Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE)
Overview
Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE) is an intelligent security policy enforcement platform that reduces security risks by providing visibility of connections between all users and devices across all network infrastructure. This product provides exceptional control over the information and locations to which users have access on the network. This solution, and all its components, have been approved and rigorously tested as an integrated system.
- Vendor: Cisco
- Supported environment: On Premise
- Version compatibility: 3.1
- Detection based on: Telemetry
- Supported application or feature:
- AAA audit
- AAA diagnostics
- Profiler
High-Level Architecture Diagram
- Type of integration: Outbound (PUSH to Sekoia.io)
- Schema
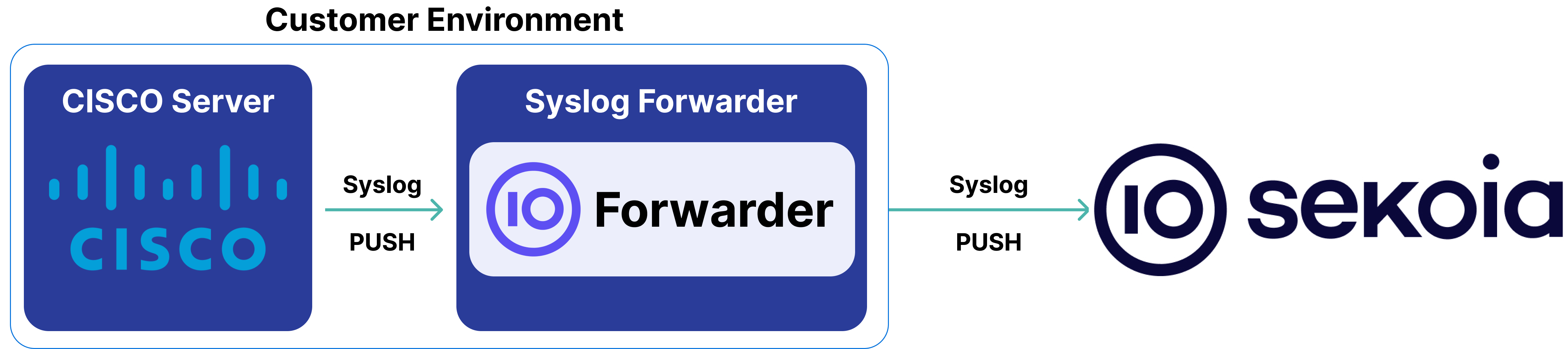
Specification
Prerequisites
- Resource:
- Self-managed syslog forwarder
- Network:
- Outbound traffic allowed
- Permissions:
- Administrator or Root access to the Cisco ISE device
- Root access to the Linux server with the syslog forwarder
Transport Protocol/Method
- Indirect Syslog
Logs details
- Supported functionalities: See section Overview
- Supported type(s) of structure: Plain text
- Supported verbosity level: Warning, Informational
Note
Log levels are based on the taxonomy of RFC5424. Adapt according to the terminology used by the editor.
Step-by-Step Configuration Procedure
Instructions on the 3rd Party Solution
This setup guide will show you how to provide an integration between Cisco Identity Services Engine events and Sekoia.io.
Enable Syslog Forwarding
- Log on your ISE Administration Interface.
- Follow this guide.
Instruction on Sekoia
Configure Your Intake
This section will guide you through creating the intake object in Sekoia, which provides a unique identifier called the "Intake key." The Intake key is essential for later configuration, as it references the Community, Entity, and Parser (Intake Format) used when receiving raw events on Sekoia.
- Go to the Sekoia Intake page.
- Click on the
+ New Intakebutton at the top right of the page. - Search for your Intake by the product name in the search bar.
- Give it a Name and associate it with an Entity (and a Community if using multi-tenant mode).
- Click on
Create.
Note
For more details on how to use the Intake page and to find the Intake key you just created, refer to this documentation.
Configure a forwarder
To forward events using syslog to Sekoia.io, you need to update the syslog header with the intake key you previously created. Here is an example of your message before the forwarder
<%pri%>1 %timestamp:::date-rfc3339% %hostname% %app-name% %procid% LOG RAW_MESSAGE
<%pri%>1 %timestamp:::date-rfc3339% %hostname% %app-name% %procid% LOG [SEKOIA@53288 intake_key=\"YOUR_INTAKE_KEY\"] RAW_MESSAGE
To achieve this you can:
- Use the Sekoia.io forwarder which is the official supported way to collect data using the syslog protocol in Sekoia.io. In charge of centralizing data coming from many equipments/sources and forwarding them to Sekoia.io with the apporpriated format, it is a prepackaged option. You only have to provide your intake key as parameter.
- Use your own Syslog service instance. Maybe you already have an intance of one of these components on your side and want to reuse it in order to centralize data before forwarding them to Sekoia.io. When using this mode, you have to configure and maintain your component in order to respect the expected Sekoia.io format.
Warning
Only the Sekoia.io forwarder is officially supported. Other options are documented for reference purposes but do not have official support.
Raw Events Samples
In this section, you will find examples of raw logs as generated natively by the source. These examples are provided to help integrators understand the data format before ingestion into Sekoia.io. It is crucial for setting up the correct parsing stages and ensuring that all relevant information is captured.
0003360952 1 0 2025-05-07 14:27:57.047 +02:00 0051005548 25002 INFO AD-Connector: ISE server TGT refresh succeeded, AD-Account-Name=JOHNDOE$@EXAMPLE.LOCAL, AD-Domain=EXAMPLE.LOCAL, AD-Log-Id=1234567890/1234567,
0003901877 1 0 2025-05-07 14:29:46.982 +02:00 0723317473 61026 NOTICE EAP-TLS: Shutdown secure connection with TLS peer, ConfigVersionId=360, PeerAddress=AA-BB-CC-DD-EE-FF, PeerName=CN=example.com, UniqueConnectionIdentifier =2ce4ef7a-0575-482b-8ed5-b3b068e873a1, ShutdownReason =ClosedByISE,
CISE_Administrative_and_Operational_Audit 0026935732 1 0 2025-10-23 14:26:49.538 +02:00 0264007760 51000 NOTICE Administrator-Login: Administrator authentication failed, ConfigVersionId=118, AdminInterface=GUI, AdminIPAddress=1.2.3.4, AdminName=jdoe, OperationMessageText=Authentication failed due to invalid user or password\, or account is disabled/locked,
0001514749 7 3 SelectedAuthenticationIdentityStores=Internal Endpoints, AuthenticationStatus=AuthenticationPassed, NetworkDeviceGroups=Location#All Locations#H7, NetworkDeviceGroups=Device Type#All Device Types#Cisco_3650, NetworkDeviceGroups=Groupe Imprimantes#Groupe Imprimantes, NetworkDeviceGroups=APs Indoor ou Outdoor#Groupe APs, IdentityPolicyMatchedRule=Dot1X, AuthorizationPolicyMatchedRule=Some rule, EapTunnel=EAP-FAST, EapAuthentication=EAP-MSCHAPv2, cisco-av-pair=AuthenticationIdentityStore=AD1, cisco-av-pair=FQSubjectName=000000-000-0000-00000000000#host/test, cisco-av-pair=UniqueSubjectID=XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX, CPMSessionID=TestSessionId, EndPointMACAddress=02:00:00:00:00:00, PostureAssessmentStatus=NotApplicable, EndPointMatchedProfile=Unknown, EapChainingResult=User failed and machine succeeded, ISEPolicySetName=WIRELESS_1X_DFS, IdentitySelectionMatchedRule=Dot1X,#015
0000248509 3 0 2025-02-18 14:34:01.264 +01:00 0005365098 5400 NOTICE Failed-Attempt: Authentication failed, ConfigVersionId=88, Device IP Address=3.4.5.6, Device Port=53874, DestinationIPAddress=5.6.7.8, DestinationPort=1812, RadiusPacketType=AccessRequest, UserName=john.doe, Protocol=Radius, NetworkDeviceName=WLAN, User-Name=john.doe, NAS-IP-Address=2.3.4.5, NAS-Port=1656127488, Called-Station-ID=1.2.3.4, Calling-Station-ID=192.0.2.1, NAS-Port-Type=Virtual, Tunnel-Client-Endpoint=(tag=0) 192.0.2.1, cisco-av-pair=mdm-tlv=device-platform=win, cisco-av-pair=mdm-tlv=device-mac=61-05-38-5c-f8-bd, cisco-av-pair=mdm-tlv=device-platform-version=10.0.26100 , cisco-av-pair=mdm-tlv=device-public-mac=61-05-38-5c-f8-bd, cisco-av-pair=mdm-tlv=device-type=Default string Default string, cisco-av-pair=mdm-tlv=ac-user-agent=AnyConnect Windows 4.6.03049,
0000005921 7 5 11-22-33-44-55-66:EVENT_REASON\,dhcp-parameter-request-list=1\, 3\, 6\, 15\, 31\, 33\, 43\, 44\, 46\, 47\, 119\, 121\, 249\, 252\,OperatingSystem=Windows\,PostureApplicable=Yes\,User-Fetch-Department=\,AD-Last-Fetch-Time=1759879885138\,Issuer=CN=COMPANY-SUB-CA\\OU=DSI\\O=COMPANY\\L=RENNES\\C=FR\,NmapSubnetScanID=0\,AD-Host-DNS-Domain=domain.asso.fr\,Device Identifier=\,Airespace-Wlan-Id=12\,ipv6=\,Issuer - Organization=COMPANY\,TotalAuthenLatency=2\,MatchedPolicyID=11111111-1111-1111-1111-111111111111\,Service-Type=Framed\,op=BOOTREQUEST\,UserName=example.com$@domain.asso.fr\,FeedService=false\,TLSVersion=TLSv1.2\,AD-Host-NetBios-Name=DOMAIN\,Issuer - Location=RENNES\,SelectedAuthorizationProfiles=PermitAccess\,host-name=example.com\,COMPANY_LAN=COMPANY_LAN#COMPANY_LAN\,Subject=CN=example.com.DOMAIN.asso.fr\,
INFO: Configuration Changed: Admin=john.doe; Object Type=EPPurgeScheduler; Object Name=f36afcff-e3af-4a70-99c0-5e5304c1c336
Oct 27 14:29:31 HOST-01 CISE_Failed_Attempts 0001027727 1 0 2025-10-27 14:29:31.301 +01:00 0015075255 5400 NOTICE Failed-Attempt: Authentication failed, ConfigVersionId=11, Device IP Address=1.2.3.4, Device Port=42568, DestinationIPAddress=1.2.3.4, DestinationPort=1812, RadiusPacketType=AccessRequest, UserName=user1, Protocol=Radius, NetworkDeviceName=DEVICE-01, User-Name=aabbccddeeff, NAS-IP-Address=1.2.3.4, NAS-Port=19, Service-Type=Call Check, Called-Station-ID=user1:, Calling-Station-ID=user1, NAS-Port-Type=Ethernet, cisco-av-pair=audit-session-id=000000000000000000000000, OriginalUserName=aabbccddeeff, NetworkDeviceProfileName=Cisco, NetworkDeviceProfileId=00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000, IsThirdPartyDeviceFlow=false, RadiusFlowType=WiredMAB, SSID=user1:, AcsSessionID=HOST-01/000000000/000000, AuthenticationIdentityStore=Internal Endpoints, AuthenticationMethod=Lookup, SelectedAccessService=Default Network Access, SelectedAuthorizationProfiles=DenyAccess, UseCase=Host Lookup, RequestLatency=25, IdentityGroup=Endpoint Identity Groups:Profiled, FailureReason=15039 Rejected per authorization profile, Step=11001, Step=11017, Step=11027, Step=15049, Step=15008, Step=15048, Step=15041, Step=15048, Step=15013, Step=24209, Step=24211, Step=22037, Step=15036, Step=15048, Step=15048, Step=15048, Step=24432, Step=24325, Step=24313, Step=24318, Step=24322, Step=24352, Step=24412, Step=15048, Step=15048, Step=15016, Step=15039, Step=11003, SelectedAuthenticationIdentityStores=Internal Endpoints, NetworkDeviceGroups=Location#All Locations#SITE-01, NetworkDeviceGroups=Device Type#All Device Types#SW_Vendor_Site, NetworkDeviceGroups=IPSEC#Is IPSEC Device#No, IdentityPolicyMatchedRule=MAB, AuthorizationPolicyMatchedRule=Default, cisco-av-pair=AuthenticationIdentityStore=Internal Endpoints, UserType=Host, CPMSessionID=000000000000000000000000, EndPointMACAddress=user1, EndPointMatchedProfile=VENDOR-Device, DeviceRegistrationStatus=notRegistered, ISEPolicySetName=POLICY-01, IdentitySelectionMatchedRule=MAB, StepLatency=1=0;2=1;3=0;4=0;5=0;6=1;7=0;8=1;9=0;10=1;11=0;12=0;13=12;14=5;15=0;23=3;24=0;25=1;26=0;27=0, StepData=5= DEVICE.Location, StepData=7= Normalised Radius.RadiusFlowType, StepData=8=Internal Endpoints, StepData=13= EndPoints.LogicalProfile, StepData=14= EndPoints.EndPointPolicy, StepData=15= DEVICE.Device Type, StepData=0=AD_EXAMPLE, StepData=1=user1, StepData=2=example.local, StepData=3=example.local, StepData=5=ERROR_NO_SUCH_USER, StepData=6=AD_EXAMPLE, StepData=23= AD_EXAMPLE.ExternalGroups, StepData=24= Radius.Called-Station-ID, TotalAuthenLatency=25, ClientLatency=0, DTLSSupport=Unknown, HostIdentityGroup=Endpoint Identity Groups:Profiled, Network Device Profile=Cisco, Location=Location#All Locations#SITE-01, Device Type=Device Type#All Device Types#SW_Vendor_Site, IPSEC=IPSEC#Is IPSEC Device#No, EndPointPolicy=00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000, Name=Endpoint Identity Groups:Profiled, Response={RadiusPacketType=AccessReject; AuthenticationResult=Passed; UserName=AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:FF; },
0000087238 3 1 AcsSessionID=ISE-CISCO/1111111/222222, AuthenticationIdentityStore=Internal Endpoints, AuthenticationMethod=Lookup, SelectedAccessService=AuthenticationMAB, SelectedAuthorizationProfiles=DenyAccess, UseCase=Host Lookup, RequestLatency=5, IdentityGroup=Endpoint Identity Groups:Unknown, FailureReason=15039 Rejected per authorization profile, Step=11001, Step=11017, Step=11027, Step=15049, Step=15008, Step=15048, Step=15048, Step=15048, Step=15041, Step=15013, Step=24209, Step=24211, Step=22037, Step=15036, Step=15016, Step=15039, Step=11003, SelectedAuthenticationIdentityStores=Internal Endpoints, NetworkDeviceGroups=Device Type#All Device Types#Switch, NetworkDeviceGroups=IPSEC#Is IPSEC Device#No, NetworkDeviceGroups=Location#All Locations, IdentityPolicyMatchedRule=Authentication Rule 1, AuthorizationPolicyMatchedRule=Default, cisco-av-pair=AuthenticationIdentityStore=Internal Endpoints, UserType=Host, CPMSessionID=ABCDEF0123456,
0000089788 3 2 EndPointMACAddress=00-11-22-33-44-55, EndPointMatchedProfile=Unknown, DeviceRegistrationStatus=notRegistered, ISEPolicySetName=MAB, IdentitySelectionMatchedRule=Authentication Rule 1, StepLatency=1=0\;2=0\;3=0\;4=0\;5=0\;6=1\;7=0\;8=0\;9=1\;10=0\;11=1\;12=0\;13=0\;14=1\;15=0\;16=0, StepData=5= DEVICE.Device Type, StepData=6= Radius.NAS-IP-Address, StepData=7= Normalised Radius.RadiusFlowType, StepData=9=Internal Endpoints, TotalAuthenLatency=4, ClientLatency=0, DTLSSupport=Unknown, HostIdentityGroup=Endpoint Identity Groups:Unknown, Network Device Profile=Cisco, Location=Location#All Locations, Device Type=Device Type#All Device Types#Switch, IPSEC=IPSEC#Is IPSEC Device#No, Name=Endpoint Identity Groups:Unknown, Response={RadiusPacketType=AccessReject; AuthenticationResult=Passed; UserName=02:00:00:00:00:00; },
INFO: 5 endpoint(s) purged successfully
2023-06-07 04:26:17.306 +0200 60198 INFO null: MnT purge event occurred, MESSAGE=completed successfully,
WARN: AcsSyslogContentAaaDiagnostics:: ACTIVE_DIRECTORY_DIAGNOSTIC_TOOL_ISSUES_FOUND need to complete
INFO: EAP Connection Timeout : Server=example.com; NAS IP Address=1.2.3.4; NAS Identifier=02:00:00:00:00:00:test1
0000738292 7 0 2025-01-09 09:28:49.914 +01:00 0043796555 5200 NOTICE Passed-Authentication: Authentication succeeded, ConfigVersionId=186, Device IP Address=192.0.2.1, DestinationIPAddress=1.2.3.4, DestinationPort=1812, UserName=user1, Protocol=Radius, NetworkDeviceName=MGCUH1-3, User-Name=user1, NAS-IP-Address=192.0.2.1, NAS-Port=1001, Service-Type=Framed, Framed-MTU=1449, State=37CPMSessionID=XXXXXXXXXXXXXX\;36SessionID=MGDFSISE2/515448264/543038\;, Called-Station-ID=a0:ec:f9:50:e2:90:DFS, Calling-Station-ID=bc:83:85:d8:88:c6, NAS-Identifier=MGCUH1-3, NAS-Port-Type=Wireless - IEEE 802.11, NAS-Port-Id=Capwap2, EAP-Key-Name=, cisco-av-pair=service-type=Framed, cisco-av-pair=audit-session-id=XXXXXXXXXXXXXX, cisco-av-pair=method=dot1x, cisco-av-pair=cisco-wlan-ssid=DFS, Airespace-Wlan-Id=5, NetworkDeviceProfileName=Cisco, NetworkDeviceProfileId=aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa,#015
CISE_RADIUS_Accounting 0002391460 1 0 2025-07-30 11:50:34.267 +02:00 0023023046 3002 NOTICE Radius-Accounting: RADIUS Accounting watchdog update, ConfigVersionId=83, Device IP Address=1.2.3.4, UserName=user1, NetworkDeviceName=Test-Network-Device-Name, User-Name=user1, NAS-IP-Address=1.2.3.4, NAS-Port=50107, Framed-IP-Address=3.4.5.6, Class=CACS:0A0D00F90000001402268B53:ise/523393559/11169221, Called-Station-ID=11-00-00-00-00-00, Calling-Station-ID=user1, Acct-Status-Type=Interim-Update, Acct-Delay-Time=0, Acct-Input-Octets=1848852125, Acct-Output-Octets=2808400785, Acct-Session-Id=00000070, Acct-Input-Packets=27991836, Acct-Output-Packets=40488347, Event-Timestamp=1753869011, NAS-Port-Type=Ethernet, NAS-Port-Id=GigabitEthernet0/7, cisco-av-pair=audit-session-id=0A0D00F90000001402268B53, cisco-av-pair=vlan-id=1330, cisco-av-pair=method=mab, AcsSessionID=MGMT-ISE01/0000000000/2185126, SelectedAccessService=Default Network Access, RequestLatency=3, Step=11004, Step=11017, Step=15049, Step=15008, Step=15048, Step=15048, Step=22094, Step=11005, NetworkDeviceGroups=Location#All Locations#Test Test#LAN#ACA, NetworkDeviceGroups=Device Type#All Device Types#Switch#2960L, NetworkDeviceGroups=IPSEC#Is IPSEC Device#No, CPMSessionID=0A0D00F90000001402268B53, StepLatency=1=0\;2=0\;3=0\;4=1\;5=0\;6=1\;7=0, StepData=4= Normalised Radius.TTTTT, StepData=5= Normalised Radius.RadiusFlowType, TotalAuthenLatency=3, ClientLatency=0, Model Name=Unknown, Software Version=Unknown, Network Device Profile=Cisco, Location=Location#All Locations#Test Test#LAN#ACA, Device Type=Device Type#All Device Types#Switch#2960L, IPSEC=IPSEC#Is IPSEC Device#No,
0000000000 1 0 2025-07-29 14:07:18.047 +02:00 0000000000 51000 NOTICE Administrator-Login: Administrator authentication failed, ConfigVersionId=XX, AdminInterface=GUI, AdminIPAddress=1.2.3.4, AdminName=user1, OperationMessageText=Authentication failed due to invalid user or password, or account is disabled/locked,
CISE_Administrative_and_Operational_Audit 0000000000 1 0 2025-07-29 14:07:18.047 +02:00 0000000000 51000 NOTICE Administrator-Login: Administrator authentication failed, ConfigVersionId=XX, AdminInterface=GUI, AdminIPAddress=1.2.3.4, AdminName=user1, OperationMessageText=Authentication failed due to invalid user or password, or account is disabled/locked,
0001514749 7 6 Response={Class=CACS:XXXXXXXXX:asdsa/000000/111111; Tunnel-Type=(tag=1) VLAN; Tunnel-Medium-Type=(tag=1) 802; Tunnel-Private-Group-ID=(tag=1) COMPUTER; EAP-Key-Name=EAP-Key-VALUE; MS-MPPE-Send-Key=****; MS-MPPE-Recv-Key=****; LicenseTypes=1; },#015
WARN: Dynamic Authorization Failed for Device : Server=example.com; Calling Station Id=N/A; Network device IP=1.2.3.4; Network Device
WARN: Profiler SNMP Request Failure : Server= example.com; NAD Address=1.2.3.4; Error Message=Request timed out.
WARN: TrustSec deploy verification failed to reach NAD.: Device Name=device005.internal.example.org; Device Ip=1.2.3.4; Device login username=admin
0003361015 2 0 2025-05-07 14:29:08.974 +02:00 0051006044 80002 INFO Profiler: Profiler EndPoint profiling event occurred, ConfigVersionId=183, OperatingSystem=Windows 11 Entreprise, EndpointCertainityMetric=50, EndpointIPAddress=1.2.3.4, EndpointMacAddress=AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:FF, EndpointMatchedPolicy=Windows11-Workstation, EndpointOUI=Intel Corporate, EndpointPolicy=Windows11-Workstation, EndpointProperty=chaddr=AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:FF,dhcp-class-identifier=MSFT 5.0,PolicyVersion=24,dhcp-message-type=DHCPREQUEST,EndPointPolicyID=57f40927-3b0a-46b8-9f03-78d47e1383c4,LogicalProfile=,client-fqdn=abcdef.example.local,EndPointVersion=340,FirstCollection=1744718839328,CacheUpdateTime=1746620948973,StaticAssignment=false,NmapScanCount=0,PostureExpiry=,hlen=6,AD-Operating-System=Windows 11 Entreprise,AD-Join-Point=EXAMPLE.LOCAL,PortalUser=,ciaddr=0.0.0.0,BYODRegistration=Unknown,dhcp-requested-address=1.2.3.4,Total Certainty Factor=50,MDMServerID=,
Oct 27 15:20:43 HOST-01 CISE_RADIUS_Accounting 0001042079 1 0 2025-10-27 15:20:43.919 +01:00 0015337799 3002 NOTICE Radius-Accounting: RADIUS Accounting watchdog update, ConfigVersionId=11, Device IP Address=1.2.3.4, UserName=user1, NetworkDeviceName=DEVICE-02, User-Name=user1, NAS-IP-Address=1.2.3.4, NAS-Port=42, Service-Type=Framed, Framed-IP-Address=1.2.3.4, Class=CACS:000000000000000000000000:HOST-01/000000000/000000, Called-Station-ID=user1:, Calling-Station-ID=user1, Acct-Status-Type=Interim-Update, Acct-Delay-Time=0, Acct-Input-Octets=921941396, Acct-Output-Octets=0, Acct-Session-Id=0000000000000000, Acct-Authentic=RADIUS, Acct-Session-Time=570009, Acct-Input-Packets=0, Acct-Output-Packets=35, Acct-Input-Gigawords=922518720, Acct-Output-Gigawords=28, Event-Timestamp=1761574843, NAS-Port-Type=Ethernet, cisco-av-pair=audit-session-id=000000000000000000000000, AcsSessionID=HOST-01/000000000/000000, SelectedAccessService=Default Network Access, RequestLatency=2, Step=11004, Step=11017, Step=15049, Step=15008, Step=22094, Step=11005, NetworkDeviceGroups=Location#All Locations#SITE-02, NetworkDeviceGroups=Device Type#All Device Types#SW_Vendor_Site, NetworkDeviceGroups=IPSEC#Is IPSEC Device#No, CPMSessionID=000000000000000000000000, StepLatency=1=0;2=0;3=1;4=0;5=0, TotalAuthenLatency=2, ClientLatency=0, Network Device Profile=Cisco, Location=Location#All Locations#SITE-02, Device Type=Device Type#All Device Types#SW_Vendor_Site, IPSEC=IPSEC#Is IPSEC Device#No,
Detection section
The following section provides information for those who wish to learn more about the detection capabilities enabled by collecting this intake. It includes details about the built-in rule catalog, event categories, and ECS fields extracted from raw events. This is essential for users aiming to create custom detection rules, perform hunting activities, or pivot in the events page.
Related Built-in Rules
The following Sekoia.io built-in rules match the intake Cisco ISE. This documentation is updated automatically and is based solely on the fields used by the intake which are checked against our rules. This means that some rules will be listed but might not be relevant with the intake.
SEKOIA.IO x Cisco ISE on ATT&CK Navigator
Burp Suite Tool Detected
Burp Suite is a cybersecurity tool. When used as a proxy service, its purpose is to intercept packets and modify them to send them to the server. Burp Collaborator is a network service that Burp Suite uses to help discover many kinds of vulnerabilities (vulnerabilities scanner).
- Effort: intermediate
Cisco Identity Services Engine Configuration Changed
Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE) has detected a device configuration changed (Added, Changed or Deleted). This should be reviewed in order to check if this an expected admin action.
- Effort: master
Correlation Potential DNS Tunnel
Detects domain name which is longer than 62 characters and requested at least 50 times in a 10 minutes range time. Long domain names are distinctive of DNS tunnels.
- Effort: advanced
Cryptomining
Detection of domain names potentially related to cryptomining activities.
- Effort: master
Dynamic DNS Contacted
Detect communication with dynamic dns domain. This kind of domain is often used by attackers. This rule can trigger false positive in non-controlled environment because dynamic dns is not always malicious.
- Effort: master
EvilProxy Phishing Domain
Detects subdomains potentially generated by the EvilProxy adversary-in-the-middle phishing platform. Inspect the other subdomains of the domain to identify the landing page, and determine if the user submitted credentials. This rule has a small percentage of false positives on legitimate domains.
- Effort: intermediate
Exfiltration Domain
Detects traffic toward a domain flagged as a possible exfiltration vector.
- Effort: master
Potential DNS Tunnel
Detects domain name which is longer than 62 characters. Long domain names are distinctive of DNS tunnels.
- Effort: advanced
Remote Access Tool Domain
Detects traffic toward a domain flagged as a Remote Administration Tool (RAT).
- Effort: master
Remote Monitoring and Management Software - AnyDesk
Detect artifacts related to the installation or execution of the Remote Monitoring and Management tool AnyDesk.
- Effort: master
Remote Monitoring and Management Software - Atera
Detect artifacts related to the installation or execution of the Remote Monitoring and Management tool Atera.
- Effort: master
SEKOIA.IO Intelligence Feed
Detect threats based on indicators of compromise (IOCs) collected by SEKOIA's Threat and Detection Research team.
- Effort: elementary
Sekoia.io EICAR Detection
Detects observables in Sekoia.io CTI tagged as EICAR, which are fake samples meant to test detection.
- Effort: master
Suspicious TOR Gateway
Detects suspicious TOR gateways. Gateways are often used by the victim to pay and decrypt the encrypted files without installing TOR. Tor intercepts the network traffic from one or more apps on user’s computer, usually the user web browser, and shuffles it through a number of randomly-chosen computers before passing it on to its destination. This disguises user location, and makes it harder for servers to pick him/her out on repeat visits, or to tie together separate visits to different sites, this making tracking and surveillance more difficult. Before a network packet starts its journey, user’s computer chooses a random list of relays and repeatedly encrypts the data in multiple layers, like an onion. Each relay knows only enough to strip off the outermost layer of encryption, before passing what’s left on to the next relay in the list.
- Effort: advanced
TOR Usage Generic Rule
Detects TOR usage globally, whether the IP is a destination or source. TOR is short for The Onion Router, and it gets its name from how it works. TOR intercepts the network traffic from one or more apps on user’s computer, usually the user web browser, and shuffles it through a number of randomly-chosen computers before passing it on to its destination. This disguises user location, and makes it harder for servers to pick him/her out on repeat visits, or to tie together separate visits to different sites, this making tracking and surveillance more difficult. Before a network packet starts its journey, user’s computer chooses a random list of relays and repeatedly encrypts the data in multiple layers, like an onion. Each relay knows only enough to strip off the outermost layer of encryption, before passing what’s left on to the next relay in the list.
- Effort: master
Telegram Bot API Request
Detects suspicious DNS queries to api.telegram.org used by Telegram Bots of any kind
- Effort: advanced
Event Categories
The following table lists the data source offered by this integration.
| Data Source | Description |
|---|---|
Authentication logs |
There's an authentification audit, control and diagnostic |
Network device configuration |
Changing conf of devices usually by the admin |
Web logs |
Cisco ISE logs provide information about the connected client and the requested resource |
In details, the following table denotes the type of events produced by this integration.
| Name | Values |
|---|---|
| Kind | `` |
| Category | authentication, configuration, network |
| Type | change, info |
Transformed Events Samples after Ingestion
This section demonstrates how the raw logs will be transformed by our parsers. It shows the extracted fields that will be available for use in the built-in detection rules and hunting activities in the events page. Understanding these transformations is essential for analysts to create effective detection mechanisms with custom detection rules and to leverage the full potential of the collected data.
{
"message": "0003360952 1 0 2025-05-07 14:27:57.047 +02:00 0051005548 25002 INFO AD-Connector: ISE server TGT refresh succeeded, AD-Account-Name=JOHNDOE$@EXAMPLE.LOCAL, AD-Domain=EXAMPLE.LOCAL, AD-Log-Id=1234567890/1234567,",
"event": {
"category": [
"authentication"
],
"reason": "ISE server TGT refresh succeeded",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"observer": {
"product": "Cisco ISE",
"vendor": "Cisco"
},
"related": {
"user": [
"JOHNDOE$@EXAMPLE.LOCAL"
]
},
"user": {
"domain": "EXAMPLE.LOCAL",
"name": "JOHNDOE$@EXAMPLE.LOCAL"
}
}
{
"message": "0003901877 1 0 2025-05-07 14:29:46.982 +02:00 0723317473 61026 NOTICE EAP-TLS: Shutdown secure connection with TLS peer, ConfigVersionId=360, PeerAddress=AA-BB-CC-DD-EE-FF, PeerName=CN=example.com, UniqueConnectionIdentifier =2ce4ef7a-0575-482b-8ed5-b3b068e873a1, ShutdownReason =ClosedByISE,",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"reason": "Shutdown secure connection with TLS peer",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"destination": {
"address": "example.com",
"domain": "example.com",
"mac": "AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:FF",
"registered_domain": "example.com",
"top_level_domain": "com"
},
"observer": {
"product": "Cisco ISE",
"vendor": "Cisco"
},
"related": {
"hosts": [
"example.com"
]
}
}
{
"message": "CISE_Administrative_and_Operational_Audit 0026935732 1 0 2025-10-23 14:26:49.538 +02:00 0264007760 51000 NOTICE Administrator-Login: Administrator authentication failed, ConfigVersionId=118, AdminInterface=GUI, AdminIPAddress=1.2.3.4, AdminName=jdoe, OperationMessageText=Authentication failed due to invalid user or password\\, or account is disabled/locked,",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"reason": "Administrator authentication failed",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"observer": {
"product": "Cisco ISE",
"vendor": "Cisco"
},
"related": {
"ip": [
"1.2.3.4"
],
"user": [
"jdoe"
]
},
"source": {
"address": "1.2.3.4",
"ip": "1.2.3.4"
},
"user": {
"name": "jdoe"
}
}
{
"message": "0001514749 7 3 SelectedAuthenticationIdentityStores=Internal Endpoints, AuthenticationStatus=AuthenticationPassed, NetworkDeviceGroups=Location#All Locations#H7, NetworkDeviceGroups=Device Type#All Device Types#Cisco_3650, NetworkDeviceGroups=Groupe Imprimantes#Groupe Imprimantes, NetworkDeviceGroups=APs Indoor ou Outdoor#Groupe APs, IdentityPolicyMatchedRule=Dot1X, AuthorizationPolicyMatchedRule=Some rule, EapTunnel=EAP-FAST, EapAuthentication=EAP-MSCHAPv2, cisco-av-pair=AuthenticationIdentityStore=AD1, cisco-av-pair=FQSubjectName=000000-000-0000-00000000000#host/test, cisco-av-pair=UniqueSubjectID=XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX, CPMSessionID=TestSessionId, EndPointMACAddress=02:00:00:00:00:00, PostureAssessmentStatus=NotApplicable, EndPointMatchedProfile=Unknown, EapChainingResult=User failed and machine succeeded, ISEPolicySetName=WIRELESS_1X_DFS, IdentitySelectionMatchedRule=Dot1X,#015",
"event": {
"category": [
"authentication"
],
"outcome": "success",
"reason": "User failed and machine succeeded",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"observer": {
"product": "Cisco ISE",
"vendor": "Cisco"
},
"related": {
"user": [
"Unknown"
]
},
"rule": {
"name": "Dot1X"
},
"source": {
"mac": "02:00:00:00:00:00"
},
"user": {
"name": "Unknown"
}
}
{
"message": "0000248509 3 0 2025-02-18 14:34:01.264 +01:00 0005365098 5400 NOTICE Failed-Attempt: Authentication failed, ConfigVersionId=88, Device IP Address=3.4.5.6, Device Port=53874, DestinationIPAddress=5.6.7.8, DestinationPort=1812, RadiusPacketType=AccessRequest, UserName=john.doe, Protocol=Radius, NetworkDeviceName=WLAN, User-Name=john.doe, NAS-IP-Address=2.3.4.5, NAS-Port=1656127488, Called-Station-ID=1.2.3.4, Calling-Station-ID=192.0.2.1, NAS-Port-Type=Virtual, Tunnel-Client-Endpoint=(tag=0) 192.0.2.1, cisco-av-pair=mdm-tlv=device-platform=win, cisco-av-pair=mdm-tlv=device-mac=61-05-38-5c-f8-bd, cisco-av-pair=mdm-tlv=device-platform-version=10.0.26100 , cisco-av-pair=mdm-tlv=device-public-mac=61-05-38-5c-f8-bd, cisco-av-pair=mdm-tlv=device-type=Default string Default string, cisco-av-pair=mdm-tlv=ac-user-agent=AnyConnect Windows 4.6.03049,",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"reason": "Authentication failed",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"cisco": {
"ise": {
"network": {
"device_name": "WLAN"
}
}
},
"destination": {
"address": "1.2.3.4",
"ip": "1.2.3.4",
"port": 1812
},
"network": {
"protocol": "Radius"
},
"observer": {
"product": "Cisco ISE",
"vendor": "Cisco"
},
"related": {
"ip": [
"1.2.3.4",
"192.0.2.1"
],
"user": [
"john.doe"
]
},
"source": {
"address": "192.0.2.1",
"ip": "192.0.2.1"
},
"user": {
"name": "john.doe"
}
}
{
"message": "0000005921 7 5 11-22-33-44-55-66:EVENT_REASON\\,dhcp-parameter-request-list=1\\, 3\\, 6\\, 15\\, 31\\, 33\\, 43\\, 44\\, 46\\, 47\\, 119\\, 121\\, 249\\, 252\\,OperatingSystem=Windows\\,PostureApplicable=Yes\\,User-Fetch-Department=\\,AD-Last-Fetch-Time=1759879885138\\,Issuer=CN=COMPANY-SUB-CA\\\\OU=DSI\\\\O=COMPANY\\\\L=RENNES\\\\C=FR\\,NmapSubnetScanID=0\\,AD-Host-DNS-Domain=domain.asso.fr\\,Device Identifier=\\,Airespace-Wlan-Id=12\\,ipv6=\\,Issuer - Organization=COMPANY\\,TotalAuthenLatency=2\\,MatchedPolicyID=11111111-1111-1111-1111-111111111111\\,Service-Type=Framed\\,op=BOOTREQUEST\\,UserName=example.com$@domain.asso.fr\\,FeedService=false\\,TLSVersion=TLSv1.2\\,AD-Host-NetBios-Name=DOMAIN\\,Issuer - Location=RENNES\\,SelectedAuthorizationProfiles=PermitAccess\\,host-name=example.com\\,COMPANY_LAN=COMPANY_LAN#COMPANY_LAN\\,Subject=CN=example.com.DOMAIN.asso.fr\\,",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"reason": "EVENT_REASON",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"cisco": {
"ise": {
"dhcp": {
"message_type": "BOOTREQUEST",
"parameter_request_list": "1\\, 3\\, 6\\, 15\\, 31\\, 33\\, 43\\, 44\\, 46\\, 47\\, 119\\, 121\\, 249\\, 252"
}
}
},
"dns": {
"question": {
"registered_domain": "domain.asso.fr"
}
},
"host": {
"name": "example.com",
"os": {
"full": "Windows"
}
},
"observer": {
"product": "Cisco ISE",
"vendor": "Cisco"
},
"related": {
"user": [
"example.com$@domain.asso.fr"
]
},
"rule": {
"id": "11111111-1111-1111-1111-111111111111"
},
"source": {
"mac": "11:22:33:44:55:66"
},
"tls": {
"client": {
"x509": {
"issuer": {
"common_name": "COMPANY-SUB-CA",
"country": "FR",
"locality": "RENNES",
"organization": "COMPANY",
"organizational_unit": "DSI"
}
}
}
},
"user": {
"name": "example.com$@domain.asso.fr"
}
}
{
"message": "INFO: Configuration Changed: Admin=john.doe; Object Type=EPPurgeScheduler; Object Name=f36afcff-e3af-4a70-99c0-5e5304c1c336",
"event": {
"category": [
"configuration"
],
"reason": "Configuration Changed",
"type": [
"change"
]
},
"cisco": {
"ise": {
"config_action": "Changed",
"config_object": {
"name": "f36afcff-e3af-4a70-99c0-5e5304c1c336",
"type": "EPPurgeScheduler"
}
}
},
"observer": {
"product": "Cisco ISE",
"vendor": "Cisco"
},
"related": {
"user": [
"john.doe"
]
},
"user": {
"name": "john.doe"
}
}
{
"message": "Oct 27 14:29:31 HOST-01 CISE_Failed_Attempts 0001027727 1 0 2025-10-27 14:29:31.301 +01:00 0015075255 5400 NOTICE Failed-Attempt: Authentication failed, ConfigVersionId=11, Device IP Address=1.2.3.4, Device Port=42568, DestinationIPAddress=1.2.3.4, DestinationPort=1812, RadiusPacketType=AccessRequest, UserName=user1, Protocol=Radius, NetworkDeviceName=DEVICE-01, User-Name=aabbccddeeff, NAS-IP-Address=1.2.3.4, NAS-Port=19, Service-Type=Call Check, Called-Station-ID=user1:, Calling-Station-ID=user1, NAS-Port-Type=Ethernet, cisco-av-pair=audit-session-id=000000000000000000000000, OriginalUserName=aabbccddeeff, NetworkDeviceProfileName=Cisco, NetworkDeviceProfileId=00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000, IsThirdPartyDeviceFlow=false, RadiusFlowType=WiredMAB, SSID=user1:, AcsSessionID=HOST-01/000000000/000000, AuthenticationIdentityStore=Internal Endpoints, AuthenticationMethod=Lookup, SelectedAccessService=Default Network Access, SelectedAuthorizationProfiles=DenyAccess, UseCase=Host Lookup, RequestLatency=25, IdentityGroup=Endpoint Identity Groups:Profiled, FailureReason=15039 Rejected per authorization profile, Step=11001, Step=11017, Step=11027, Step=15049, Step=15008, Step=15048, Step=15041, Step=15048, Step=15013, Step=24209, Step=24211, Step=22037, Step=15036, Step=15048, Step=15048, Step=15048, Step=24432, Step=24325, Step=24313, Step=24318, Step=24322, Step=24352, Step=24412, Step=15048, Step=15048, Step=15016, Step=15039, Step=11003, SelectedAuthenticationIdentityStores=Internal Endpoints, NetworkDeviceGroups=Location#All Locations#SITE-01, NetworkDeviceGroups=Device Type#All Device Types#SW_Vendor_Site, NetworkDeviceGroups=IPSEC#Is IPSEC Device#No, IdentityPolicyMatchedRule=MAB, AuthorizationPolicyMatchedRule=Default, cisco-av-pair=AuthenticationIdentityStore=Internal Endpoints, UserType=Host, CPMSessionID=000000000000000000000000, EndPointMACAddress=user1, EndPointMatchedProfile=VENDOR-Device, DeviceRegistrationStatus=notRegistered, ISEPolicySetName=POLICY-01, IdentitySelectionMatchedRule=MAB, StepLatency=1=0;2=1;3=0;4=0;5=0;6=1;7=0;8=1;9=0;10=1;11=0;12=0;13=12;14=5;15=0;23=3;24=0;25=1;26=0;27=0, StepData=5= DEVICE.Location, StepData=7= Normalised Radius.RadiusFlowType, StepData=8=Internal Endpoints, StepData=13= EndPoints.LogicalProfile, StepData=14= EndPoints.EndPointPolicy, StepData=15= DEVICE.Device Type, StepData=0=AD_EXAMPLE, StepData=1=user1, StepData=2=example.local, StepData=3=example.local, StepData=5=ERROR_NO_SUCH_USER, StepData=6=AD_EXAMPLE, StepData=23= AD_EXAMPLE.ExternalGroups, StepData=24= Radius.Called-Station-ID, TotalAuthenLatency=25, ClientLatency=0, DTLSSupport=Unknown, HostIdentityGroup=Endpoint Identity Groups:Profiled, Network Device Profile=Cisco, Location=Location#All Locations#SITE-01, Device Type=Device Type#All Device Types#SW_Vendor_Site, IPSEC=IPSEC#Is IPSEC Device#No, EndPointPolicy=00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000, Name=Endpoint Identity Groups:Profiled, Response={RadiusPacketType=AccessReject; AuthenticationResult=Passed; UserName=AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:FF; },",
"event": {
"category": [
"authentication"
],
"reason": "{RadiusPacketType=AccessReject; AuthenticationResult=Passed; UserName=AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:FF; }",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"cisco": {
"ise": {
"network": {
"device_name": "DEVICE-01"
},
"step_data": {
"5_code": "DEVICE.Location"
},
"type": "CISE_Failed_Attempts"
}
},
"destination": {
"address": "1.2.3.4",
"ip": "1.2.3.4",
"port": 1812
},
"network": {
"protocol": "Radius"
},
"observer": {
"product": "Cisco ISE",
"vendor": "Cisco"
},
"related": {
"ip": [
"1.2.3.4"
],
"user": [
"user1"
]
},
"rule": {
"name": "MAB"
},
"source": {
"address": "1.2.3.4",
"ip": "1.2.3.4"
},
"user": {
"name": "user1"
}
}
{
"message": "0000087238 3 1 AcsSessionID=ISE-CISCO/1111111/222222, AuthenticationIdentityStore=Internal Endpoints, AuthenticationMethod=Lookup, SelectedAccessService=AuthenticationMAB, SelectedAuthorizationProfiles=DenyAccess, UseCase=Host Lookup, RequestLatency=5, IdentityGroup=Endpoint Identity Groups:Unknown, FailureReason=15039 Rejected per authorization profile, Step=11001, Step=11017, Step=11027, Step=15049, Step=15008, Step=15048, Step=15048, Step=15048, Step=15041, Step=15013, Step=24209, Step=24211, Step=22037, Step=15036, Step=15016, Step=15039, Step=11003, SelectedAuthenticationIdentityStores=Internal Endpoints, NetworkDeviceGroups=Device Type#All Device Types#Switch, NetworkDeviceGroups=IPSEC#Is IPSEC Device#No, NetworkDeviceGroups=Location#All Locations, IdentityPolicyMatchedRule=Authentication Rule 1, AuthorizationPolicyMatchedRule=Default, cisco-av-pair=AuthenticationIdentityStore=Internal Endpoints, UserType=Host, CPMSessionID=ABCDEF0123456,",
"event": {
"category": [
"authentication"
],
"reason": "15039 Rejected per authorization profile",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"observer": {
"product": "Cisco ISE",
"vendor": "Cisco"
},
"rule": {
"name": "Authentication Rule 1"
}
}
{
"message": "0000089788 3 2 EndPointMACAddress=00-11-22-33-44-55, EndPointMatchedProfile=Unknown, DeviceRegistrationStatus=notRegistered, ISEPolicySetName=MAB, IdentitySelectionMatchedRule=Authentication Rule 1, StepLatency=1=0\\;2=0\\;3=0\\;4=0\\;5=0\\;6=1\\;7=0\\;8=0\\;9=1\\;10=0\\;11=1\\;12=0\\;13=0\\;14=1\\;15=0\\;16=0, StepData=5= DEVICE.Device Type, StepData=6= Radius.NAS-IP-Address, StepData=7= Normalised Radius.RadiusFlowType, StepData=9=Internal Endpoints, TotalAuthenLatency=4, ClientLatency=0, DTLSSupport=Unknown, HostIdentityGroup=Endpoint Identity Groups:Unknown, Network Device Profile=Cisco, Location=Location#All Locations, Device Type=Device Type#All Device Types#Switch, IPSEC=IPSEC#Is IPSEC Device#No, Name=Endpoint Identity Groups:Unknown, Response={RadiusPacketType=AccessReject; AuthenticationResult=Passed; UserName=02:00:00:00:00:00; },",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"reason": "{RadiusPacketType=AccessReject; AuthenticationResult=Passed; UserName=02:00:00:00:00:00; }",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"cisco": {
"ise": {
"step_data": {
"5_code": "DEVICE.Device Type"
}
}
},
"observer": {
"product": "Cisco ISE",
"vendor": "Cisco"
},
"source": {
"mac": "00:11:22:33:44:55"
}
}
{
"message": "INFO: 5 endpoint(s) purged successfully",
"event": {
"reason": "5 endpoint(s) purged successfully",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"observer": {
"product": "Cisco ISE",
"vendor": "Cisco"
}
}
{
"message": "2023-06-07 04:26:17.306 +0200 60198 INFO null: MnT purge event occurred, MESSAGE=completed successfully,",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"reason": "MnT purge event occurred",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"cisco": {
"ise": {
"event": {
"outcome": "success"
}
}
},
"observer": {
"product": "Cisco ISE",
"vendor": "Cisco"
}
}
{
"message": "WARN: AcsSyslogContentAaaDiagnostics:: ACTIVE_DIRECTORY_DIAGNOSTIC_TOOL_ISSUES_FOUND need to complete",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"reason": "AcsSyslogContentAaaDiagnostics:: ACTIVE_DIRECTORY_DIAGNOSTIC_TOOL_ISSUES_FOUND need to complete",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"observer": {
"product": "Cisco ISE",
"vendor": "Cisco"
}
}
{
"message": "INFO: EAP Connection Timeout : Server=example.com; NAS IP Address=1.2.3.4; NAS Identifier=02:00:00:00:00:00:test1",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"reason": "EAP Connection Timeout",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"observer": {
"product": "Cisco ISE",
"vendor": "Cisco"
},
"related": {
"hosts": [
"example.com"
],
"ip": [
"1.2.3.4"
]
},
"source": {
"address": "example.com",
"domain": "example.com",
"ip": "1.2.3.4",
"mac": "02:00:00:00:00:00",
"registered_domain": "example.com",
"top_level_domain": "com"
}
}
{
"message": "0000738292 7 0 2025-01-09 09:28:49.914 +01:00 0043796555 5200 NOTICE Passed-Authentication: Authentication succeeded, ConfigVersionId=186, Device IP Address=192.0.2.1, DestinationIPAddress=1.2.3.4, DestinationPort=1812, UserName=user1, Protocol=Radius, NetworkDeviceName=MGCUH1-3, User-Name=user1, NAS-IP-Address=192.0.2.1, NAS-Port=1001, Service-Type=Framed, Framed-MTU=1449, State=37CPMSessionID=XXXXXXXXXXXXXX\\;36SessionID=MGDFSISE2/515448264/543038\\;, Called-Station-ID=a0:ec:f9:50:e2:90:DFS, Calling-Station-ID=bc:83:85:d8:88:c6, NAS-Identifier=MGCUH1-3, NAS-Port-Type=Wireless - IEEE 802.11, NAS-Port-Id=Capwap2, EAP-Key-Name=, cisco-av-pair=service-type=Framed, cisco-av-pair=audit-session-id=XXXXXXXXXXXXXX, cisco-av-pair=method=dot1x, cisco-av-pair=cisco-wlan-ssid=DFS, Airespace-Wlan-Id=5, NetworkDeviceProfileName=Cisco, NetworkDeviceProfileId=aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa,#015",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"reason": "Authentication succeeded",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"cisco": {
"ise": {
"network": {
"device_name": "MGCUH1-3"
}
}
},
"destination": {
"address": "1.2.3.4",
"ip": "1.2.3.4",
"mac": "A0:EC:F9:50:E2:90:DF:S",
"port": 1812
},
"network": {
"protocol": "Radius"
},
"observer": {
"product": "Cisco ISE",
"vendor": "Cisco"
},
"related": {
"ip": [
"1.2.3.4",
"192.0.2.1"
],
"user": [
"user1"
]
},
"source": {
"address": "192.0.2.1",
"ip": "192.0.2.1",
"mac": "BC:83:85:D8:88:C6"
},
"user": {
"name": "user1"
}
}
{
"message": "CISE_RADIUS_Accounting 0002391460 1 0 2025-07-30 11:50:34.267 +02:00 0023023046 3002 NOTICE Radius-Accounting: RADIUS Accounting watchdog update, ConfigVersionId=83, Device IP Address=1.2.3.4, UserName=user1, NetworkDeviceName=Test-Network-Device-Name, User-Name=user1, NAS-IP-Address=1.2.3.4, NAS-Port=50107, Framed-IP-Address=3.4.5.6, Class=CACS:0A0D00F90000001402268B53:ise/523393559/11169221, Called-Station-ID=11-00-00-00-00-00, Calling-Station-ID=user1, Acct-Status-Type=Interim-Update, Acct-Delay-Time=0, Acct-Input-Octets=1848852125, Acct-Output-Octets=2808400785, Acct-Session-Id=00000070, Acct-Input-Packets=27991836, Acct-Output-Packets=40488347, Event-Timestamp=1753869011, NAS-Port-Type=Ethernet, NAS-Port-Id=GigabitEthernet0/7, cisco-av-pair=audit-session-id=0A0D00F90000001402268B53, cisco-av-pair=vlan-id=1330, cisco-av-pair=method=mab, AcsSessionID=MGMT-ISE01/0000000000/2185126, SelectedAccessService=Default Network Access, RequestLatency=3, Step=11004, Step=11017, Step=15049, Step=15008, Step=15048, Step=15048, Step=22094, Step=11005, NetworkDeviceGroups=Location#All Locations#Test Test#LAN#ACA, NetworkDeviceGroups=Device Type#All Device Types#Switch#2960L, NetworkDeviceGroups=IPSEC#Is IPSEC Device#No, CPMSessionID=0A0D00F90000001402268B53, StepLatency=1=0\\;2=0\\;3=0\\;4=1\\;5=0\\;6=1\\;7=0, StepData=4= Normalised Radius.TTTTT, StepData=5= Normalised Radius.RadiusFlowType, TotalAuthenLatency=3, ClientLatency=0, Model Name=Unknown, Software Version=Unknown, Network Device Profile=Cisco, Location=Location#All Locations#Test Test#LAN#ACA, Device Type=Device Type#All Device Types#Switch#2960L, IPSEC=IPSEC#Is IPSEC Device#No,",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"reason": "RADIUS Accounting watchdog update",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"cisco": {
"ise": {
"network": {
"device_name": "Test-Network-Device-Name"
},
"step_data": {
"5_code": "Normalised Radius.RadiusFlowType"
}
}
},
"destination": {
"mac": "11:00:00:00:00:00"
},
"observer": {
"product": "Cisco ISE",
"vendor": "Cisco"
},
"related": {
"ip": [
"1.2.3.4"
],
"user": [
"user1"
]
},
"source": {
"address": "1.2.3.4",
"ip": "1.2.3.4"
},
"user": {
"name": "user1"
}
}
{
"message": "0000000000 1 0 2025-07-29 14:07:18.047 +02:00 0000000000 51000 NOTICE Administrator-Login: Administrator authentication failed, ConfigVersionId=XX, AdminInterface=GUI, AdminIPAddress=1.2.3.4, AdminName=user1, OperationMessageText=Authentication failed due to invalid user or password, or account is disabled/locked,",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"reason": "Administrator authentication failed",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"observer": {
"product": "Cisco ISE",
"vendor": "Cisco"
},
"related": {
"ip": [
"1.2.3.4"
],
"user": [
"user1"
]
},
"source": {
"address": "1.2.3.4",
"ip": "1.2.3.4"
},
"user": {
"name": "user1"
}
}
{
"message": "CISE_Administrative_and_Operational_Audit 0000000000 1 0 2025-07-29 14:07:18.047 +02:00 0000000000 51000 NOTICE Administrator-Login: Administrator authentication failed, ConfigVersionId=XX, AdminInterface=GUI, AdminIPAddress=1.2.3.4, AdminName=user1, OperationMessageText=Authentication failed due to invalid user or password, or account is disabled/locked,",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"reason": "Administrator authentication failed",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"observer": {
"product": "Cisco ISE",
"vendor": "Cisco"
},
"related": {
"ip": [
"1.2.3.4"
],
"user": [
"user1"
]
},
"source": {
"address": "1.2.3.4",
"ip": "1.2.3.4"
},
"user": {
"name": "user1"
}
}
{
"message": "0001514749 7 6 Response={Class=CACS:XXXXXXXXX:asdsa/000000/111111; Tunnel-Type=(tag=1) VLAN; Tunnel-Medium-Type=(tag=1) 802; Tunnel-Private-Group-ID=(tag=1) COMPUTER; EAP-Key-Name=EAP-Key-VALUE; MS-MPPE-Send-Key=****; MS-MPPE-Recv-Key=****; LicenseTypes=1; },#015",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"reason": "{Class=CACS:XXXXXXXXX:asdsa/000000/111111; Tunnel-Type=(tag=1) VLAN; Tunnel-Medium-Type=(tag=1) 802; Tunnel-Private-Group-ID=(tag=1) COMPUTER; EAP-Key-Name=EAP-Key-VALUE; MS-MPPE-Send-Key=****; MS-MPPE-Recv-Key=****; LicenseTypes=1; }",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"observer": {
"product": "Cisco ISE",
"vendor": "Cisco"
}
}
{
"message": "WARN: Dynamic Authorization Failed for Device : Server=example.com; Calling Station Id=N/A; Network device IP=1.2.3.4; Network Device",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"reason": "Dynamic Authorization Failed for Device",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"observer": {
"product": "Cisco ISE",
"vendor": "Cisco"
},
"related": {
"hosts": [
"example.com"
],
"ip": [
"1.2.3.4"
],
"user": [
"N/A"
]
},
"source": {
"address": "example.com",
"domain": "example.com",
"ip": "1.2.3.4",
"registered_domain": "example.com",
"top_level_domain": "com"
},
"user": {
"name": "N/A"
}
}
{
"message": "WARN: Profiler SNMP Request Failure : Server= example.com; NAD Address=1.2.3.4; Error Message=Request timed out.",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"reason": "Profiler SNMP Request Failure",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"cisco": {
"ise": {
"network_calling_station": {
"id": "Request timed out."
}
}
},
"observer": {
"product": "Cisco ISE",
"vendor": "Cisco"
},
"related": {
"hosts": [
"example.com"
],
"ip": [
"1.2.3.4"
]
},
"source": {
"address": "example.com",
"domain": "example.com",
"ip": "1.2.3.4",
"registered_domain": "example.com",
"top_level_domain": "com"
}
}
{
"message": "WARN: TrustSec deploy verification failed to reach NAD.: Device Name=device005.internal.example.org; Device Ip=1.2.3.4; Device login username=admin",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"reason": "TrustSec deploy verification failed to reach NAD.",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"observer": {
"product": "Cisco ISE",
"vendor": "Cisco"
},
"related": {
"hosts": [
"device005.internal.example.org"
],
"ip": [
"1.2.3.4"
],
"user": [
"admin"
]
},
"source": {
"address": "device005.internal.example.org",
"domain": "device005.internal.example.org",
"ip": "1.2.3.4",
"registered_domain": "example.org",
"subdomain": "device005.internal",
"top_level_domain": "org"
},
"user": {
"name": "admin"
}
}
{
"message": "0003361015 2 0 2025-05-07 14:29:08.974 +02:00 0051006044 80002 INFO Profiler: Profiler EndPoint profiling event occurred, ConfigVersionId=183, OperatingSystem=Windows 11 Entreprise, EndpointCertainityMetric=50, EndpointIPAddress=1.2.3.4, EndpointMacAddress=AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:FF, EndpointMatchedPolicy=Windows11-Workstation, EndpointOUI=Intel Corporate, EndpointPolicy=Windows11-Workstation, EndpointProperty=chaddr=AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:FF,dhcp-class-identifier=MSFT 5.0,PolicyVersion=24,dhcp-message-type=DHCPREQUEST,EndPointPolicyID=57f40927-3b0a-46b8-9f03-78d47e1383c4,LogicalProfile=,client-fqdn=abcdef.example.local,EndPointVersion=340,FirstCollection=1744718839328,CacheUpdateTime=1746620948973,StaticAssignment=false,NmapScanCount=0,PostureExpiry=,hlen=6,AD-Operating-System=Windows 11 Entreprise,AD-Join-Point=EXAMPLE.LOCAL,PortalUser=,ciaddr=0.0.0.0,BYODRegistration=Unknown,dhcp-requested-address=1.2.3.4,Total Certainty Factor=50,MDMServerID=,",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"reason": "Profiler EndPoint profiling event occurred",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"cisco": {
"ise": {
"dhcp": {
"message_type": "DHCPREQUEST",
"requested_address": "1.2.3.4"
}
}
},
"host": {
"os": {
"full": "Windows 11 Entreprise"
}
},
"observer": {
"product": "Cisco ISE",
"vendor": "Cisco"
},
"related": {
"ip": [
"1.2.3.4"
]
},
"rule": {
"id": "57f40927-3b0a-46b8-9f03-78d47e1383c4",
"name": "Windows11-Workstation"
},
"source": {
"address": "1.2.3.4",
"ip": "1.2.3.4",
"mac": "AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:FF"
}
}
{
"message": "Oct 27 15:20:43 HOST-01 CISE_RADIUS_Accounting 0001042079 1 0 2025-10-27 15:20:43.919 +01:00 0015337799 3002 NOTICE Radius-Accounting: RADIUS Accounting watchdog update, ConfigVersionId=11, Device IP Address=1.2.3.4, UserName=user1, NetworkDeviceName=DEVICE-02, User-Name=user1, NAS-IP-Address=1.2.3.4, NAS-Port=42, Service-Type=Framed, Framed-IP-Address=1.2.3.4, Class=CACS:000000000000000000000000:HOST-01/000000000/000000, Called-Station-ID=user1:, Calling-Station-ID=user1, Acct-Status-Type=Interim-Update, Acct-Delay-Time=0, Acct-Input-Octets=921941396, Acct-Output-Octets=0, Acct-Session-Id=0000000000000000, Acct-Authentic=RADIUS, Acct-Session-Time=570009, Acct-Input-Packets=0, Acct-Output-Packets=35, Acct-Input-Gigawords=922518720, Acct-Output-Gigawords=28, Event-Timestamp=1761574843, NAS-Port-Type=Ethernet, cisco-av-pair=audit-session-id=000000000000000000000000, AcsSessionID=HOST-01/000000000/000000, SelectedAccessService=Default Network Access, RequestLatency=2, Step=11004, Step=11017, Step=15049, Step=15008, Step=22094, Step=11005, NetworkDeviceGroups=Location#All Locations#SITE-02, NetworkDeviceGroups=Device Type#All Device Types#SW_Vendor_Site, NetworkDeviceGroups=IPSEC#Is IPSEC Device#No, CPMSessionID=000000000000000000000000, StepLatency=1=0;2=0;3=1;4=0;5=0, TotalAuthenLatency=2, ClientLatency=0, Network Device Profile=Cisco, Location=Location#All Locations#SITE-02, Device Type=Device Type#All Device Types#SW_Vendor_Site, IPSEC=IPSEC#Is IPSEC Device#No,",
"event": {
"category": [
"network"
],
"reason": "RADIUS Accounting watchdog update",
"type": [
"info"
]
},
"cisco": {
"ise": {
"network": {
"device_name": "DEVICE-02"
},
"type": "CISE_RADIUS_Accounting"
}
},
"observer": {
"product": "Cisco ISE",
"vendor": "Cisco"
},
"related": {
"ip": [
"1.2.3.4"
],
"user": [
"user1"
]
},
"source": {
"address": "1.2.3.4",
"ip": "1.2.3.4"
},
"user": {
"name": "user1"
}
}
Extracted Fields
The following table lists the fields that are extracted, normalized under the ECS format, analyzed and indexed by the parser. It should be noted that infered fields are not listed.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
cisco.ise.config_action |
keyword |
The action in a configuration events. (Added, Changed, Deleted) |
cisco.ise.config_object.name |
keyword |
The name of the object in the conf events |
cisco.ise.config_object.type |
keyword |
The type of the objection in the conf events |
cisco.ise.dhcp.message_type |
keyword |
DHCP message type |
cisco.ise.dhcp.parameter_request_list |
keyword |
DHCP parameter request list |
cisco.ise.dhcp.requested_address |
keyword |
DHCP requested address |
cisco.ise.event.outcome |
keyword |
The outcome of the event |
cisco.ise.network.device_name |
keyword |
The network device name |
cisco.ise.network_calling_station.id |
keyword |
the calling station id |
cisco.ise.step_data.5_code |
keyword |
The step data code |
cisco.ise.type |
keyword |
The type of Cisco ISE event |
destination.domain |
keyword |
The domain name of the destination. |
destination.ip |
ip |
IP address of the destination. |
destination.mac |
keyword |
MAC address of the destination. |
destination.port |
long |
Port of the destination. |
dns.question.registered_domain |
keyword |
The highest registered domain, stripped of the subdomain. |
event.category |
keyword |
Event category. The second categorization field in the hierarchy. |
event.outcome |
keyword |
The outcome of the event. The lowest level categorization field in the hierarchy. |
event.reason |
keyword |
Reason why this event happened, according to the source |
event.type |
keyword |
Event type. The third categorization field in the hierarchy. |
host.name |
keyword |
Name of the host. |
host.os.full |
keyword |
Operating system name, including the version or code name. |
network.protocol |
keyword |
Application protocol name. |
observer.product |
keyword |
The product name of the observer. |
observer.vendor |
keyword |
Vendor name of the observer. |
rule.id |
keyword |
Rule ID |
rule.name |
keyword |
Rule name |
source.domain |
keyword |
The domain name of the source. |
source.ip |
ip |
IP address of the source. |
source.mac |
keyword |
MAC address of the source. |
tls.client.x509.issuer.common_name |
keyword |
List of common name (CN) of issuing certificate authority. |
tls.client.x509.issuer.country |
keyword |
List of country (C) codes |
tls.client.x509.issuer.locality |
keyword |
List of locality names (L) |
tls.client.x509.issuer.organization |
keyword |
List of organizations (O) of issuing certificate authority. |
tls.client.x509.issuer.organizational_unit |
keyword |
List of organizational units (OU) of issuing certificate authority. |
user.domain |
keyword |
Name of the directory the user is a member of. |
user.name |
keyword |
Short name or login of the user. |
For more information on the Intake Format, please find the code of the Parser, Smart Descriptions, and Supported Events here.