Azure Application Gateway
Overview
Azure Application Gateway is a web traffic load balancer that manages traffic to your web applications with advanced routing, SSL termination, and Web Application Firewall (WAF) features. It ensures high availability, scalability, and integrates seamlessly with other Azure services for efficient deployment and management. Additionally, it offers insights and diagnostics to monitor and optimize application performance.
- Vendor: Azure
- Supported environment: SaaS
- Detection based on: Telemetry
- Supported application or feature: Access logs, Firewall logs
Specification
Prerequisites
- You need to have
Contributorrole in Azure. - You should have properly configured Azure Event Hub
Step-by-Step Configuration Procedure
How to setup Event Hub
Azure Event Hubs is a cloud-based event streaming platform and event ingestion service provided by Microsoft Azure. It is designed to handle large amounts of event data generated by various applications, devices, and services in real-time. Event Hubs enables you to ingest, process, and store events, logs, telemetry data, and other streaming data for further analysis, monitoring, and processing. Two ways are suggested in order to set up everything you need to forward your events on Sekoia.io.
If you are not an expert and want an easy way to configure the ressources on Azure, we recommend to use to Automatic way as it is easier to set up.
These two ways will create an Azure Event Hub and a Storage Account.
** Use the template to create the ressources**
To get started, click on the button below and fill the form on Azure to set up the required environment for Sekoia
Some fields must be filled in.
Project details
- Subscription: select the Azure subscription you want to use
- Resource Group: select or create a new Resource Group. A Resource Group is a container that holds related resources
Instance details
- Region: select the appropriated region
- Project Name: give a name for this project. Here is how the names of the resources will be affected by this project name
| Ressource | Name |
|---|---|
| Event Hub Namespace | <project_name>ehns |
| Event Hub | <project_name>eh |
| Shared Access Policy | <project_name>ap |
| Consumer Group | <project_name>cp |
| Storage Account | <project_name>sa |
- Event Hub Sku: Select the messaging tier for Event Hub Namespace between
Basic,StandardorPremium. We do not recommendBasicmodel due to its limitation. Please follow this Microsoft web page to get more information avec the different messaging tier. - Troughput Unit: A unit gives you up to 1 MB/s or 1,000 events per second (whichever comes first) per Event Hub Namespace. Please adapt it to your need.
- Enable Auto Inflate: When checked, the Auto-inflate feature of Event Hubs automatically scales up by increasing the number of troughput units, to meet usage needs.
- Auto Inflate Maximum Throughput Unit: When Enable Auto Inflate is checked, you can specify the maximum throughput units you allow.
- Partition Count: The number of event hub partitions. Microsoft recommends a maximum throughput of 1 MB/s per partition. Unless you plan to add more Event hubs to the Event Hub Namespace, the Partition Count and Throughput Unit variables should have the same values.
- Retention Time: How long you will keep events in the Event hub in days.
** Use the output variables to create a Sekoia playbook**
When the message Your deployment is complete is displayed, click on Outputs.

Keep these 5 pieces of information displayed carefully, it will used to configure the Trigger Configuration of the Sekoia playbook.
Overview
This setup guide will show you how to create an Event Hub manually.
Theses changes have to be made from the Azure Web Portal.
Some resources created during this procedure are needed to connect Sekoia.io to the Event Hub, you can complete the following table to save all the useful informations for later use.
| Name | Value | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| hub_name | To be completed at step 3 | Name of the Event Hub | sekoia_event_hub |
| hub_connection_string | To be completed at step 5 | Connection string–primary key | Endpoint=sb://company-eventhub.servicebus.windows.net/;SharedAccessKeyName=sekoiaio;SharedAccessKey=XXXXXX;EntityPath=sekoia_event_hub |
| hub_consumer_group | To be completed at step 6 | Name of the comsumer group | consumergroup_sekoiaio |
| storage_container_name | To be completed at step 7 | Name of your container | sekoiaio |
| storage_connection_string | To be completed at step 8 | Storage connection string | DefaultEndpointsProtocol=https;AccountName=sekoiaiocheckpoint;AccountKey=XXXXX |
As a prerequisite, you need to choose an existing Resource group, or create a new one (e.g. company-resource-group).
Step 1: Find your Subscription ID
- Go to: Home > Cost Management + Billing > Subscriptions.
- From there, keep the relevant “Subscription ID” that will be used along the process.

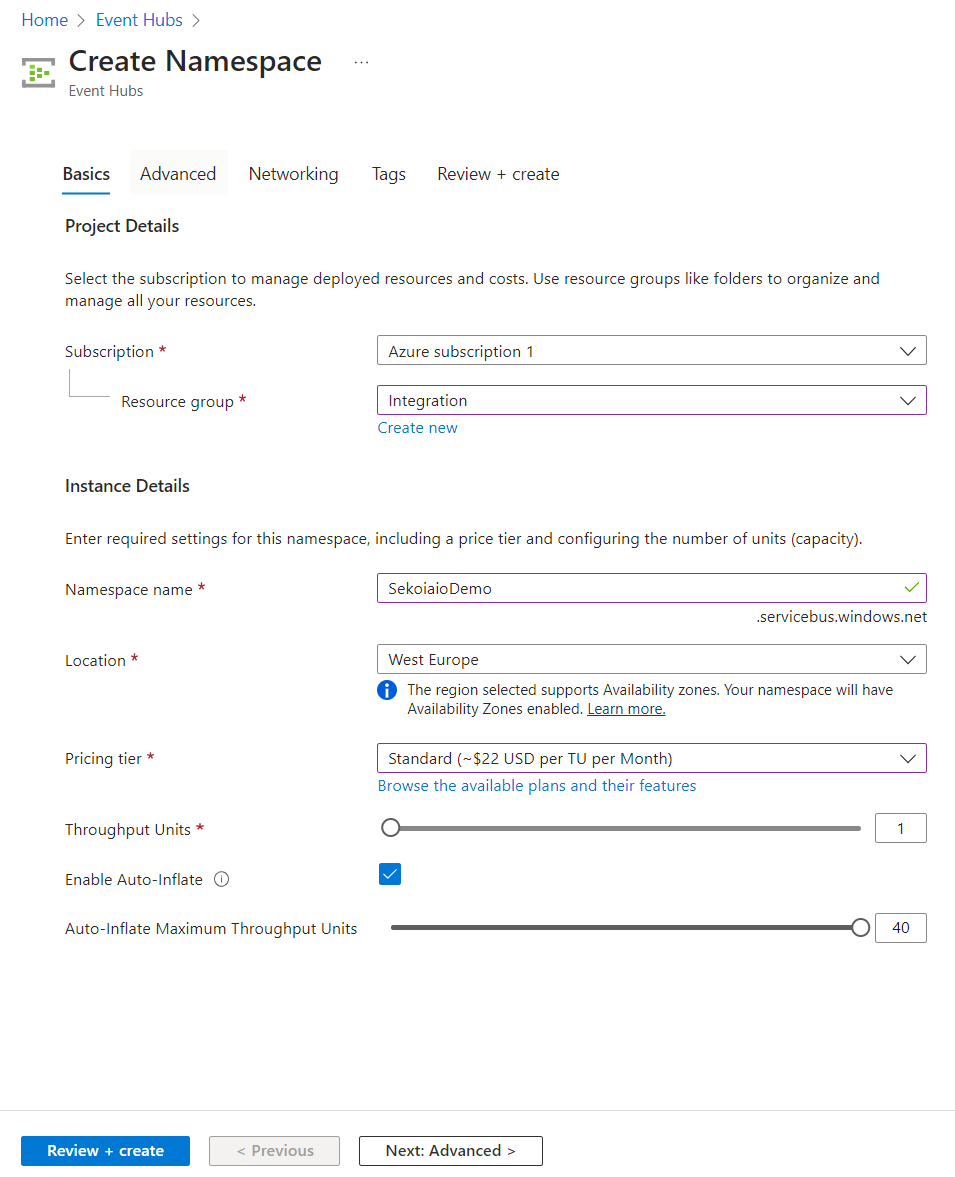
Step 2: Create Event Hub Namespace
- Navigate to Home > Event Hubs.
- Create an Event Hub Namespace.
- Select your Subscription and your Resource group. Click on create new if you want your Event Hub Namespace in a new Resource group.
- Choose a namespace name.
- Select a location based on your events location.
- Select the pricing tier plan based on your utilisation: Standard or Premimum (We don't recommend to choose the Basic plan due to its limitations.)
- Select the throughput units number based on your events, or enable the auto inflate mode:
1 throughput unit can process up to 1 MB per second or 1000 events per second (whichever comes first).
Step 3: Create Event Hub Instance
When your Event Hub Namespace is created you can create an Event Hub inside:
- Navigate to Home > Event Hubs > company-eventhubnamespace.
- Create an Event Hub.
- Select 4 as default partition count
- Select
Deleteas cleanup policy - Type 168h (7 days) as retention time
- Click
Create
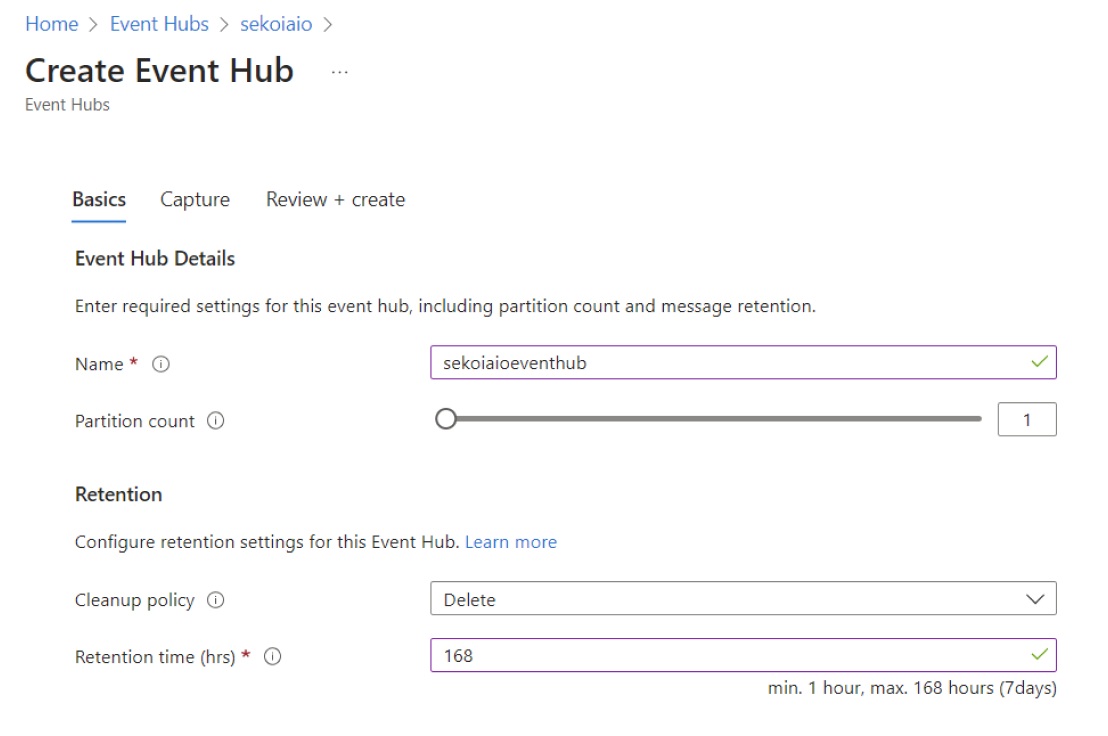
Info
Carefully store the Event Hub name that will be used for sekoia playbook configuration.
Step 4: Create “Shared Access Policies” for the Event Hub
- Navigate to Home > Event Hubs > company-eventhubnamespace > eventhubname | Shared access policies.
-
Create a policy (e.g.
sekoiaio) with the claimsListen.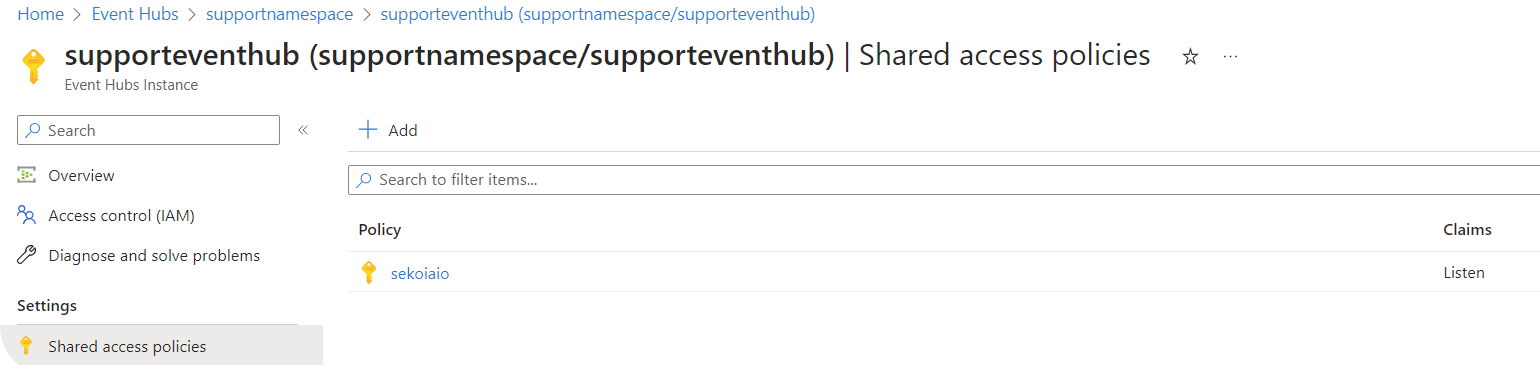
-
Once created, click on the policy.
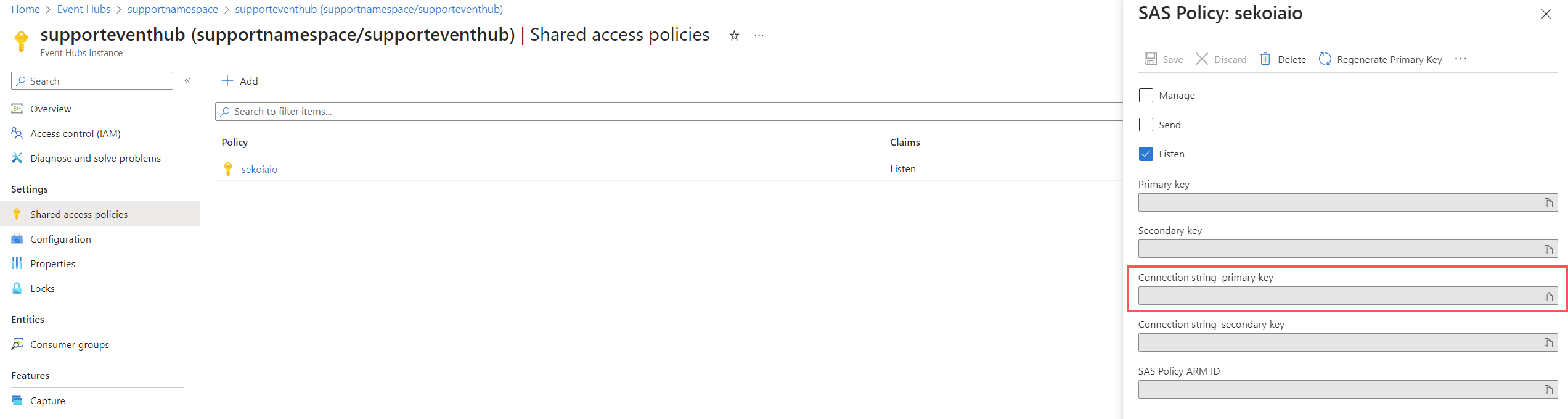
Info
Carefully store the connection string–primary key that will be used for sekoia playbook configuration.
Step 5: Create a Consumer group
- Navigate to Home > Event Hubs > company-eventhubnamespace > eventhubname | Consumer groups.
- Create a Consumer group (e.g.
consumergroup_sekoiaio).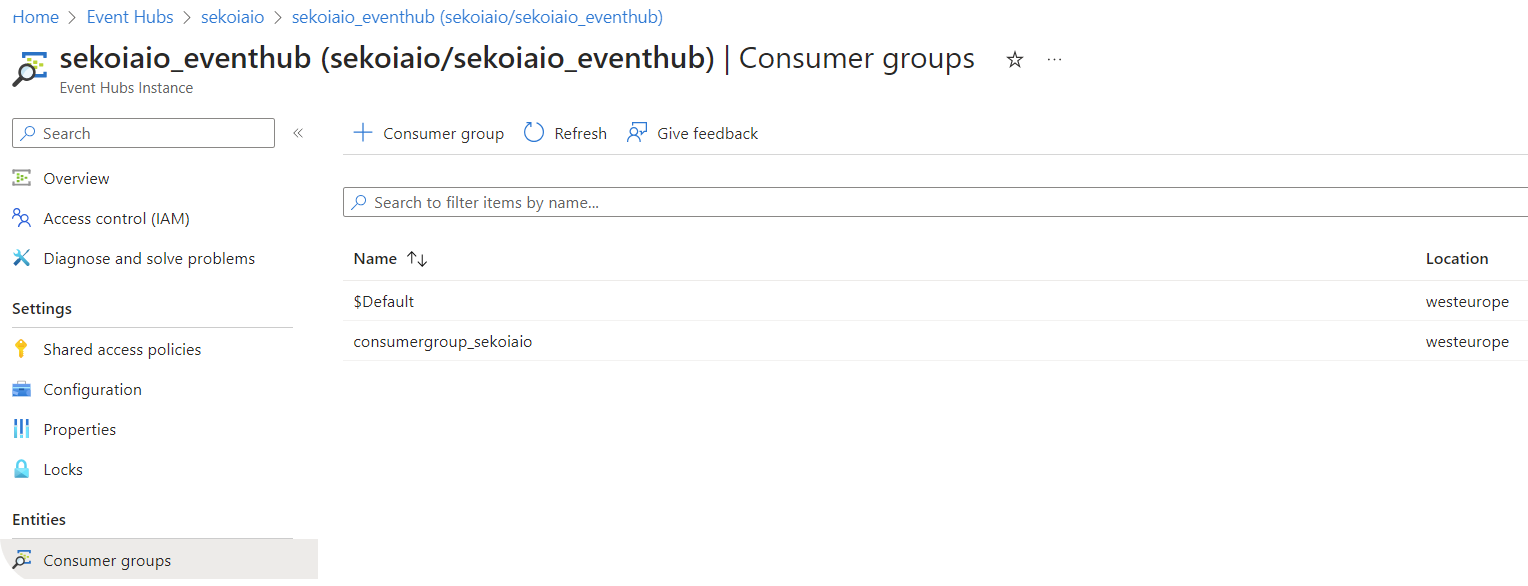
Info
Carefully store the Consumer group name that will be used for sekoia playbook configuration.
Step 6: Create a Storage Account with a container
In order to allow Sekoia.io keep track of the consumed events, the next step consists in creating a dedicated Storage account.
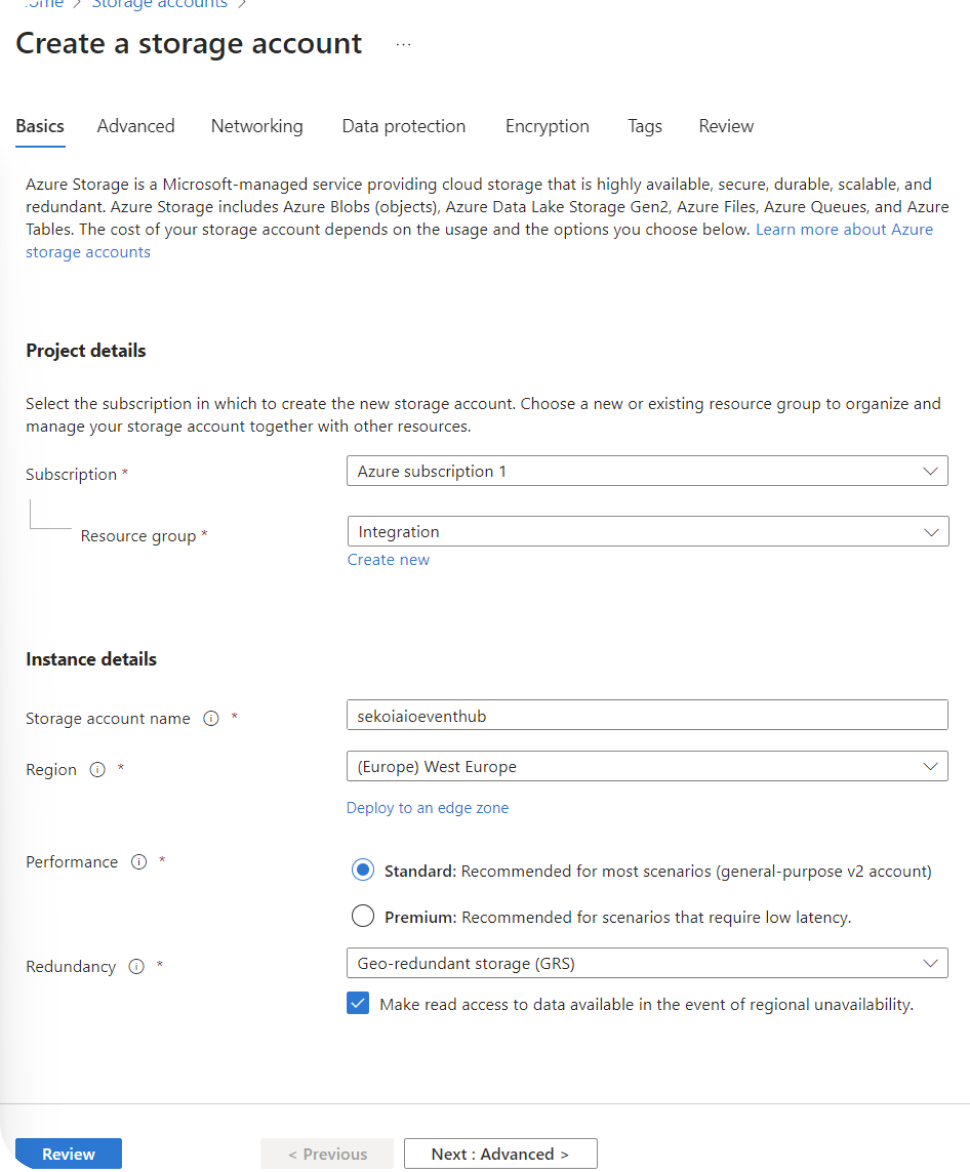
- Navigate to Home > Storage accounts.
- Create a Storage account.
- Select your Subscription and your Resource group.
- Choose a Storage account name.
-
Select a Region.
Info
You must choose the Region used during the Event Hub Namespace creation.
-
Select your perfomance and redundancy parameters.
Info
We advise at least the following values: - performance: standard - redundancy: Geo-Redundancy storage (GRS)
When your storage account is created you can create an container inside. 1. Navigate to Home > Storage accounts > storageaccoutname | containers. 2. Create an container.
Keep the Public Acces Level to Private.
Info
The container name should be the same as the Event Hub name. Carefully store that container name that will be used for sekoia playbook configuration.
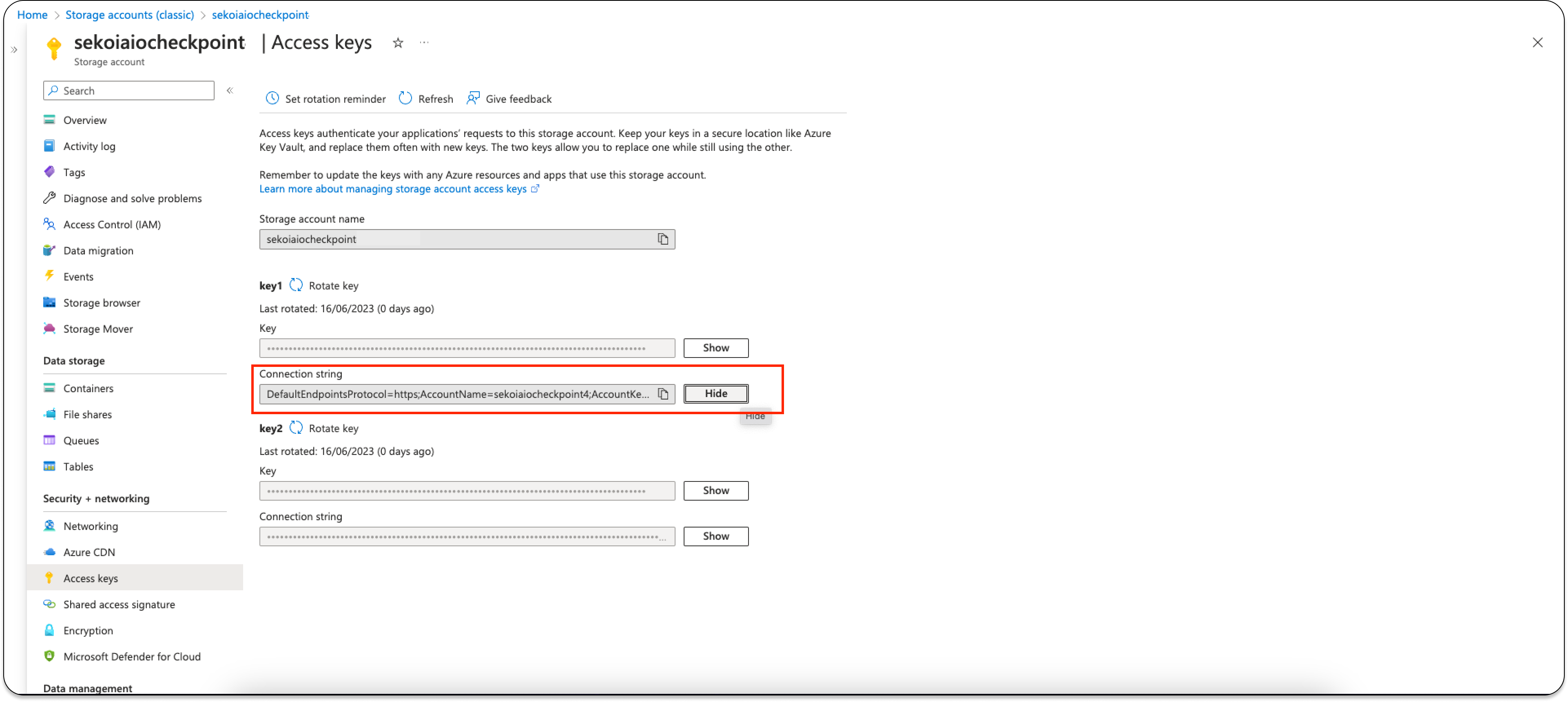
Step 7: Retrieve Connection String
You have to retrieve the connection string from Azure Web Portal.
- Go to Home > Storage accounts > storageaccoutname | Access Keys.
- Click on "Show Keys" on the first Connection String.
Info
Carefully store the Connection String that will be used for sekoia playbook configuration.
Further Readings
Enable Application Gateway diagnostics logs
The following instructions are provided for the Azure web portal (https://portal.azure.com).
- In the Azure portal, find your resource and select Diagnostic settings.
- To start collecting data, select Turn on diagnostics.
- The Diagnostics settings page provides the settings for the diagnostic logs. You should use Event Hub configuration. More details about how it works you can find here
- Please select Access Logs and Firewall Logs to stream them to the Event Hub.
- Type a name for the settings, confirm the settings, and select Save.
These instructions are illustrated and more detailed here.
Create the intake in Sekoia.io
- Go to the intake page and create a new intake from the format
Azure Application Gateway. - Set up the intake configuration with the EventHub's
Connection string-primary key, the hub name, the consumer group, the storage'sConnection string-primary keyand the container name.
Raw Events Samples
In this section, you will find examples of raw logs as generated natively by the source. These examples are provided to help integrators understand the data format before ingestion into Sekoia.io. It is crucial for setting up the correct parsing stages and ensuring that all relevant information is captured.
{
"resourceId": "/SUBSCRIPTIONS/<subscription id>/RESOURCEGROUPS/<resoource group name>/PROVIDERS/MICROSOFT.NETWORK/APPLICATIONGATEWAYS/<application gateway name>",
"operationName": "ApplicationGatewayAccess",
"time": "2016-04-11T04:24:37Z",
"category": "ApplicationGatewayAccessLog",
"properties": {
"instanceId": "ApplicationGatewayRole_IN_0",
"clientIP": "37.186.113.170",
"clientPort": "12345",
"httpMethod": "HEAD",
"requestUri": "/xyz/portal",
"requestQuery": "",
"userAgent": "-",
"httpStatus": "200",
"httpVersion": "HTTP/1.0",
"receivedBytes": "27",
"sentBytes": "202",
"timeTaken": "359",
"sslEnabled": "off"
}
}
{
"timeStamp": "2021-10-14T22:17:11+00:00",
"resourceId": "/SUBSCRIPTIONS/{subscriptionId}/RESOURCEGROUPS/{resourceGroupName}/PROVIDERS/MICROSOFT.NETWORK/APPLICATIONGATEWAYS/{applicationGatewayName}",
"listenerName": "HTTP-Listener",
"ruleName": "Storage-Static-Rule",
"backendPoolName": "StaticStorageAccount",
"backendSettingName": "StorageStatic-HTTPS-Setting",
"operationName": "ApplicationGatewayAccess",
"category": "ApplicationGatewayAccessLog",
"properties": {
"instanceId": "appgw_2",
"clientIP": "185.42.129.24",
"clientPort": 45057,
"httpMethod": "GET",
"originalRequestUriWithArgs": "/",
"requestUri": "/",
"requestQuery": "",
"userAgent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/52.0.2743.116 Safari/537.36",
"httpStatus": 200,
"httpVersion": "HTTP/1.1",
"receivedBytes": 184,
"sentBytes": 466,
"clientResponseTime": 0,
"timeTaken": 0.034,
"WAFEvaluationTime": "0.000",
"WAFMode": "Detection",
"transactionId": "592d1649f75a8d480a3c4dc6a975309d",
"sslEnabled": "on",
"sslCipher": "ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384",
"sslProtocol": "TLSv1.2",
"sslClientVerify": "NONE",
"sslClientCertificateFingerprint": "",
"sslClientCertificateIssuerName": "",
"serverRouted": "52.239.221.65:443",
"serverStatus": "200",
"serverResponseLatency": "0.028",
"upstreamSourcePort": "21564",
"originalHost": "20.110.30.194",
"host": "20.110.30.194",
"error_info": "ERRORINFO_NO_ERROR",
"contentType": "application/json"
}
}
{
"timeStamp": "2021-10-14T22:17:11+00:00",
"resourceId": "/SUBSCRIPTIONS/{subscriptionId}/RESOURCEGROUPS/{resourceGroupName}/PROVIDERS/MICROSOFT.NETWORK/APPLICATIONGATEWAYS/{applicationGatewayName}",
"operationName": "ApplicationGatewayFirewall",
"category": "ApplicationGatewayFirewallLog",
"properties": {
"instanceId": "appgw_2",
"clientIp": "185.42.129.24",
"clientPort": "",
"requestUri": "/",
"ruleSetType": "OWASP_CRS",
"ruleSetVersion": "3.0.0",
"ruleId": "920350",
"message": "Host header is a numeric IP address",
"action": "Matched",
"site": "Global",
"details": {
"message": "Warning. Pattern match \\\"^[\\\\d.:]+$\\\" at REQUEST_HEADERS:Host .... ",
"data": "20.110.30.194:80",
"file": "rules/REQUEST-920-PROTOCOL-ENFORCEMENT.conf",
"line": "791"
},
"hostname": "20.110.30.194:80",
"transactionId": "592d1649f75a8d480a3c4dc6a975309d",
"policyId": "default",
"policyScope": "Global",
"policyScopeName": "Global"
}
}
Detection section
The following section provides information for those who wish to learn more about the detection capabilities enabled by collecting this intake. It includes details about the built-in rule catalog, event categories, and ECS fields extracted from raw events. This is essential for users aiming to create custom detection rules, perform hunting activities, or pivot in the events page.
Related Built-in Rules
The following Sekoia.io built-in rules match the intake Azure Application Gateway. This documentation is updated automatically and is based solely on the fields used by the intake which are checked against our rules. This means that some rules will be listed but might not be relevant with the intake.
SEKOIA.IO x Azure Application Gateway on ATT&CK Navigator
Burp Suite Tool Detected
Burp Suite is a cybersecurity tool. When used as a proxy service, its purpose is to intercept packets and modify them to send them to the server. Burp Collaborator is a network service that Burp Suite uses to help discover many kinds of vulnerabilities (vulnerabilities scanner).
- Effort: intermediate
CVE-2018-11776 Apache Struts2
Apache Struts versions 2.3 to 2.3.34 and 2.5 to 2.5.16 suffer from possible Remote Code Execution when alwaysSelectFullNamespace is true (either by user or a plugin like Convention Plugin) and then: results are used with no namespace and in same time, its upper package have no or wildcard namespace and similar to results, same possibility when using url tag which doesn't have value and action set and in same time, its upper package have no or wildcard namespace.
- Effort: intermediate
CVE-2018-13379 Fortinet Exploit
Detects the successful exploitation of the Fortinet FortiOS CVE-2018-13379. This CVE is one of the most exploited CVEs since 2018. It is exploited by APT threat actors as well as cybercriminals. The exploitation of this CVE lead an unauthenticated user to get full access to FortiOS system file through SSL VPN via specially crafted HTTP resource requests. The exploit read /dev/cmdb/sslvpn_websession file, that contains login and passwords in (clear/text). An HTTP response status code = 200, means the file was successfully accessed. This vulnerability affects FortiOS 5.6.3 to 5.6.7 and FortiOS 6.0.0 to 6.0.4.
- Effort: advanced
CVE-2019-0604 SharePoint
Detects the exploitation of the SharePoint vulnerability (CVE-2019-0604).
- Effort: advanced
CVE-2019-11510 Pulse Secure Exploit
Detects the successful exploitation of the Pulse Secure vulnerability CVE-2019-11510. This CVE is one of the most exploited CVEs since 2019. It is exploited by diverse threat actors, leading sometimes in ransomware deployement among these groups: Maze, Conti, Egregor, DoppelPaymer, NetWalker and REvil. But also APT actors such as APT29. The exploitation of this CVE allows a remote, unauthenticated attacker to compromise a vulnerable VPN server. The attacker may be able to gain access to all active users and their plain-text credentials. It may also be possible for the attacker to execute arbitrary commands on each VPN client as it successfully connects to the VPN server. The exploit reads /etc/passwd file to get access to login and passwords in (clear/text). An HTTP response status code = 200, means the file was successfully accessed. This vulnerability affects 8.1R15.1, 8.2 before 8.2R12.1, 8.3 before 8.3R7.1, and 9.0 before 9.0R3.4 products.
- Effort: elementary
CVE-2019-19781 Citrix NetScaler (ADC)
Detects CVE-2019-19781 exploitation attempt against Citrix NetScaler (ADC), Application Delivery Controller and Citrix Gateway Attack.
- Effort: elementary
CVE-2019-2725 Oracle Weblogic Exploit
Detects the successful exploitation of a deserialization vulnerability in Oracle Weblogic Server, CVE-2019-2725. This vulnerability affects versions 10.X and 12.1.3 of WebLogic that have the components wls9_async_response.war and wls-wsat.war enabled. It is a remote code execution which can be exploited without authentication via HTTP. An HTTP response status code = 202, means the target is vulnerable, the analyst then has to look in depth to check if a webshell has been uploaded or something else has been done.
- Effort: elementary
CVE-2020-0688 Microsoft Exchange Server Exploit
Detects the exploitation of CVE-2020-0688. The POC exploit a .NET serialization vulnerability in the Exchange Control Panel (ECP) web page. The vulnerability is due to Microsoft Exchange Server not randomizing the keys on a per-installation basis resulting in them using the same validationKey and decryptionKey values. With knowledge of these, values an attacker can craft a special viewstate to use an OS command to be executed by NT_AUTHORITY\SYSTEM using .NET deserialization. To exploit this vulnerability, an attacker needs to leverage the credentials of an account it had already compromised to authenticate to OWA.
- Effort: elementary
CVE-2020-1147 SharePoint
Detection of SharePoint vulnerability CVE-2020-1147.
- Effort: advanced
CVE-2020-14882 Oracle WebLogic Server
Detects the exploitation of the Oracle WebLogic Server vulnerability (CVE-2020-16952).
- Effort: advanced
CVE-2020-17530 Apache Struts RCE
Detects the exploitation of the Apache Struts RCE vulnerability (CVE-2020-17530).
- Effort: intermediate
CVE-2020-5902 F5 BIG-IP Exploitation Attempts
Detects the exploitation attempt of the vulnerability found in F5 BIG-IP and described in CVE-2020-5902.
- Effort: elementary
CVE-2021-20021 SonicWall Unauthenticated Administrator Access
Detects the exploitation of SonicWall Unauthenticated Admin Access.
- Effort: advanced
CVE-2021-20023 SonicWall Arbitrary File Read
Detects Arbitrary File Read, which can be used with other vulnerabilities as a mean to obtain outputs generated by attackers, or sensitive data.
- Effort: advanced
CVE-2021-21972 VMware vCenter
The vSphere Client (HTML5) contains a remote code execution vulnerability in a vCenter Server plugin. A malicious actor with network access to port 443 may exploit this issue to execute commands with unrestricted privileges on the underlying operating system that hosts vCenter Server. This affects VMware vCenter Server (7.x before 7.0 U1c, 6.7 before 6.7 U3l and 6.5 before 6.5 U3n) and VMware Cloud Foundation (4.x before 4.2 and 3.x before 3.10.1.2). POST request on the following PATH "/ui/vropspluginui/rest/services/uploadova". If in response body (500) the words it has "uploadFile", that means the vCenter is available to accept files via POST without any restrictions.
- Effort: intermediate
CVE-2021-21985 VMware vCenter
The VMware vSphere Client (HTML5) contains a remote code execution vulnerability due to lack of input validation in the Virtual SAN Health Check plug-in which is enabled by default in vCenter Server. A malicious actor with network access to port 443 may exploit this issue to execute commands with unrestricted privileges on the underlying operating system that hosts vCenter Server. This affects VMware vCenter Server (7.0 before 7.0 U2b, 6.7 before 6.7 U3n and 6.5 before 6.5 U3p) and VMware Cloud Foundation (4.x before 4.2.1 and 3.x before 3.10.2.1).
- Effort: advanced
CVE-2021-22123 Fortinet FortiWeb OS Command Injection
Detects Fortinet FortiWeb OS Command Injection (August 2021) vulnerability exploitation attempt. A remote, authenticated attacker can execute arbitrary commands on the system hosting a vulnerable FortiWeb WAF by sending a POST request with the command in the name field. At the time of writing this rule, it would appear that the request would respond in code 500 for a successful exploitation attempt.
- Effort: advanced
CVE-2021-22893 Pulse Connect Secure RCE Vulnerability
Detects potential exploitation of the authentication by-pass vulnerability that can allow an unauthenticated user to perform remote arbitrary file execution on the Pulse Connect Secure gateway. It is highly recommended to apply the Pulse Secure mitigations and seach for indicators of compromise on affected servers if you are in doubt over the integrity of your Pulse Connect Secure product.
- Effort: intermediate
CVE-2021-26855 Exchange SSRF
Detects the exploitation of ProyxLogon vulerability on Exchange servers.
- Effort: advanced
CVE-2021-34473 ProxyShell Attempt
Detects CVE-2021-34473 ProxyShell attempt against Microsoft Exchange Server, Remote Code Execution Vulnerability.
- Effort: advanced
CVE-2021-41773 Apache 2.4.49 Path Traversal
Detects successful exploitation of the Apache Path Traversal CVE-2021-41773.
- Effort: advanced
CVE-2021-43798 Grafana Directory Traversal
Grafana version 8.x has a 0day arbitrary file read (with no fix yet) based on a directory traversal vulnerability
- Effort: intermediate
Covenant Default HTTP Beaconing
Detects potential Covenant communications through the user-agent and specific urls
- Effort: intermediate
Cryptomining
Detection of domain names potentially related to cryptomining activities.
- Effort: master
Detect requests to Konni C2 servers
This rule detects requests to Konni C2 servers. These patterns come from an analysis done in 2022, September.
- Effort: elementary
Discord Suspicious Download
Discord is a messaging application. It allows users to create their own communities to share messages and attachments. Those attachments have little to no overview and can be downloaded by almost anyone, which has been abused by attackers to host malicious payloads.
- Effort: advanced
Dynamic DNS Contacted
Detect communication with dynamic dns domain. This kind of domain is often used by attackers. This rule can trigger false positive in non-controlled environment because dynamic dns is not always malicious.
- Effort: master
Exfiltration Domain
Detects traffic toward a domain flagged as a possible exfiltration vector.
- Effort: master
FoggyWeb HTTP Default GET/POST Requests
Detects GET or POST request pattern observed within the first FoggyWeb campaign detected by Microsoft.
- Effort: advanced
GitLab CVE-2021-22205
Detects GitLab vulnerability CVE-2021-22205 exploitation success. It allows an attacker to do some remote code execution with user git. The HTTP return code 422 indicates a successfull exploitation.
- Effort: intermediate
Koadic MSHTML Command
Detects Koadic payload using MSHTML module
- Effort: intermediate
LokiBot Default C2 URL
Detects default C2 URL for trojan LokiBot
- Effort: elementary
Nimbo-C2 User Agent
Nimbo-C2 Uses an unusual User-Agent format in its implants.
- Effort: intermediate
Possible Malicious File Double Extension
Detects request to potential malicious file with double extension
- Effort: elementary
Potential Bazar Loader User-Agents
Detects potential Bazar loader communications through the user-agent
- Effort: elementary
Potential Lemon Duck User-Agent
Detects LemonDuck user agent. The format used two sets of alphabetical characters separated by dashes, for example "User-Agent: Lemon-Duck-[A-Z]-[A-Z]".
- Effort: elementary
Potential LokiBot User-Agent
Detects potential LokiBot communications through the user-agent
- Effort: intermediate
Privilege Escalation Awesome Scripts (PEAS)
Detect PEAS privileges escalation scripts and binaries
- Effort: elementary
ProxyShell Microsoft Exchange Suspicious Paths
Detects suspicious calls to Microsoft Exchange resources, in locations related to webshells observed in campaigns using this vulnerability.
- Effort: elementary
Raccoon Stealer 2.0 Legitimate Third-Party DLL Download URL
Detects Raccoon Stealer 2.0 malware downloading legitimate third-party DLLs from its C2 server. These legitimate DLLs are used by the information stealer to collect data on the compromised hosts.
- Effort: elementary
Remote Access Tool Domain
Detects traffic toward a domain flagged as a Remote Administration Tool (RAT).
- Effort: master
Remote Monitoring and Management Software - AnyDesk
Detect artifacts related to the installation or execution of the Remote Monitoring and Management tool AnyDesk.
- Effort: master
SEKOIA.IO Intelligence Feed
Detect threats based on indicators of compromise (IOCs) collected by SEKOIA's Threat and Detection Research team.
- Effort: elementary
Sekoia.io EICAR Detection
Detects observables in Sekoia.io CTI tagged as EICAR, which are fake samples meant to test detection.
- Effort: master
SharePoint Authenticated SSRF
Detects succesful SSRF from an authenticated SharePoint user.
- Effort: elementary
Suspicious Download Links From Legitimate Services
Detects users clicking on Google docs links to download suspicious files. This technique was used a lot by Bazar Loader in the past.
- Effort: intermediate
Suspicious TOR Gateway
Detects suspicious TOR gateways. Gateways are often used by the victim to pay and decrypt the encrypted files without installing TOR. Tor intercepts the network traffic from one or more apps on user’s computer, usually the user web browser, and shuffles it through a number of randomly-chosen computers before passing it on to its destination. This disguises user location, and makes it harder for servers to pick him/her out on repeat visits, or to tie together separate visits to different sites, this making tracking and surveillance more difficult. Before a network packet starts its journey, user’s computer chooses a random list of relays and repeatedly encrypts the data in multiple layers, like an onion. Each relay knows only enough to strip off the outermost layer of encryption, before passing what’s left on to the next relay in the list.
- Effort: advanced
Suspicious URI Used In A Lazarus Campaign
Detects suspicious requests to a specific URI, usually on an .asp page. The website is often compromised.
- Effort: intermediate
TOR Usage Generic Rule
Detects TOR usage globally, whether the IP is a destination or source. TOR is short for The Onion Router, and it gets its name from how it works. TOR intercepts the network traffic from one or more apps on user’s computer, usually the user web browser, and shuffles it through a number of randomly-chosen computers before passing it on to its destination. This disguises user location, and makes it harder for servers to pick him/her out on repeat visits, or to tie together separate visits to different sites, this making tracking and surveillance more difficult. Before a network packet starts its journey, user’s computer chooses a random list of relays and repeatedly encrypts the data in multiple layers, like an onion. Each relay knows only enough to strip off the outermost layer of encryption, before passing what’s left on to the next relay in the list.
- Effort: master
TrevorC2 HTTP Communication
Detects TrevorC2 HTTP communication based on the HTTP request URI and the user-agent.
- Effort: elementary
Event Categories
The following table lists the data source offered by this integration.
| Data Source | Description |
|---|---|
Web application firewall logs |
Azure Application Gateway protect web application with its web application firewall |
Web logs |
Web logs coming from Azure Application Gateway |
In details, the following table denotes the type of events produced by this integration.
| Name | Values |
|---|---|
| Kind | `` |
| Category | network |
| Type | access, connection |
Transformed Events Samples after Ingestion
This section demonstrates how the raw logs will be transformed by our parsers. It shows the extracted fields that will be available for use in the built-in detection rules and hunting activities in the events page. Understanding these transformations is essential for analysts to create effective detection mechanisms with custom detection rules and to leverage the full potential of the collected data.
{
"message": "{\n\t\"resourceId\": \"/SUBSCRIPTIONS/<subscription id>/RESOURCEGROUPS/<resoource group name>/PROVIDERS/MICROSOFT.NETWORK/APPLICATIONGATEWAYS/<application gateway name>\",\n\t\"operationName\": \"ApplicationGatewayAccess\",\n\t\"time\": \"2016-04-11T04:24:37Z\",\n\t\"category\": \"ApplicationGatewayAccessLog\",\n\t\"properties\": {\n\t\t\"instanceId\":\"ApplicationGatewayRole_IN_0\",\n\t\t\"clientIP\":\"37.186.113.170\",\n\t\t\"clientPort\":\"12345\",\n\t\t\"httpMethod\":\"HEAD\",\n\t\t\"requestUri\":\"/xyz/portal\",\n\t\t\"requestQuery\":\"\",\n\t\t\"userAgent\":\"-\",\n\t\t\"httpStatus\":\"200\",\n\t\t\"httpVersion\":\"HTTP/1.0\",\n\t\t\"receivedBytes\":\"27\",\n\t\t\"sentBytes\":\"202\",\n\t\t\"timeTaken\":\"359\",\n\t\t\"sslEnabled\":\"off\"\n\t}\n}",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"dataset": "ApplicationGatewayAccess",
"type": [
"access",
"connection"
]
},
"cloud": {
"instance": {
"id": "ApplicationGatewayRole_IN_0"
},
"provider": "Azure",
"service": {
"name": "Azure Application Gateway"
}
},
"destination": {
"bytes": 202
},
"http": {
"request": {
"method": "HEAD"
},
"response": {
"status_code": 200
}
},
"network": {
"bytes": 27202
},
"related": {
"ip": [
"37.186.113.170"
]
},
"source": {
"address": "37.186.113.170",
"bytes": 27,
"ip": "37.186.113.170",
"port": 12345
},
"user_agent": {
"device": {
"name": "Other"
},
"name": "Other",
"original": "-",
"os": {
"name": "Other"
}
}
}
{
"message": "{\n \"timeStamp\": \"2021-10-14T22:17:11+00:00\",\n \"resourceId\": \"/SUBSCRIPTIONS/{subscriptionId}/RESOURCEGROUPS/{resourceGroupName}/PROVIDERS/MICROSOFT.NETWORK/APPLICATIONGATEWAYS/{applicationGatewayName}\",\n \"listenerName\": \"HTTP-Listener\",\n \"ruleName\": \"Storage-Static-Rule\",\n \"backendPoolName\": \"StaticStorageAccount\",\n \"backendSettingName\": \"StorageStatic-HTTPS-Setting\",\n \"operationName\": \"ApplicationGatewayAccess\",\n \"category\": \"ApplicationGatewayAccessLog\",\n \"properties\": {\n \"instanceId\": \"appgw_2\",\n \"clientIP\": \"185.42.129.24\",\n \"clientPort\": 45057,\n \"httpMethod\": \"GET\",\n \"originalRequestUriWithArgs\": \"\\/\",\n \"requestUri\": \"\\/\",\n \"requestQuery\": \"\",\n \"userAgent\": \"Mozilla\\/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit\\/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome\\/52.0.2743.116 Safari\\/537.36\",\n \"httpStatus\": 200,\n \"httpVersion\": \"HTTP\\/1.1\",\n \"receivedBytes\": 184,\n \"sentBytes\": 466,\n \"clientResponseTime\": 0,\n \"timeTaken\": 0.034,\n \"WAFEvaluationTime\": \"0.000\",\n \"WAFMode\": \"Detection\",\n \"transactionId\": \"592d1649f75a8d480a3c4dc6a975309d\",\n \"sslEnabled\": \"on\",\n \"sslCipher\": \"ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384\",\n \"sslProtocol\": \"TLSv1.2\",\n \"sslClientVerify\": \"NONE\",\n \"sslClientCertificateFingerprint\": \"\",\n \"sslClientCertificateIssuerName\": \"\",\n \"serverRouted\": \"52.239.221.65:443\",\n \"serverStatus\": \"200\",\n \"serverResponseLatency\": \"0.028\",\n \"upstreamSourcePort\": \"21564\",\n \"originalHost\": \"20.110.30.194\",\n \"host\": \"20.110.30.194\",\n \"error_info\":\"ERRORINFO_NO_ERROR\",\n \"contentType\":\"application/json\"\n }\n}",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"dataset": "ApplicationGatewayAccess",
"type": [
"access",
"connection"
]
},
"@timestamp": "2021-10-14T22:17:11Z",
"azure": {
"application_gateway": {
"error_info": "ERRORINFO_NO_ERROR",
"serverStatus": "200",
"sslClientVerify": "NONE",
"transactionId": "592d1649f75a8d480a3c4dc6a975309d"
}
},
"cloud": {
"instance": {
"id": "appgw_2"
},
"provider": "Azure",
"service": {
"name": "Azure Application Gateway"
}
},
"destination": {
"bytes": 466
},
"http": {
"request": {
"method": "GET"
},
"response": {
"status_code": 200
}
},
"network": {
"bytes": 650
},
"related": {
"ip": [
"185.42.129.24"
]
},
"source": {
"address": "185.42.129.24",
"bytes": 184,
"ip": "185.42.129.24",
"port": 45057
},
"url": {
"original": "/",
"path": "/"
},
"user_agent": {
"device": {
"name": "Other"
},
"name": "Chrome",
"original": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/52.0.2743.116 Safari/537.36",
"os": {
"name": "Windows",
"version": "7"
},
"version": "52.0.2743"
}
}
{
"message": "{\n \"timeStamp\": \"2021-10-14T22:17:11+00:00\",\n \"resourceId\": \"/SUBSCRIPTIONS/{subscriptionId}/RESOURCEGROUPS/{resourceGroupName}/PROVIDERS/MICROSOFT.NETWORK/APPLICATIONGATEWAYS/{applicationGatewayName}\",\n \"operationName\": \"ApplicationGatewayFirewall\",\n \"category\": \"ApplicationGatewayFirewallLog\",\n \"properties\": {\n \"instanceId\": \"appgw_2\",\n \"clientIp\": \"185.42.129.24\",\n \"clientPort\": \"\",\n \"requestUri\": \"\\/\",\n \"ruleSetType\": \"OWASP_CRS\",\n \"ruleSetVersion\": \"3.0.0\",\n \"ruleId\": \"920350\",\n \"message\": \"Host header is a numeric IP address\",\n \"action\": \"Matched\",\n \"site\": \"Global\",\n \"details\": {\n \"message\": \"Warning. Pattern match \\\\\\\"^[\\\\\\\\d.:]+$\\\\\\\" at REQUEST_HEADERS:Host .... \",\n \"data\": \"20.110.30.194:80\",\n \"file\": \"rules\\/REQUEST-920-PROTOCOL-ENFORCEMENT.conf\",\n \"line\": \"791\"\n },\n \"hostname\": \"20.110.30.194:80\",\n \"transactionId\": \"592d1649f75a8d480a3c4dc6a975309d\",\n \"policyId\": \"default\",\n \"policyScope\": \"Global\",\n \"policyScopeName\": \"Global\"\n }\n}",
"event": {
"action": "Matched",
"category": [
"network"
],
"dataset": "ApplicationGatewayFirewall",
"reason": "Host header is a numeric IP address",
"type": [
"access",
"connection"
]
},
"@timestamp": "2021-10-14T22:17:11Z",
"azure": {
"application_gateway": {
"details": {
"message": "Warning. Pattern match \\\"^[\\\\d.:]+$\\\" at REQUEST_HEADERS:Host .... "
},
"message": "Host header is a numeric IP address",
"transactionId": "592d1649f75a8d480a3c4dc6a975309d"
}
},
"cloud": {
"instance": {
"id": "appgw_2"
},
"provider": "Azure",
"service": {
"name": "Azure Application Gateway"
}
},
"destination": {
"address": "20.110.30.194",
"ip": "20.110.30.194",
"port": 80
},
"network": {
"bytes": 0
},
"related": {
"ip": [
"185.42.129.24",
"20.110.30.194"
]
},
"source": {
"address": "185.42.129.24",
"ip": "185.42.129.24"
}
}
Extracted Fields
The following table lists the fields that are extracted, normalized under the ECS format, analyzed and indexed by the parser. It should be noted that infered fields are not listed.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
@timestamp |
date |
Date/time when the event originated. |
azure.application_gateway.details.message |
keyword |
The details message. |
azure.application_gateway.error_info |
keyword |
The error information. |
azure.application_gateway.message |
keyword |
The application gateway message. |
azure.application_gateway.serverStatus |
keyword |
The status of the server. |
azure.application_gateway.sslClientVerify |
keyword |
The SSL client verification status. |
azure.application_gateway.transactionId |
keyword |
The unique identifier for the transaction. |
cloud.instance.id |
keyword |
Instance ID of the host machine. |
cloud.provider |
keyword |
Name of the cloud provider. |
cloud.service.name |
keyword |
The cloud service name. |
destination.bytes |
long |
Bytes sent from the destination to the source. |
destination.ip |
ip |
IP address of the destination. |
destination.port |
long |
Port of the destination. |
event.action |
keyword |
The action captured by the event. |
event.category |
keyword |
Event category. The second categorization field in the hierarchy. |
event.dataset |
keyword |
Name of the dataset. |
event.reason |
keyword |
Reason why this event happened, according to the source |
event.type |
keyword |
Event type. The third categorization field in the hierarchy. |
http.request.method |
keyword |
HTTP request method. |
http.response.status_code |
long |
HTTP response status code. |
network.bytes |
long |
Total bytes transferred in both directions. |
source.bytes |
long |
Bytes sent from the source to the destination. |
source.ip |
ip |
IP address of the source. |
source.port |
long |
Port of the source. |
url.original |
wildcard |
Unmodified original url as seen in the event source. |
user_agent.original |
keyword |
Unparsed user_agent string. |
For more information on the Intake Format, please find the code of the Parser, Smart Descriptions, and Supported Events here.