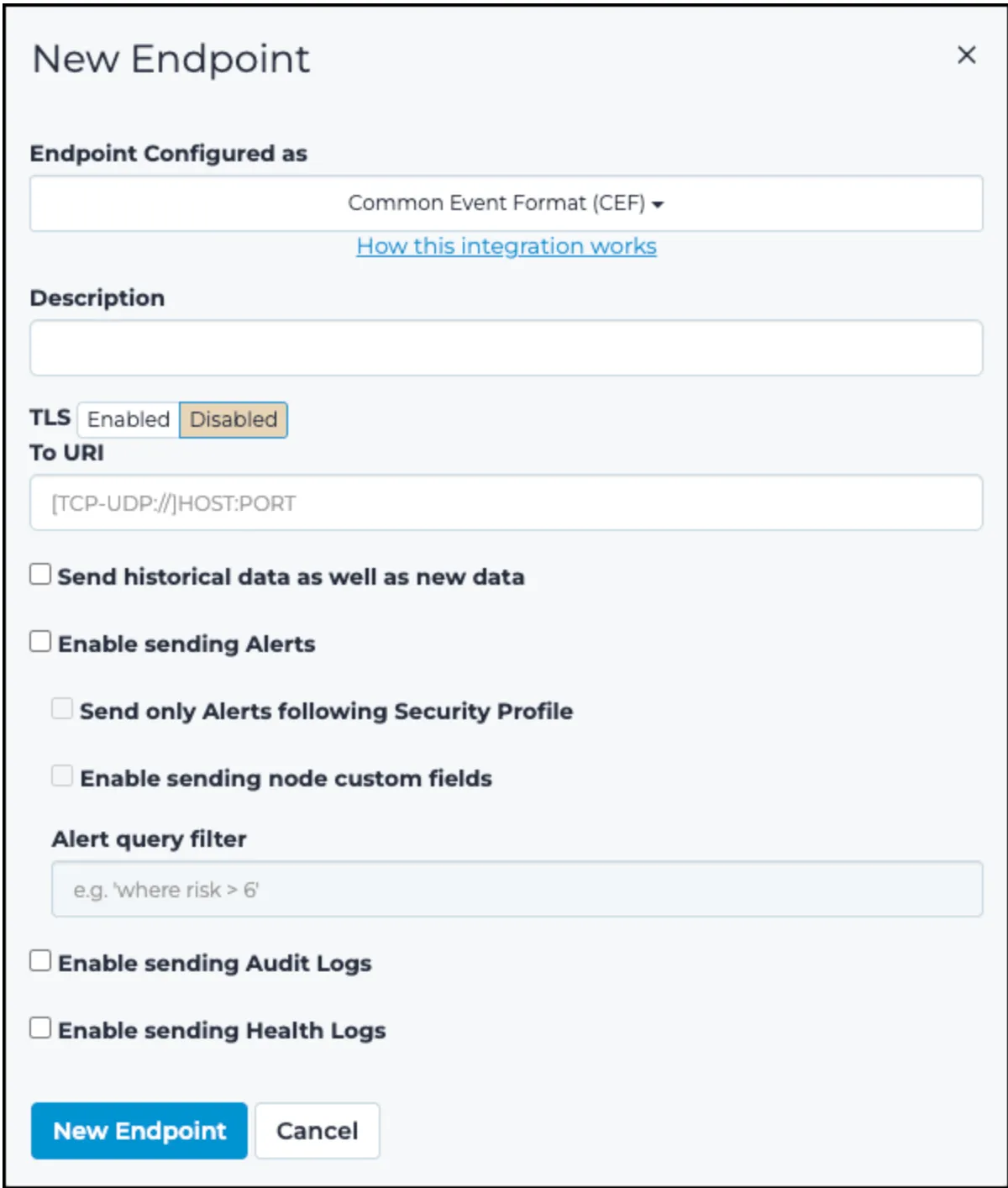
- Type a description.
- In
To URI, typetcp://following by the address of the log concentrator and the port for the intake - Check
Enable sending Alerts - Check
Enable sending Audit Logs - Check
Enable sending Health Logs
Instruction on Sekoia
Configure Your Intake
This section will guide you through creating the intake object in Sekoia, which provides a unique identifier called the "Intake key." The Intake key is essential for later configuration, as it references the Community, Entity, and Parser (Intake Format) used when receiving raw events on Sekoia.
- Go to the Sekoia Intake page.
- Click on the
+ New Intakebutton at the top right of the page. - Search for your Intake by the product name in the search bar.
- Give it a Name and associate it with an Entity (and a Community if using multi-tenant mode).
- Click on
Create.
Note
For more details on how to use the Intake page and to find the Intake key you just created, refer to this documentation.
Configure a forwarder
To forward events using syslog to Sekoia.io, you need to update the syslog header with the intake key you previously created. Here is an example of your message before the forwarder
<%pri%>1 %timestamp:::date-rfc3339% %hostname% %app-name% %procid% LOG RAW_MESSAGE
<%pri%>1 %timestamp:::date-rfc3339% %hostname% %app-name% %procid% LOG [SEKOIA@53288 intake_key=\"YOUR_INTAKE_KEY\"] RAW_MESSAGE
To achieve this you can:
- Use the Sekoia.io forwarder which is the official supported way to collect data using the syslog protocol in Sekoia.io. In charge of centralizing data coming from many equipments/sources and forwarding them to Sekoia.io with the apporpriated format, it is a prepackaged option. You only have to provide your intake key as parameter.
- Use your own Syslog service instance. Maybe you already have an intance of one of these components on your side and want to reuse it in order to centralize data before forwarding them to Sekoia.io. When using this mode, you have to configure and maintain your component in order to respect the expected Sekoia.io format.
Warning
Only the Sekoia.io forwarder is officially supported. Other options are documented for reference purposes but do not have official support.
Raw Events Samples
In this section, you will find examples of raw logs as generated natively by the source. These examples are provided to help integrators understand the data format before ingestion into Sekoia.io. It is crucial for setting up the correct parsing stages and ensuring that all relevant information is captured.
CEF:0|Nozomi Networks|N2OS|19.0.3-10142120_A2F44|SIGN:MALWARE-DETECTED
|Malware detected|9|
app=smb
dvc=4.5.6.7
dvchost=test-host-name
cs1=9.0
cs2=true
cs3=d25c520f-7f79-4820-b5ae-d1b334b05c75
cs4={trigger_type: yara_rules, trigger_id: MALW_DragonFly2.yar}
cs5=["5740a157-08e8-490f-85ad-eef23657e3cb"]
cs6=1
cs1Label=Risk
cs2Label=IsSecurity
cs3Label=Id
cs4Label=Detail
cs5Label=Parents
cs6Label=n2os_schema
flexString1=T0843
flexString1Label=mitre_attack_techniques
flexString2=Impair process (etc)
flexString2Label=mitre_attack_tactics
flexString3=Suspicious Activity
flexString3Label=name
dst=2.3.4.5
dmac=00:00:00:00:00:00
dpt=445
msg=Suspicious transferring of malware named 'TemplateAttack_DragonFly_2_0'
was detected involving resource '\\2.3.4.5\ADMIN
\CVcontrolEngineer.docx' after a 'read' operation [rule author: US-CERT
Code Analysis Team - improved by Nozomi Networks] [yara file name:
MALW_DragonFly2.yar]
src=1.2.3.4
smac=00:11:22:33:44:55
spt=1148
proto=TCP
start=1571351543431
CEF:0|Nozomi Networks|N2OS|19.0.3-10201846_FD825|AUDIT:SESSIONS:CREATE|
User signed in|0|
dvchost=local-sg-19.x
cs1=Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10.15; rv:69.0) Gecko/20100101
Firefox/69.0
cs6=1
cs1Label=browser
cs6Label=n2os_schema
msg=User signed in
src=1.2.3.4
suser=admin
start=1570723218425
CEF:0|Nozomi Networks|N2OS|19.0.3-10201846_FD825|HEALTH|Health problem|0|
dvchost=local-sg-19.x
cs6=1
cs6Label=n2os_schema
msg=LINK_DOWN_on_port_em0
Detection section
The following section provides information for those who wish to learn more about the detection capabilities enabled by collecting this intake. It includes details about the built-in rule catalog, event categories, and ECS fields extracted from raw events. This is essential for users aiming to create custom detection rules, perform hunting activities, or pivot in the events page.
Related Built-in Rules
The following Sekoia.io built-in rules match the intake Nozomi CMC. This documentation is updated automatically and is based solely on the fields used by the intake which are checked against our rules. This means that some rules will be listed but might not be relevant with the intake.
SEKOIA.IO x Nozomi CMC on ATT&CK Navigator
Cryptomining
Detection of domain names potentially related to cryptomining activities.
- Effort: master
Dynamic DNS Contacted
Detect communication with dynamic dns domain. This kind of domain is often used by attackers. This rule can trigger false positive in non-controlled environment because dynamic dns is not always malicious.
- Effort: master
Exfiltration Domain
Detects traffic toward a domain flagged as a possible exfiltration vector.
- Effort: master
Nimbo-C2 User Agent
Nimbo-C2 Uses an unusual User-Agent format in its implants.
- Effort: intermediate
Potential Bazar Loader User-Agents
Detects potential Bazar loader communications through the user-agent
- Effort: elementary
Potential Lemon Duck User-Agent
Detects LemonDuck user agent. The format used two sets of alphabetical characters separated by dashes, for example "User-Agent: Lemon-Duck-[A-Z]-[A-Z]".
- Effort: elementary
Remote Access Tool Domain
Detects traffic toward a domain flagged as a Remote Administration Tool (RAT).
- Effort: master
Remote Monitoring and Management Software - AnyDesk
Detect artifacts related to the installation or execution of the Remote Monitoring and Management tool AnyDesk.
- Effort: master
SEKOIA.IO Intelligence Feed
Detect threats based on indicators of compromise (IOCs) collected by SEKOIA's Threat and Detection Research team.
- Effort: elementary
Sekoia.io EICAR Detection
Detects observables in Sekoia.io CTI tagged as EICAR, which are fake samples meant to test detection.
- Effort: master
TOR Usage
Detects TOR usage, based on the IP address and the destination port (filtered on NTP). TOR is short for The Onion Router, and it gets its name from how it works. TOR intercepts the network traffic from one or more apps on user’s computer, usually the user web browser, and shuffles it through a number of randomly-chosen computers before passing it on to its destination. This disguises user location, and makes it harder for servers to pick him/her out on repeat visits, or to tie together separate visits to different sites, this making tracking and surveillance more difficult. Before a network packet starts its journey, user’s computer chooses a random list of relays and repeatedly encrypts the data in multiple layers, like an onion. Each relay knows only enough to strip off the outermost layer of encryption, before passing what’s left on to the next relay in the list.
- Effort: master
TOR Usage Generic Rule
Detects TOR usage globally, whether the IP is a destination or source. TOR is short for The Onion Router, and it gets its name from how it works. TOR intercepts the network traffic from one or more apps on user’s computer, usually the user web browser, and shuffles it through a number of randomly-chosen computers before passing it on to its destination. This disguises user location, and makes it harder for servers to pick him/her out on repeat visits, or to tie together separate visits to different sites, this making tracking and surveillance more difficult. Before a network packet starts its journey, user’s computer chooses a random list of relays and repeatedly encrypts the data in multiple layers, like an onion. Each relay knows only enough to strip off the outermost layer of encryption, before passing what’s left on to the next relay in the list.
- Effort: master
Event Categories
The following table lists the data source offered by this integration.
| Data Source | Description |
|---|---|
Network device logs |
None |
In details, the following table denotes the type of events produced by this integration.
| Name | Values |
|---|---|
| Kind | alert |
| Category | host, malware, session |
| Type | indicator, info |
Transformed Events Samples after Ingestion
This section demonstrates how the raw logs will be transformed by our parsers. It shows the extracted fields that will be available for use in the built-in detection rules and hunting activities in the events page. Understanding these transformations is essential for analysts to create effective detection mechanisms with custom detection rules and to leverage the full potential of the collected data.
{
"message": "CEF:0|Nozomi Networks|N2OS|19.0.3-10142120_A2F44|SIGN:MALWARE-DETECTED\n |Malware detected|9|\n app=smb\n dvc=4.5.6.7\n dvchost=test-host-name\n cs1=9.0\n cs2=true\n cs3=d25c520f-7f79-4820-b5ae-d1b334b05c75\n cs4={trigger_type: yara_rules, trigger_id: MALW_DragonFly2.yar}\n cs5=[\"5740a157-08e8-490f-85ad-eef23657e3cb\"]\n cs6=1\n cs1Label=Risk\n cs2Label=IsSecurity\n cs3Label=Id\n cs4Label=Detail\n cs5Label=Parents\n cs6Label=n2os_schema\n flexString1=T0843\n flexString1Label=mitre_attack_techniques\n flexString2=Impair process (etc)\n flexString2Label=mitre_attack_tactics\n flexString3=Suspicious Activity\n flexString3Label=name\n dst=2.3.4.5\n dmac=00:00:00:00:00:00\n dpt=445\n msg=Suspicious transferring of malware named 'TemplateAttack_DragonFly_2_0'\n was detected involving resource '\\\\2.3.4.5\\ADMIN\n \\CVcontrolEngineer.docx' after a 'read' operation [rule author: US-CERT\n Code Analysis Team - improved by Nozomi Networks] [yara file name:\n MALW_DragonFly2.yar]\n src=1.2.3.4\n smac=00:11:22:33:44:55\n spt=1148\n proto=TCP\n start=1571351543431",
"event": {
"action": "Malware detected",
"category": [
"malware"
],
"dataset": "SIGN:MALWARE-DETECTED",
"kind": "alert",
"module": "nozomi.cmc",
"outcome": "success",
"reason": "Suspicious transferring of malware named 'TemplateAttack_DragonFly_2_0'\n was detected involving resource '\\\\2.3.4.5\\ADMIN\n \\CVcontrolEngineer.docx' after a 'read' operation [rule author: US-CERT\n Code Analysis Team - improved by Nozomi Networks] [yara file name:\n MALW_DragonFly2.yar]",
"severity": 9,
"type": [
"indicator"
]
},
"@timestamp": "2019-10-17T22:32:23.431000Z",
"destination": {
"address": "2.3.4.5",
"ip": "2.3.4.5",
"mac": "00:00:00:00:00:00",
"port": 445
},
"host": {
"hostname": "test-host-name",
"ip": [
"4.5.6.7"
],
"name": "test-host-name"
},
"network": {
"protocol": "smb",
"transport": "TCP"
},
"nozomi": {
"cmc": {
"alert": {
"detail": "{trigger_type: yara_rules, trigger_id: MALW_DragonFly2.yar}",
"id": "d25c520f-7f79-4820-b5ae-d1b334b05c75",
"is_security": true,
"parents": [
"5740a157-08e8-490f-85ad-eef23657e3cb"
],
"risk": 9.0
},
"version": "19.0.3-10142120_A2F44"
}
},
"observer": {
"product": "Nozomi CMC",
"vendor": "Nozomi"
},
"related": {
"hosts": [
"test-host-name"
],
"ip": [
"1.2.3.4",
"2.3.4.5",
"4.5.6.7"
]
},
"source": {
"address": "1.2.3.4",
"ip": "1.2.3.4",
"mac": "00:11:22:33:44:55",
"port": 1148
},
"threat": {
"tactic": {
"name": [
"Impair process (etc)"
]
},
"technique": {
"id": [
"T0843"
]
}
}
}
{
"message": "CEF:0|Nozomi Networks|N2OS|19.0.3-10201846_FD825|AUDIT:SESSIONS:CREATE|\nUser signed in|0|\ndvchost=local-sg-19.x\ncs1=Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10.15; rv:69.0) Gecko/20100101\nFirefox/69.0\ncs6=1\ncs1Label=browser\ncs6Label=n2os_schema\nmsg=User signed in\nsrc=1.2.3.4\nsuser=admin\nstart=1570723218425",
"event": {
"category": [
"session"
],
"dataset": "AUDIT:SESSIONS:CREATE",
"module": "nozomi.cmc",
"outcome": "success",
"reason": "User signed in",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"@timestamp": "2019-10-10T16:00:18.425000Z",
"host": {
"hostname": "local-sg-19.x",
"name": "local-sg-19.x"
},
"nozomi": {
"cmc": {
"version": "19.0.3-10201846_FD825"
}
},
"observer": {
"product": "Nozomi CMC",
"vendor": "Nozomi"
},
"related": {
"hosts": [
"local-sg-19.x"
],
"ip": [
"1.2.3.4"
],
"user": [
"admin"
]
},
"source": {
"address": "1.2.3.4",
"ip": "1.2.3.4",
"user": {
"name": "admin"
}
},
"user_agent": {
"device": {
"name": "Mac"
},
"name": "Firefox",
"original": "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10.15; rv:69.0) Gecko/20100101\nFirefox/69.0",
"os": {
"name": "Mac OS X",
"version": "10.15"
},
"version": "69.0"
}
}
{
"message": "CEF:0|Nozomi Networks|N2OS|19.0.3-10201846_FD825|HEALTH|Health problem|0|\ndvchost=local-sg-19.x\ncs6=1\ncs6Label=n2os_schema\nmsg=LINK_DOWN_on_port_em0",
"event": {
"category": [
"host"
],
"dataset": "HEALTH",
"module": "nozomi.cmc",
"outcome": "success",
"reason": "LINK_DOWN_on_port_em0",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"host": {
"hostname": "local-sg-19.x",
"name": "local-sg-19.x"
},
"nozomi": {
"cmc": {
"version": "19.0.3-10201846_FD825"
}
},
"observer": {
"product": "Nozomi CMC",
"vendor": "Nozomi"
},
"related": {
"hosts": [
"local-sg-19.x"
]
}
}
Extracted Fields
The following table lists the fields that are extracted, normalized under the ECS format, analyzed and indexed by the parser. It should be noted that infered fields are not listed.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
@timestamp |
date |
Date/time when the event originated. |
destination.domain |
keyword |
The domain name of the destination. |
destination.ip |
ip |
IP address of the destination. |
destination.mac |
keyword |
MAC address of the destination. |
destination.port |
long |
Port of the destination. |
event.action |
keyword |
The action captured by the event. |
event.category |
keyword |
Event category. The second categorization field in the hierarchy. |
event.dataset |
keyword |
Name of the dataset. |
event.kind |
keyword |
The kind of the event. The highest categorization field in the hierarchy. |
event.module |
keyword |
Name of the module this data is coming from. |
event.outcome |
keyword |
The outcome of the event. The lowest level categorization field in the hierarchy. |
event.reason |
keyword |
Reason why this event happened, according to the source |
event.severity |
long |
Numeric severity of the event. |
event.type |
keyword |
Event type. The third categorization field in the hierarchy. |
host.hostname |
keyword |
Hostname of the host. |
host.ip |
ip |
Host ip addresses. |
network.protocol |
keyword |
Application protocol name. |
network.transport |
keyword |
Protocol Name corresponding to the field iana_number. |
nozomi.cmc.alert.detail |
keyword |
The detail of the alert |
nozomi.cmc.alert.id |
keyword |
The identifier of the alert |
nozomi.cmc.alert.is_security |
boolean |
Indicates whether the alert represents a security issue |
nozomi.cmc.alert.parents |
keyword |
The parents of the alert |
nozomi.cmc.alert.risk |
number |
The risk of the alert |
nozomi.cmc.version |
keyword |
The version of the Nozomi Central Management Console |
observer.product |
keyword |
The product name of the observer. |
observer.vendor |
keyword |
Vendor name of the observer. |
source.domain |
keyword |
The domain name of the source. |
source.ip |
ip |
IP address of the source. |
source.mac |
keyword |
MAC address of the source. |
source.port |
long |
Port of the source. |
source.user.name |
keyword |
Short name or login of the user. |
threat.tactic.name |
keyword |
Threat tactic. |
threat.technique.id |
keyword |
Threat technique id. |
user_agent.original |
keyword |
Unparsed user_agent string. |
For more information on the Intake Format, please find the code of the Parser, Smart Descriptions, and Supported Events here.