ArubaOS Switch
Overview
Aruba OS-S is the operating system developed by Aruba Networks, designed for their networking devices and infrastructure. It offers advanced features for wireless and wired networking, security, and management, enhancing network performance and reliability.
- Vendor: Aruba Networks
- Supported environment: On Premise
- Version compatibility: AOS-S 16.10 (Latest version as of now)
- Detection based on: Telemetry
- Supported application or feature: Network management and performance monitoring
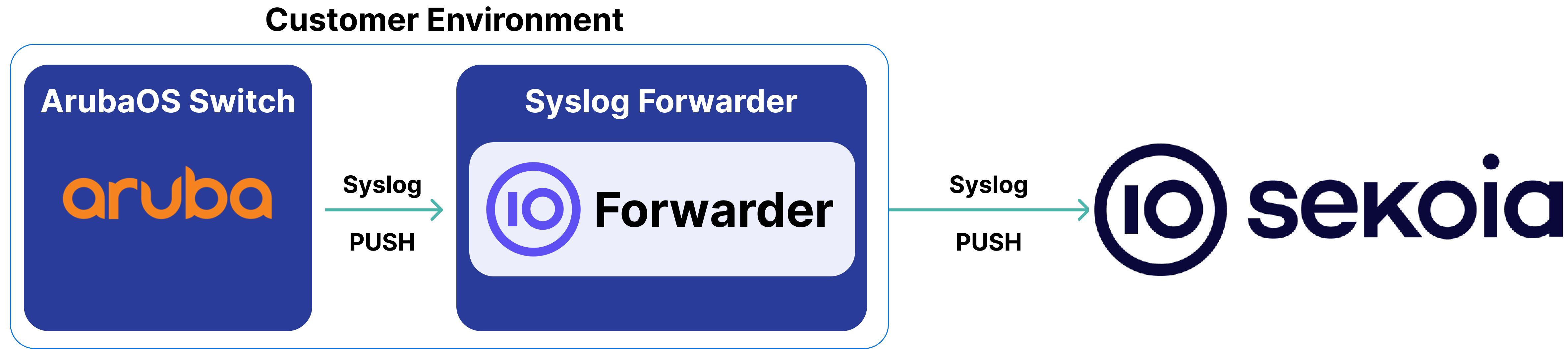
High-Level Architecture Diagram
- Type of integration: Outbound (PUSH to Sekoia.io)
- Schema
Specification
Prerequisites
- Resource:
- Self-managed syslog forwarder
- Network:
- Outbound traffic allowed
- Permissions:
- Administrator or Root access to the ArubaOS device
- Root access to the Linux server with the syslog forwarder
Transport Protocol/Method
- Indirect Syslog
Logs details
- Supported functionalities: See section Overview
- Supported type(s) of structure: Plain Text
- Supported verbosity level: Informational
Note
Log levels are based on the taxonomy of RFC5424. Adapt according to the terminology used by the editor.
Step-by-Step Configuration Procedure
Instructions on the 3rd Party Solution
This setup guide will show you how to forward your ArubaOS logs to Sekoia.io by means of a syslog transport channel.
Enable Syslog Forwarding for ArubaOS
- Log in to your ArubaOS device using SSH, Telnet, or the web-based management interface, depending on your preferred method.
- Access the configuration mode on your ArubaOS device. For example, if you are using the CLI, you might use the
configure terminalcommand.
Configure Syslog Settings
- Use the following command to specify the syslog server's IP address:
Replace
logging x.x.x.xx.x.x.xwith the IP address of your syslog concentrator. - Additionally, you can specify the syslog server's UDP port using the
portkeyword:Replacelogging x.x.x.x port yyyyyyyywith the port number your syslog concentrator is configured to listen on.
Set Log Severity Levels
- Configure the severity level of logs that will be sent to the syslog server.
logging level informational
Save Configuration Changes
- Save your configuration changes by issuing the appropriate command (e.g.,
write memoryorcopy running-config startup-config) to ensure that the syslog configuration persists across reboots.
Test Syslog Forwarding (Optional)
- You can generate a test log entry to ensure that logs are being forwarded to the syslog server.
For example, use the following command:
This will generate a test log message that should appear in your syslog server's logs.
logging x.x.x.x testing
Verify Syslog Server Configuration
- On your syslog server, verify that it is configured to accept syslog messages in UDP from the ArubaOS device on the specified port.
Instruction on Sekoia
Configure Your Intake
This section will guide you through creating the intake object in Sekoia, which provides a unique identifier called the "Intake key." The Intake key is essential for later configuration, as it references the Community, Entity, and Parser (Intake Format) used when receiving raw events on Sekoia.
- Go to the Sekoia Intake page.
- Click on the
+ New Intakebutton at the top right of the page. - Search for your Intake by the product name in the search bar.
- Give it a Name and associate it with an Entity (and a Community if using multi-tenant mode).
- Click on
Create.
Note
For more details on how to use the Intake page and to find the Intake key you just created, refer to this documentation.
Configure a forwarder
To forward events using syslog to Sekoia.io, you need to update the syslog header with the intake key you previously created. Here is an example of your message before the forwarder
<%pri%>1 %timestamp:::date-rfc3339% %hostname% %app-name% %procid% LOG RAW_MESSAGE
<%pri%>1 %timestamp:::date-rfc3339% %hostname% %app-name% %procid% LOG [SEKOIA@53288 intake_key=\"YOUR_INTAKE_KEY\"] RAW_MESSAGE
To achieve this you can:
- Use the Sekoia.io forwarder which is the official supported way to collect data using the syslog protocol in Sekoia.io. In charge of centralizing data coming from many equipments/sources and forwarding them to Sekoia.io with the apporpriated format, it is a prepackaged option. You only have to provide your intake key as parameter.
- Use your own Syslog service instance. Maybe you already have an intance of one of these components on your side and want to reuse it in order to centralize data before forwarding them to Sekoia.io. When using this mode, you have to configure and maintain your component in order to respect the expected Sekoia.io format.
Warning
Only the Sekoia.io forwarder is officially supported. Other options are documented for reference purposes but do not have official support.
Raw Events Samples
In this section, you will find examples of raw logs as generated natively by the source. These examples are provided to help integrators understand the data format before ingestion into Sekoia.io. It is crucial for setting up the correct parsing stages and ensuring that all relevant information is captured.
auth: ST1-CMDR: Invalid user name/password on SSH session User 'john.doe' is trying to login from 1.2.3.4
auth: ST1-CMDR: User 'john.doe' logged in from 1.2.3.4 to SSH session
stm[8447]: <501093> <NOTI> AP:02:00:00:00:00:01 <1.2.3.4 02:00:00:00:00:01> Auth success: 02:00:00:00:00:02: AP 1.2.3.4-02:00:00:00:00:03-02:00:00:00:00:01
dhcp-snoop: ST1-CMDR: backplane: Attempt to release address 3.4.5.6 leased to port Trk7 detected on port Trk8
dhcp-snoop: ST1-CMDR: backplane: Ceasing bad release logs for 5m
LEEF:1.0|Aruba Networks|ClearPass|1.0.0.0|3003|messageId=1111-1-1 devTime=May 01 2025 18:00:02.009 CEST component=RADIUS level=INFO sub-cat=Authentication action=None description=Retired a EAP-FAST key for 10.20.30.40 Server. src=1.2.3.4 devTimeFormat=MMM dd yyyy HH:mm:ss.SSS z cat=System Events
Event|105|LOG_INFO|AMM|1/1|LLDP neighbor 02:00:00:00:00:00 updated on 1/1/18
Event|106|LOG_INFO|AMM|1/1|LLDP neighbor example.com deleted on 1/1/15
mgr: ST1-CMDR: SME SSH from 1.2.3.4 - MANAGER Mode
crypto: ST1-CMDR: Certificate used by http-ssl application is expired.
<133006> <6069> <ERRS> <FR0002SR021 10.33.17.8> User admin Failed Authentication (Processing USER_REQUEST on UserDB)
<133019> <6069> <ERRS> <FR0002SR021 10.33.17.8> User admin was not found in the database
<133121> <6069> <WARN> <FR0002SR021 1.2.3.4> make_response: Sending USERDB_REJ-msg to 127.0.0.1:8214 with msgtype:23 id:232 reqtype:1 dbtype:0
<522274> <5962> <ERRS> <FR0002SR021 3.4.5.6> Mgmt User Authentication failed. username=admin userip=1.2.3.4 servername=example.com serverip=3.4.5.6
<133006> <6069> <FR0002SR021 1.2.3.4> User user1 Failed Authentication (Processing USER_REQUEST on UserDB)
<133121> <6069> <FR0002SR021 1.2.3.4> make_response: Sending USERDB_REJ-msg to 192.0.2.1:8214 with msgtype:23 id:17 reqtype:1 dbtype:0
cli[5159]: <541004> <WARN> AP:AP-EXAMPLE <1.2.3.4 00:11:22:33:44:55> recv_sta_update: receive station msg, mac-02:00:00:00:00:00 bssid-22:11:22:33:44:55 essid-EXAMPLE timestamp-1746625272-529980.
stm[4826]: <501199> <NOTI> AP:IAP-RIYADH-02 <192.0.2.1 11:11:11:11:11:11> User authenticated, mac-02:00:00:00:00:00, username-test@test.com, IP-1.2.3.4, method-802.1x, role-Test_No_Corporate_Role
dhcp-server: ST1-CMDR: No IP addresses to offer from pool Adm-wifi (8 times in 60 seconds)
dhcp-server: ST1-CMDR: High threshold reached for pool Adm-wifi. Active bindings: 2, Free bindings: 0
FFI: ST1-CMDR: port 1/11-High collision or drop rate. See help.
ports: ST1-CMDR: port 2/16 in Trk7 is now on-line
ports: ST1-CMDR: port 2/16 is Blocked by LACP
ports: ST1-CMDR: port 1/8 is now on-line
ports: ST1-CMDR: port 1/8 is now off-line
<133006> <6069> <ERRS> <FR0002SR021 1.2.3.4> User user1 Failed Authentication (Processing USER_REQUEST on UserDB)
Event|403|LOG_INFO|AMM|1/1|Link status for interface 1/1/14 is up at 100 Mbps
Event|2012|LOG_INFO|AMM|1/1|CIST - Topology Change generated on port 1/1/14 going in to forwarding
Event|6303|LOG_INFO|AMM|1/1|Current system memory usage for module 1/1 is 25%
ports: port 15 is now off-line
snmp: ST1-CMDR: Security access violation from 1.2.3.4 for the community name or user name : internal
snmp: ST1-CMDR: Security access violation from 1.2.3.4 for the community name or user name : internal (1 times in 60 seconds)
SNTP: ST1-CMDR: Updated time by 4 seconds from server at 1.2.3.4. Previous time was Mon Aug 28 11:53:06 2023. Current time is Mon Aug 28 11:53:10 2023.
ssl: ST1-CMDR: User :TLS connection failed for WEB-UI session from 1.2.3.4. (1 times in 60 seconds)
ssl: ST1-CMDR: SSL/TLS session closed for WEB-UI from 1.2.3.4.
Detection section
The following section provides information for those who wish to learn more about the detection capabilities enabled by collecting this intake. It includes details about the built-in rule catalog, event categories, and ECS fields extracted from raw events. This is essential for users aiming to create custom detection rules, perform hunting activities, or pivot in the events page.
Related Built-in Rules
The following Sekoia.io built-in rules match the intake ArubaOS Switch. This documentation is updated automatically and is based solely on the fields used by the intake which are checked against our rules. This means that some rules will be listed but might not be relevant with the intake.
SEKOIA.IO x ArubaOS Switch on ATT&CK Navigator
Account Added To A Security Enabled Group
Detection in order to investigate who has added a specific Domain User in Domain Admins or Group Policy Creator Owners (Security event 4728)
- Effort: master
Account Removed From A Security Enabled Group
Detection in order to investigate who has removed a specific Domain User in Domain Admins or Group Policy Creator Owners (Security event 4729)
- Effort: master
Backup Catalog Deleted
The rule detects when the Backup Catalog has been deleted. It means the administrators will not be able to access any backups that were created earlier to perform recoveries. This is often being done using the wbadmin.exe tool.
- Effort: intermediate
Burp Suite Tool Detected
Burp Suite is a cybersecurity tool. When used as a proxy service, its purpose is to intercept packets and modify them to send them to the server. Burp Collaborator is a network service that Burp Suite uses to help discover many kinds of vulnerabilities (vulnerabilities scanner).
- Effort: intermediate
Computer Account Deleted
Detects computer account deletion.
- Effort: master
Correlation Potential DNS Tunnel
Detects domain name which is longer than 62 characters and requested at least 50 times in a 10 minutes range time. Long domain names are distinctive of DNS tunnels.
- Effort: advanced
Cryptomining
Detection of domain names potentially related to cryptomining activities.
- Effort: master
DHCP Server Error Failed Loading the CallOut DLL
This rule detects a DHCP server error in which a specified Callout DLL (in registry) could not be loaded.
- Effort: intermediate
DHCP Server Loaded the CallOut DLL
This rule detects a DHCP server in which a specified Callout DLL (in registry) was loaded. This would indicate a succesful attack against DHCP service allowing to disrupt the service or alter the integrity of the responses.
- Effort: intermediate
DNS Server Error Failed Loading The ServerLevelPluginDLL
This rule detects a DNS server error in which a specified plugin DLL (in registry) could not be loaded. This requires the dedicated Windows event provider Microsoft-Windows-DNS-Server-Service.
- Effort: master
Domain Trust Created Or Removed
A trust was created or removed to a domain. An attacker could perform that in order to do lateral movement easily between domains or shutdown the ability of two domains to communicate.
- Effort: advanced
Dynamic DNS Contacted
Detect communication with dynamic dns domain. This kind of domain is often used by attackers. This rule can trigger false positive in non-controlled environment because dynamic dns is not always malicious.
- Effort: master
EvilProxy Phishing Domain
Detects subdomains potentially generated by the EvilProxy adversary-in-the-middle phishing platform. Inspect the other subdomains of the domain to identify the landing page, and determine if the user submitted credentials. This rule has a small percentage of false positives on legitimate domains.
- Effort: intermediate
Exfiltration Domain
Detects traffic toward a domain flagged as a possible exfiltration vector.
- Effort: master
Login Brute-Force Successful On ArubaOS Switch
A user has attempted to login several times (brute-force) on ArubaOS switch and succeeded to login.
- Effort: advanced
Microsoft Defender Antivirus History Deleted
Windows Defender history has been deleted. Could be an attempt by an attacker to remove its traces.
- Effort: master
Microsoft Defender Antivirus Tampering Detected
Detection of Windows Defender Tampering, from definitions' deletion to deactivation of parts or all of Defender.
- Effort: advanced
Microsoft Defender Antivirus Threat Detected
Detection of a windows defender alert indicating the presence of potential malware
- Effort: advanced
Password Change On Directory Service Restore Mode (DSRM) Account
The Directory Service Restore Mode (DSRM) account is a local administrator account on Domain Controllers. Attackers may change the password to gain persistence.
- Effort: intermediate
Possible Replay Attack
This event can be a sign of Kerberos replay attack or, among other things, network device configuration or routing problems.
- Effort: master
Potential DNS Tunnel
Detects domain name which is longer than 62 characters. Long domain names are distinctive of DNS tunnels.
- Effort: advanced
Remote Access Tool Domain
Detects traffic toward a domain flagged as a Remote Administration Tool (RAT).
- Effort: master
Remote Monitoring and Management Software - AnyDesk
Detect artifacts related to the installation or execution of the Remote Monitoring and Management tool AnyDesk.
- Effort: master
Remote Monitoring and Management Software - Atera
Detect artifacts related to the installation or execution of the Remote Monitoring and Management tool Atera.
- Effort: master
SEKOIA.IO Intelligence Feed
Detect threats based on indicators of compromise (IOCs) collected by SEKOIA's Threat and Detection Research team.
- Effort: elementary
Sekoia.io EICAR Detection
Detects observables in Sekoia.io CTI tagged as EICAR, which are fake samples meant to test detection.
- Effort: master
Sign-In Via Known AiTM Phishing Kit
Detects a sign-in attempt from an IP address belonging to a known adversary-in-the-middle phishing kit.
- Effort: elementary
Suspicious TOR Gateway
Detects suspicious TOR gateways. Gateways are often used by the victim to pay and decrypt the encrypted files without installing TOR. Tor intercepts the network traffic from one or more apps on user’s computer, usually the user web browser, and shuffles it through a number of randomly-chosen computers before passing it on to its destination. This disguises user location, and makes it harder for servers to pick him/her out on repeat visits, or to tie together separate visits to different sites, this making tracking and surveillance more difficult. Before a network packet starts its journey, user’s computer chooses a random list of relays and repeatedly encrypts the data in multiple layers, like an onion. Each relay knows only enough to strip off the outermost layer of encryption, before passing what’s left on to the next relay in the list.
- Effort: advanced
TOR Usage Generic Rule
Detects TOR usage globally, whether the IP is a destination or source. TOR is short for The Onion Router, and it gets its name from how it works. TOR intercepts the network traffic from one or more apps on user’s computer, usually the user web browser, and shuffles it through a number of randomly-chosen computers before passing it on to its destination. This disguises user location, and makes it harder for servers to pick him/her out on repeat visits, or to tie together separate visits to different sites, this making tracking and surveillance more difficult. Before a network packet starts its journey, user’s computer chooses a random list of relays and repeatedly encrypts the data in multiple layers, like an onion. Each relay knows only enough to strip off the outermost layer of encryption, before passing what’s left on to the next relay in the list.
- Effort: master
Telegram Bot API Request
Detects suspicious DNS queries to api.telegram.org used by Telegram Bots of any kind
- Effort: advanced
User Account Created
Detects user creation on windows servers, which shouldn't happen in an Active Directory environment. Apply this on your windows server logs and not on your DC logs. One default account defaultuser0 is excluded as only used during Windows set-up. This detection use Security Event ID 4720.
- Effort: master
User Account Deleted
Detects local user deletion
- Effort: master
Event Categories
The following table lists the data source offered by this integration.
| Data Source | Description |
|---|---|
Network device logs |
None |
In details, the following table denotes the type of events produced by this integration.
| Name | Values |
|---|---|
| Kind | alert |
| Category | authentication, network, session |
| Type | connection, end, info, start |
Transformed Events Samples after Ingestion
This section demonstrates how the raw logs will be transformed by our parsers. It shows the extracted fields that will be available for use in the built-in detection rules and hunting activities in the events page. Understanding these transformations is essential for analysts to create effective detection mechanisms with custom detection rules and to leverage the full potential of the collected data.
{
"message": "auth: ST1-CMDR: Invalid user name/password on SSH session User 'john.doe' is trying to login from 1.2.3.4",
"event": {
"category": [
"authentication"
],
"dataset": "auth",
"outcome": "failure",
"reason": "Invalid user name/password on SSH session User 'john.doe' is trying to login from 1.2.3.4",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"related": {
"ip": [
"1.2.3.4"
],
"user": [
"john.doe"
]
},
"source": {
"address": "1.2.3.4",
"ip": "1.2.3.4"
},
"user": {
"name": "john.doe"
}
}
{
"message": "auth: ST1-CMDR: User 'john.doe' logged in from 1.2.3.4 to SSH session",
"event": {
"category": [
"authentication"
],
"dataset": "auth",
"outcome": "success",
"reason": "User 'john.doe' logged in from 1.2.3.4 to SSH session",
"type": [
"start"
]
},
"related": {
"ip": [
"1.2.3.4"
],
"user": [
"john.doe"
]
},
"source": {
"address": "1.2.3.4",
"ip": "1.2.3.4"
},
"user": {
"name": "john.doe"
}
}
{
"message": "stm[8447]: <501093> <NOTI> AP:02:00:00:00:00:01 <1.2.3.4 02:00:00:00:00:01> Auth success: 02:00:00:00:00:02: AP 1.2.3.4-02:00:00:00:00:03-02:00:00:00:00:01",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"reason": "Auth success: 02:00:00:00:00:02: AP 1.2.3.4-02:00:00:00:00:03-02:00:00:00:00:01",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"destination": {
"mac": "02:00:00:00:00:03"
},
"related": {
"ip": [
"1.2.3.4"
]
},
"source": {
"address": "1.2.3.4",
"ip": "1.2.3.4",
"mac": "02:00:00:00:00:01"
}
}
{
"message": "dhcp-snoop: ST1-CMDR: backplane: Attempt to release address 3.4.5.6 leased to port Trk7 detected on port Trk8",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"dataset": "dhcp-snoop",
"reason": "backplane: Attempt to release address 3.4.5.6 leased to port Trk7 detected on port Trk8",
"type": [
"connection"
]
},
"related": {
"ip": [
"3.4.5.6"
]
},
"source": {
"address": "3.4.5.6",
"ip": "3.4.5.6"
}
}
{
"message": "dhcp-snoop: ST1-CMDR: backplane: Ceasing bad release logs for 5m",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"dataset": "dhcp-snoop",
"reason": "backplane: Ceasing bad release logs for 5m",
"type": [
"connection"
]
}
}
{
"message": "LEEF:1.0|Aruba Networks|ClearPass|1.0.0.0|3003|messageId=1111-1-1 devTime=May 01 2025 18:00:02.009 CEST component=RADIUS level=INFO sub-cat=Authentication action=None description=Retired a EAP-FAST key for 10.20.30.40 Server. src=1.2.3.4 devTimeFormat=MMM dd yyyy HH:mm:ss.SSS z cat=System Events",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"code": "3003",
"dataset": "System Events",
"outcome": "unknown",
"provider": "RADIUS",
"reason": "Retired a EAP-FAST key for 10.20.30.40 Server.",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"@timestamp": "2025-05-01T18:00:02.009000Z",
"related": {
"ip": [
"1.2.3.4"
]
},
"source": {
"address": "1.2.3.4",
"ip": "1.2.3.4"
}
}
{
"message": "Event|105|LOG_INFO|AMM|1/1|LLDP neighbor 02:00:00:00:00:00 updated on 1/1/18",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"code": "105",
"dataset": "lldp",
"reason": "LLDP neighbor 02:00:00:00:00:00 updated on 1/1/18",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"observer": {
"ingress": {
"interface": {
"name": "1/1/18"
}
}
},
"source": {
"mac": "02:00:00:00:00:00"
}
}
{
"message": "Event|106|LOG_INFO|AMM|1/1|LLDP neighbor example.com deleted on 1/1/15",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"code": "106",
"dataset": "lldp",
"reason": "LLDP neighbor example.com deleted on 1/1/15",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"host": {
"name": "example.com"
},
"observer": {
"ingress": {
"interface": {
"name": "1/1/15"
}
}
}
}
{
"message": "mgr: ST1-CMDR: SME SSH from 1.2.3.4 - MANAGER Mode",
"event": {
"category": [
"session"
],
"dataset": "mgr",
"reason": "SME SSH from 1.2.3.4 - MANAGER Mode",
"type": [
"start"
]
},
"related": {
"ip": [
"1.2.3.4"
]
},
"source": {
"address": "1.2.3.4",
"ip": "1.2.3.4"
}
}
{
"message": "crypto: ST1-CMDR: Certificate used by http-ssl application is expired.",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"dataset": "crypto",
"reason": "Certificate used by http-ssl application is expired.",
"type": [
"connection"
]
}
}
{
"message": "<133006> <6069> <ERRS> <FR0002SR021 10.33.17.8> User admin Failed Authentication (Processing USER_REQUEST on UserDB)",
"event": {
"category": [
"authentication"
],
"outcome": "failure",
"reason": "User admin Failed Authentication (Processing USER_REQUEST on UserDB)",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"related": {
"ip": [
"10.33.17.8"
],
"user": [
"admin"
]
},
"source": {
"address": "10.33.17.8",
"ip": "10.33.17.8"
},
"user": {
"name": "admin"
}
}
{
"message": "<133019> <6069> <ERRS> <FR0002SR021 10.33.17.8> User admin was not found in the database",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"reason": "User admin was not found in the database",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"related": {
"ip": [
"10.33.17.8"
],
"user": [
"admin"
]
},
"source": {
"address": "10.33.17.8",
"ip": "10.33.17.8"
},
"user": {
"name": "admin"
}
}
{
"message": "<133121> <6069> <WARN> <FR0002SR021 1.2.3.4> make_response: Sending USERDB_REJ-msg to 127.0.0.1:8214 with msgtype:23 id:232 reqtype:1 dbtype:0",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"reason": "Sending USERDB_REJ-msg to 127.0.0.1:8214 with msgtype:23 id:232 reqtype:1 dbtype:0",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"destination": {
"address": "127.0.0.1",
"ip": "127.0.0.1",
"port": 8214
},
"related": {
"ip": [
"1.2.3.4",
"127.0.0.1"
]
},
"source": {
"address": "1.2.3.4",
"ip": "1.2.3.4"
}
}
{
"message": "<522274> <5962> <ERRS> <FR0002SR021 3.4.5.6> Mgmt User Authentication failed. username=admin userip=1.2.3.4 servername=example.com serverip=3.4.5.6",
"event": {
"category": [
"authentication"
],
"outcome": "failure",
"reason": "Mgmt User Authentication failed. username=admin userip=1.2.3.4 servername=example.com serverip=3.4.5.6",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"destination": {
"address": "example.com",
"domain": "example.com",
"ip": "3.4.5.6",
"registered_domain": "example.com",
"top_level_domain": "com"
},
"related": {
"hosts": [
"example.com"
],
"ip": [
"1.2.3.4",
"3.4.5.6"
],
"user": [
"admin"
]
},
"source": {
"address": "1.2.3.4",
"ip": "1.2.3.4"
},
"user": {
"name": "admin"
}
}
{
"message": "<133006> <6069> <FR0002SR021 1.2.3.4> User user1 Failed Authentication (Processing USER_REQUEST on UserDB)",
"event": {
"category": [
"authentication"
],
"outcome": "failure",
"reason": "User user1 Failed Authentication (Processing USER_REQUEST on UserDB)",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"related": {
"ip": [
"1.2.3.4"
],
"user": [
"user1"
]
},
"source": {
"address": "1.2.3.4",
"ip": "1.2.3.4"
},
"user": {
"name": "user1"
}
}
{
"message": "<133121> <6069> <FR0002SR021 1.2.3.4> make_response: Sending USERDB_REJ-msg to 192.0.2.1:8214 with msgtype:23 id:17 reqtype:1 dbtype:0",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"reason": "Sending USERDB_REJ-msg to 192.0.2.1:8214 with msgtype:23 id:17 reqtype:1 dbtype:0",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"destination": {
"address": "192.0.2.1",
"ip": "192.0.2.1",
"port": 8214
},
"related": {
"ip": [
"1.2.3.4",
"192.0.2.1"
]
},
"source": {
"address": "1.2.3.4",
"ip": "1.2.3.4"
}
}
{
"message": "cli[5159]: <541004> <WARN> AP:AP-EXAMPLE <1.2.3.4 00:11:22:33:44:55> recv_sta_update: receive station msg, mac-02:00:00:00:00:00 bssid-22:11:22:33:44:55 essid-EXAMPLE timestamp-1746625272-529980.",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"reason": "recv_sta_update: receive station msg, mac-02:00:00:00:00:00 bssid-22:11:22:33:44:55 essid-EXAMPLE timestamp-1746625272-529980.",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"related": {
"ip": [
"1.2.3.4"
]
},
"source": {
"address": "1.2.3.4",
"ip": "1.2.3.4",
"mac": "02:00:00:00:00:00"
}
}
{
"message": "stm[4826]: <501199> <NOTI> AP:IAP-RIYADH-02 <192.0.2.1 11:11:11:11:11:11> User authenticated, mac-02:00:00:00:00:00, username-test@test.com, IP-1.2.3.4, method-802.1x, role-Test_No_Corporate_Role",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"reason": "User authenticated, mac-02:00:00:00:00:00, username-test@test.com, IP-1.2.3.4, method-802.1x, role-Test_No_Corporate_Role",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"related": {
"ip": [
"192.0.2.1"
]
},
"source": {
"address": "192.0.2.1",
"ip": "192.0.2.1",
"mac": "02:00:00:00:00:00"
},
"user": {
"email": "test@test.com"
}
}
{
"message": "dhcp-server: ST1-CMDR: No IP addresses to offer from pool Adm-wifi (8 times in 60 seconds)",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"dataset": "dhcp-server",
"reason": "No IP addresses to offer from pool Adm-wifi (8 times in 60 seconds)",
"type": [
"connection"
]
}
}
{
"message": "dhcp-server: ST1-CMDR: High threshold reached for pool Adm-wifi. Active bindings: 2, Free bindings: 0",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"dataset": "dhcp-server",
"reason": "High threshold reached for pool Adm-wifi. Active bindings: 2, Free bindings: 0",
"type": [
"connection"
]
}
}
{
"message": "FFI: ST1-CMDR: port 1/11-High collision or drop rate. See help.",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"dataset": "FFI",
"reason": "port 1/11-High collision or drop rate. See help.",
"type": [
"connection"
]
}
}
{
"message": "ports: ST1-CMDR: port 2/16 in Trk7 is now on-line",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"dataset": "ports",
"reason": "port 2/16 in Trk7 is now on-line",
"type": [
"connection"
]
}
}
{
"message": "ports: ST1-CMDR: port 2/16 is Blocked by LACP",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"dataset": "ports",
"reason": "port 2/16 is Blocked by LACP",
"type": [
"connection"
]
}
}
{
"message": "ports: ST1-CMDR: port 1/8 is now on-line",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"dataset": "ports",
"reason": "port 1/8 is now on-line",
"type": [
"connection"
]
}
}
{
"message": "ports: ST1-CMDR: port 1/8 is now off-line",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"dataset": "ports",
"reason": "port 1/8 is now off-line",
"type": [
"connection"
]
}
}
{
"message": "<133006> <6069> <ERRS> <FR0002SR021 1.2.3.4> User user1 Failed Authentication (Processing USER_REQUEST on UserDB)",
"event": {
"category": [
"authentication"
],
"outcome": "failure",
"reason": "User user1 Failed Authentication (Processing USER_REQUEST on UserDB)",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"related": {
"ip": [
"1.2.3.4"
],
"user": [
"user1"
]
},
"source": {
"address": "1.2.3.4",
"ip": "1.2.3.4"
},
"user": {
"name": "user1"
}
}
{
"message": "Event|403|LOG_INFO|AMM|1/1|Link status for interface 1/1/14 is up at 100 Mbps",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"code": "403",
"reason": "Link status for interface 1/1/14 is up at 100 Mbps",
"type": [
"info"
]
}
}
{
"message": "Event|2012|LOG_INFO|AMM|1/1|CIST - Topology Change generated on port 1/1/14 going in to forwarding",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"code": "2012",
"reason": "CIST - Topology Change generated on port 1/1/14 going in to forwarding",
"type": [
"info"
]
}
}
{
"message": "Event|6303|LOG_INFO|AMM|1/1|Current system memory usage for module 1/1 is 25%",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"code": "6303",
"reason": "Current system memory usage for module 1/1 is 25%",
"type": [
"info"
]
}
}
{
"message": "ports: port 15 is now off-line",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"dataset": "ports",
"reason": "port 15 is now off-line",
"type": [
"connection"
]
}
}
{
"message": "snmp: ST1-CMDR: Security access violation from 1.2.3.4 for the community name or user name : internal",
"event": {
"category": [
"session"
],
"dataset": "snmp",
"kind": "alert",
"reason": "Security access violation from 1.2.3.4 for the community name or user name : internal",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"related": {
"ip": [
"1.2.3.4"
]
},
"source": {
"address": "1.2.3.4",
"ip": "1.2.3.4"
}
}
{
"message": "snmp: ST1-CMDR: Security access violation from 1.2.3.4 for the community name or user name : internal (1 times in 60 seconds)",
"event": {
"category": [
"session"
],
"dataset": "snmp",
"kind": "alert",
"reason": "Security access violation from 1.2.3.4 for the community name or user name : internal (1 times in 60 seconds)",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"related": {
"ip": [
"1.2.3.4"
]
},
"source": {
"address": "1.2.3.4",
"ip": "1.2.3.4"
}
}
{
"message": "SNTP: ST1-CMDR: Updated time by 4 seconds from server at 1.2.3.4. Previous time was Mon Aug 28 11:53:06 2023. Current time is Mon Aug 28 11:53:10 2023.",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"dataset": "SNTP",
"reason": "Updated time by 4 seconds from server at 1.2.3.4. Previous time was Mon Aug 28 11:53:06 2023. Current time is Mon Aug 28 11:53:10 2023.",
"type": [
"connection"
]
},
"related": {
"ip": [
"1.2.3.4"
]
},
"source": {
"address": "1.2.3.4",
"ip": "1.2.3.4"
}
}
{
"message": "ssl: ST1-CMDR: User :TLS connection failed for WEB-UI session from 1.2.3.4. (1 times in 60 seconds)",
"event": {
"category": [
"session"
],
"dataset": "ssl",
"reason": "User :TLS connection failed for WEB-UI session from 1.2.3.4. (1 times in 60 seconds)",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"related": {
"ip": [
"1.2.3.4"
]
},
"source": {
"address": "1.2.3.4",
"ip": "1.2.3.4"
}
}
{
"message": "ssl: ST1-CMDR: SSL/TLS session closed for WEB-UI from 1.2.3.4.",
"event": {
"category": [
"session"
],
"dataset": "ssl",
"reason": "SSL/TLS session closed for WEB-UI from 1.2.3.4.",
"type": [
"end"
]
},
"related": {
"ip": [
"1.2.3.4"
]
},
"source": {
"address": "1.2.3.4",
"ip": "1.2.3.4"
}
}
Extracted Fields
The following table lists the fields that are extracted, normalized under the ECS format, analyzed and indexed by the parser. It should be noted that infered fields are not listed.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
@timestamp |
date |
Date/time when the event originated. |
destination.domain |
keyword |
The domain name of the destination. |
destination.ip |
ip |
IP address of the destination. |
destination.mac |
keyword |
MAC address of the destination. |
destination.port |
long |
Port of the destination. |
event.action |
keyword |
The action captured by the event. |
event.category |
keyword |
Event category. The second categorization field in the hierarchy. |
event.code |
keyword |
Identification code for this event. |
event.dataset |
keyword |
Name of the dataset. |
event.kind |
keyword |
The kind of the event. The highest categorization field in the hierarchy. |
event.outcome |
keyword |
The outcome of the event. The lowest level categorization field in the hierarchy. |
event.provider |
keyword |
Source of the event. |
event.reason |
keyword |
Reason why this event happened, according to the source |
event.type |
keyword |
Event type. The third categorization field in the hierarchy. |
host.name |
keyword |
Name of the host. |
observer.ingress.interface.name |
keyword |
Interface name |
source.ip |
ip |
IP address of the source. |
source.mac |
keyword |
MAC address of the source. |
user.email |
keyword |
User email address. |
user.name |
keyword |
Short name or login of the user. |
For more information on the Intake Format, please find the code of the Parser, Smart Descriptions, and Supported Events here.