FortiWeb
Overview
This documentation details one way to collect and send FortiWeb logs to Sekoia.io: from the FortiWeb machine to an internal syslog concentrator, then forwarded to Sekoia.io.
- Vendor: Fortinet
- Supported environment: On Premise
- Version compatibility, if applicable:
- Detection based on: Network Telemetry
- Supported application or feature: WAF
High-Level Architecture Diagram
- Type of integration: Outbound (PUSH to Sekoia.io)
- Schema
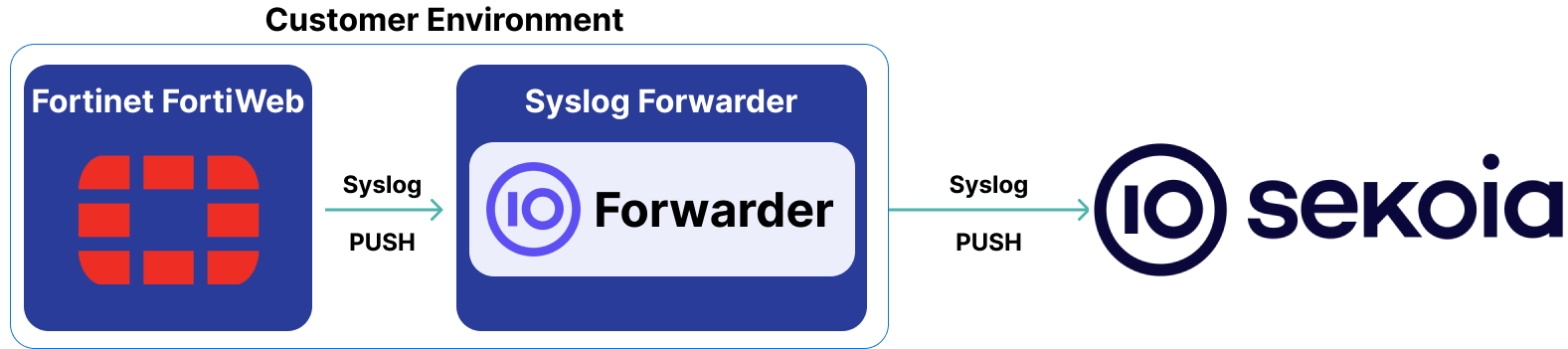
Alternative
This will not be detailed in this documentation, but logs can also be sent directly to Sekoia.io over HTTPS using the Sekoia.io Endpoint Agent and the "Collect logs in files" method. This provides an alternative to the specified syslog collection method and may be preferable in certain environments.
Specification
Prerequisites
- Resource:
- Self-managed syslog forwarder
- Network:
- Outbound traffic allowed
- Permissions:
- Administrator rights on the FortiWeb (read & write permission)
- Root access to the Linux server with the syslog forwarder
Transport Protocol/Method
- Indirect Syslog
Logs details
- Supported functionalities: See section Overview
- Supported type(s) of structure: Key-Value
- Supported verbosity level: Informational
Note
Log levels are based on the taxonomy of RFC5424. Adapt according to the terminology used by the editor.
Step-by-Step Configuration Procedure
Instructions on the 3rd Party Solution
Forward FortiWeb Logs to Sekoia.io
This setup guide will show you how to forward your FortiWeb logs to Sekoia.io by means of a syslog transport channel.
Detailed Procedure:
-
FortiWeb Logs:
- On FortiWeb appliances, most of the important hardware and software activities that are relevant for security detection and analysis are logged into three files:
- Traffic: Displays traffic flow information, such as HTTP/HTTPS requests and responses.
- Event: Displays administrative events, such as downloading a backup copy of the configuration, and hardware failures.
- Attack: Displays attack and intrusion attempt events.
-
Transport to the Concentrator:
- Prerequisites:
- Administrator rights on the FortiWeb (read & write permission)
-
Traffic towards the syslog concentrator must be open on
UDP 514 -
Configure FortiWeb:
Enable logging via trigger mechanism:
- Go to
Log&Report > Log Config > Other Log Settings. - Tick the boxes: Enable Attack Log / Enable Traffic Log / Enable Event Log.
Configure Syslog Policies:
- Go to
Log&Report > Log Policy > Syslog Policy. - Click
Create New. - In
IP Address, enter the address of the remote Syslog server. - In
Port, enter the listening port number of the Syslog server. The default is 514. - Click
OK.
Configure Log Destinations:
- Go to
Log&Report > Log Config > Global Log Settings. - Tick the syslog box.
- Select the relevant Syslog Policy, Log Level, and Facility.
- Click
Apply.
For more information, please refer to the official documentation of FortiWeb.
Configure a forwarder
To forward events using syslog to Sekoia.io, you need to update the syslog header with the intake key you previously created. Here is an example of your message before the forwarder
<%pri%>1 %timestamp:::date-rfc3339% %hostname% %app-name% %procid% LOG RAW_MESSAGE
<%pri%>1 %timestamp:::date-rfc3339% %hostname% %app-name% %procid% LOG [SEKOIA@53288 intake_key=\"YOUR_INTAKE_KEY\"] RAW_MESSAGE
To achieve this you can:
- Use the Sekoia.io forwarder which is the official supported way to collect data using the syslog protocol in Sekoia.io. In charge of centralizing data coming from many equipments/sources and forwarding them to Sekoia.io with the apporpriated format, it is a prepackaged option. You only have to provide your intake key as parameter.
- Use your own Syslog service instance. Maybe you already have an intance of one of these components on your side and want to reuse it in order to centralize data before forwarding them to Sekoia.io. When using this mode, you have to configure and maintain your component in order to respect the expected Sekoia.io format.
Warning
Only the Sekoia.io forwarder is officially supported. Other options are documented for reference purposes but do not have official support.
Instruction on Sekoia
Configure Your Intake
This section will guide you through creating the intake object in Sekoia, which provides a unique identifier called the "Intake key." The Intake key is essential for later configuration, as it references the Community, Entity, and Parser (Intake Format) used when receiving raw events on Sekoia.
- Go to the Sekoia Intake page.
- Click on the
+ New Intakebutton at the top right of the page. - Search for your Intake by the product name in the search bar.
- Give it a Name and associate it with an Entity (and a Community if using multi-tenant mode).
- Click on
Create.
Note
For more details on how to use the Intake page and to find the Intake key you just created, refer to this documentation.
Raw Events Samples
In this section, you will find examples of raw logs as generated natively by the source. These examples are provided to help integrators understand the data format before ingestion into Sekoia.io. It is crucial for setting up the correct parsing stages and ensuring that all relevant information is captured.
cat=attack date_time=2023-12-08T02:34:17+01:00 user_id=9a8d2e96-0d28-48ef-ac6c-8e23236e9eaf user_name=jdoe@example.org login_user="Unknown" ep_id=5446331978 app_name="Staging" ep_region=europe-west3 ep_domain=staging.example.org src_ip=1.2.3.4 src_port=45344 backend_service=unknown dst_port=443 srccountry="Ireland" service=https/tls1.3 action=Block main_type="Known Bots Detection" sub_type="Crawler" threat_level=Moderate threat_weight=25 http_host=staging.example.org http_url=/ http_version=1.x http_method=GET http_agent="Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; NetcraftSurveyAgent/1.0; +info@netcraft.com)" http_refer=none length=1546 signature_id=N/A signature_cve_id=N/A owasp_top10="N/A" msg="Known Bots: Malicious Bot Netcraft in category Crawler Violation" log_id=20000213 msg_id=001415055359
time=10:29:22 devname=DEV_NAME_TEST device_id=DEV_ID_TEST log_id=0202006010 type=attack subtype=waf pri=alert vd=waf msg_id=55878889 count=1 severity="medium" proto=6 service="https" src="3.4.5.6" src_port=51982 dst="1.2.3.4" dst_port=443 policy="VS_FRED_PROD_WEB" action="alert" sigid=1060000000 owasp_top10="A5:2021-Security Misconfiguration" subcat="waf_json_check" http_method="POST" http_host="test.test" http_url="/api/Rapport/ApplyRGCIOnRapport" user_agent="Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/137.0.0.0 Safari/537.36" pkt_hdr="Connection: keep-alive#011#011Content-Length: 4111#011#011sec-ch-ua-platform: \"Windows\"#011#011Content-Encoding: gzip#011#011sec-ch-ua: \"Google Chro" matched_part="none" srccountry="France" dstcountry="Reserved" msg="Attack ID: 1060000000 Module: \"JSON validation detection\" Check Type: \"JSON format check\" Desc: \"JSON content is not wellformed\""
timestamp=1759321598 devname="MYDEVICE" devid="11111111111111111" vd="root" date=2025-10-01 time=12:26:38 eventtime=1759314399181844149 tz="+0200" logid="0123456789" type="utm" subtype="anomaly" eventtype="anomaly" level="alert" severity="critical" srcip=1.2.3.4 srccountry="France" dstip=5.6.7.8 dstcountry="Reserved" srcintf="port1" srcintfrole="undefined" sessionid=0 action="clear_session" proto=6 service="jeton flex token" count=32 attack="tcp_src_session" srcport=52330 dstport=2080 attackid=100663402 policyid=1 policytype="DoS-policy" ref="http://www.fortinet.com/ids/VID100663402" msg="anomaly: tcp_src_session, 101 > threshold 100, repeats 32 times since last log" crscore=50 craction=4096 crlevel="critical"
time=16:58:13 log_id=30001000 msg_id=000669319381 device_id=FVVM010000207514 vd="root" timezone="(GMT+1:00)Brussels,Copenhagen,Madrid,Paris" timezone_dayst="GMTc-2" type=traffic subtype="https" pri=notice proto=tcp service=https/tls1.2 status=success reason=none policy=extranet original_src=192.168.36.2 src=192.168.36.2 src_port=48152 dst=172.26.8.20 dst_port=80 http_request_time=0 http_response_time=0 http_request_bytes=549 http_response_bytes=11272 http_method=get http_url="/apiv1/wan/list?take=12&skip=84&orderBy=ponderationValue&sortDirection=desc&filter[]=monitor,equalsBool,true&filter[]=status,equal,DOWN" http_agent="Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux armv7l) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Raspbian Chromium/72.0.3626.121 Chrome/72.0.3626.121 Safari/537.36" http_retcode=200 msg="HTTPS get request from 192.168.36.2:48152 to 172.26.8.20:80" original_srccountry="Reserved" srccountry="Reserved" content_switch_name="none" server_pool_name="extranet.sns-security.fr" http_host="api.sns-security.fr" user_name="Unknown" http_refer="https://technet.sns-security.fr/" http_version="1.x" dev_id=none cipher_suite="TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384"
time=10:16:29 devname=MYDEVICE device_id=1111111111111111111111 log_id=30001000 type=traffic subtype=slb_http pri=information vd=waf msg_id=123456 duration=39186 ibytes=4723 obytes=220 proto=6 service="https" src="1.2.3.4" src_port=56058 dst="5.6.7.8" dst_port=443 trans_src="9.10.11.12" trans_src_port=45124 trans_dst="13.14.15.16" trans_dst_port=80 policy="POLICYNAME" action="none" http_method="get" http_host="example.com" http_agent="Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/138.0.0.0 Safari/537.36" http_url="/api/users" http_qry="none" http_referer="https://example.com/index" http_cookie="COOKIE" http_retcode="200" user="none" usrgrp="none" auth_status="none" srccountry="Reserved" dstcountry="Reserved" real_server="PROD_WEB01_13.14.15.16"
time=10:48:07 log_id=11005607 msg_id=000669559376 device_id=FVVM010000207514 vd="root" timezone="(GMT+1:00)Brussels,Copenhagen,Madrid,Paris" timezone_dayst="GMTc-2" type=event subtype="system" pri=notice trigger_policy="" user=daemon ui=daemon action=check-resource status=success msg="The logdisk usage is too high"
Detection section
The following section provides information for those who wish to learn more about the detection capabilities enabled by collecting this intake. It includes details about the built-in rule catalog, event categories, and ECS fields extracted from raw events. This is essential for users aiming to create custom detection rules, perform hunting activities, or pivot in the events page.
Related Built-in Rules
The following Sekoia.io built-in rules match the intake Fortinet FortiWeb. This documentation is updated automatically and is based solely on the fields used by the intake which are checked against our rules. This means that some rules will be listed but might not be relevant with the intake.
SEKOIA.IO x Fortinet FortiWeb on ATT&CK Navigator
Bazar Loader DGA (Domain Generation Algorithm)
Detects Bazar Loader domains based on the Bazar Loader DGA
- Effort: elementary
Covenant Default HTTP Beaconing
Detects potential Covenant communications through the user-agent and specific urls
- Effort: intermediate
Cryptomining
Detection of domain names potentially related to cryptomining activities.
- Effort: master
Discord Suspicious Download
Discord is a messaging application. It allows users to create their own communities to share messages and attachments. Those attachments have little to no overview and can be downloaded by almost anyone, which has been abused by attackers to host malicious payloads.
- Effort: advanced
Dynamic DNS Contacted
Detect communication with dynamic dns domain. This kind of domain is often used by attackers. This rule can trigger false positive in non-controlled environment because dynamic dns is not always malicious.
- Effort: master
EvilProxy Phishing Domain
Detects subdomains potentially generated by the EvilProxy adversary-in-the-middle phishing platform. Inspect the other subdomains of the domain to identify the landing page, and determine if the user submitted credentials. This rule has a small percentage of false positives on legitimate domains.
- Effort: intermediate
Exfiltration Domain
Detects traffic toward a domain flagged as a possible exfiltration vector.
- Effort: master
Koadic MSHTML Command
Detects Koadic payload using MSHTML module
- Effort: intermediate
Nimbo-C2 User Agent
Nimbo-C2 Uses an unusual User-Agent format in its implants.
- Effort: intermediate
Potential Azure AD Phishing Page (Adversary-in-the-Middle)
Detects an HTTP request to an URL typical of the Azure AD authentication flow, but towards a domain that is not one the legitimate Microsoft domains used for Azure AD authentication.
- Effort: intermediate
Potential Bazar Loader User-Agents
Detects potential Bazar loader communications through the user-agent
- Effort: elementary
Potential Lemon Duck User-Agent
Detects LemonDuck user agent. The format used two sets of alphabetical characters separated by dashes, for example "User-Agent: Lemon-Duck-[A-Z]-[A-Z]".
- Effort: elementary
Potential LokiBot User-Agent
Detects potential LokiBot communications through the user-agent
- Effort: intermediate
Remote Access Tool Domain
Detects traffic toward a domain flagged as a Remote Administration Tool (RAT).
- Effort: master
Remote Monitoring and Management Software - AnyDesk
Detect artifacts related to the installation or execution of the Remote Monitoring and Management tool AnyDesk.
- Effort: master
SEKOIA.IO Intelligence Feed
Detect threats based on indicators of compromise (IOCs) collected by SEKOIA's Threat and Detection Research team.
- Effort: elementary
Sekoia.io EICAR Detection
Detects observables in Sekoia.io CTI tagged as EICAR, which are fake samples meant to test detection.
- Effort: master
Sign-In Via Known AiTM Phishing Kit
Detects a sign-in attempt from an IP address belonging to a known adversary-in-the-middle phishing kit.
- Effort: elementary
TOR Usage Generic Rule
Detects TOR usage globally, whether the IP is a destination or source. TOR is short for The Onion Router, and it gets its name from how it works. TOR intercepts the network traffic from one or more apps on user’s computer, usually the user web browser, and shuffles it through a number of randomly-chosen computers before passing it on to its destination. This disguises user location, and makes it harder for servers to pick him/her out on repeat visits, or to tie together separate visits to different sites, this making tracking and surveillance more difficult. Before a network packet starts its journey, user’s computer chooses a random list of relays and repeatedly encrypts the data in multiple layers, like an onion. Each relay knows only enough to strip off the outermost layer of encryption, before passing what’s left on to the next relay in the list.
- Effort: master
Event Categories
The following table lists the data source offered by this integration.
| Data Source | Description |
|---|---|
Web application firewall logs |
date_source: "Fortinet WAF" |
Transformed Events Samples after Ingestion
This section demonstrates how the raw logs will be transformed by our parsers. It shows the extracted fields that will be available for use in the built-in detection rules and hunting activities in the events page. Understanding these transformations is essential for analysts to create effective detection mechanisms with custom detection rules and to leverage the full potential of the collected data.
{
"message": "cat=attack date_time=2023-12-08T02:34:17+01:00 user_id=9a8d2e96-0d28-48ef-ac6c-8e23236e9eaf user_name=jdoe@example.org login_user=\"Unknown\" ep_id=5446331978 app_name=\"Staging\" ep_region=europe-west3 ep_domain=staging.example.org src_ip=1.2.3.4 src_port=45344 backend_service=unknown dst_port=443 srccountry=\"Ireland\" service=https/tls1.3 action=Block main_type=\"Known Bots Detection\" sub_type=\"Crawler\" threat_level=Moderate threat_weight=25 http_host=staging.example.org http_url=/ http_version=1.x http_method=GET http_agent=\"Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; NetcraftSurveyAgent/1.0; +info@netcraft.com)\" http_refer=none length=1546 signature_id=N/A signature_cve_id=N/A owasp_top10=\"N/A\" msg=\"Known Bots: Malicious Bot Netcraft in category Crawler Violation\" log_id=20000213 msg_id=001415055359",
"event": {
"action": "Block",
"message": "Known Bots: Malicious Bot Netcraft in category Crawler Violation"
},
"action": {
"properties": {
"cat": "attack",
"log_id": "20000213",
"service": "https/tls1.3"
}
},
"destination": {
"port": 443
},
"http": {
"request": {
"method": "GET",
"referrer": "none"
},
"version": "1.x"
},
"log": {
"hostname": "tyR4LrYORLPlEIBp"
},
"related": {
"hosts": [
"staging.example.org"
],
"ip": [
"1.2.3.4"
],
"user": [
"jdoe"
]
},
"source": {
"address": "1.2.3.4",
"geo": {
"name": "Ireland"
},
"ip": "1.2.3.4",
"port": 45344
},
"url": {
"domain": "staging.example.org",
"path": "/",
"registered_domain": "example.org",
"subdomain": "staging",
"top_level_domain": "org",
"username": "jdoe@example.org"
},
"user": {
"domain": "example.org",
"email": "jdoe@example.org",
"id": "9a8d2e96-0d28-48ef-ac6c-8e23236e9eaf",
"name": "jdoe"
},
"user_agent": {
"device": {
"name": "Other"
},
"name": "Other",
"original": "Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; NetcraftSurveyAgent/1.0; +info@netcraft.com)",
"os": {
"name": "Other"
}
}
}
{
"message": "time=10:29:22 devname=DEV_NAME_TEST device_id=DEV_ID_TEST log_id=0202006010 type=attack subtype=waf pri=alert vd=waf msg_id=55878889 count=1 severity=\"medium\" proto=6 service=\"https\" src=\"3.4.5.6\" src_port=51982 dst=\"1.2.3.4\" dst_port=443 policy=\"VS_FRED_PROD_WEB\" action=\"alert\" sigid=1060000000 owasp_top10=\"A5:2021-Security Misconfiguration\" subcat=\"waf_json_check\" http_method=\"POST\" http_host=\"test.test\" http_url=\"/api/Rapport/ApplyRGCIOnRapport\" user_agent=\"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/137.0.0.0 Safari/537.36\" pkt_hdr=\"Connection: keep-alive#011#011Content-Length: 4111#011#011sec-ch-ua-platform: \\\"Windows\\\"#011#011Content-Encoding: gzip#011#011sec-ch-ua: \\\"Google Chro\" matched_part=\"none\" srccountry=\"France\" dstcountry=\"Reserved\" msg=\"Attack ID: 1060000000 Module: \\\"JSON validation detection\\\" Check Type: \\\"JSON format check\\\" Desc: \\\"JSON content is not wellformed\\\"\"",
"event": {
"action": "alert",
"category": "waf",
"kind": "attack",
"message": "Attack ID: 1060000000 Module: \\\"JSON validation detection\\\" Check Type: \\\"JSON format check\\\" Desc: \\\"JSON content is not wellformed\\\""
},
"action": {
"properties": {
"device_id": "DEV_ID_TEST",
"log_id": "0202006010",
"service": "https",
"severity": "medium"
}
},
"destination": {
"address": "1.2.3.4",
"ip": "1.2.3.4",
"port": 443
},
"http": {
"request": {
"method": "\"POST\""
}
},
"log": {
"hostname": "test_hostname",
"level": "alert"
},
"network": {
"protocol": "6"
},
"related": {
"hosts": [
"test.test"
],
"ip": [
"1.2.3.4",
"3.4.5.6"
]
},
"rule": {
"ruleset": "VS_FRED_PROD_WEB"
},
"source": {
"address": "3.4.5.6",
"geo": {
"name": "France"
},
"ip": "3.4.5.6",
"port": 51982
},
"url": {
"domain": "test.test",
"path": "/api/Rapport/ApplyRGCIOnRapport",
"subdomain": "test"
},
"user_agent": {
"device": {
"name": "Other"
},
"name": "Chrome",
"original": "\"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/137.0.0.0 Safari/537.36\"",
"os": {
"name": "Windows",
"version": "10"
},
"version": "137.0.0"
}
}
{
"message": "timestamp=1759321598 devname=\"MYDEVICE\" devid=\"11111111111111111\" vd=\"root\" date=2025-10-01 time=12:26:38 eventtime=1759314399181844149 tz=\"+0200\" logid=\"0123456789\" type=\"utm\" subtype=\"anomaly\" eventtype=\"anomaly\" level=\"alert\" severity=\"critical\" srcip=1.2.3.4 srccountry=\"France\" dstip=5.6.7.8 dstcountry=\"Reserved\" srcintf=\"port1\" srcintfrole=\"undefined\" sessionid=0 action=\"clear_session\" proto=6 service=\"jeton flex token\" count=32 attack=\"tcp_src_session\" srcport=52330 dstport=2080 attackid=100663402 policyid=1 policytype=\"DoS-policy\" ref=\"http://www.fortinet.com/ids/VID100663402\" msg=\"anomaly: tcp_src_session, 101 > threshold 100, repeats 32 times since last log\" crscore=50 craction=4096 crlevel=\"critical\"",
"event": {
"action": "clear_session",
"category": "anomaly",
"kind": "utm",
"message": "anomaly: tcp_src_session, 101 > threshold 100, repeats 32 times since last log"
},
"action": {
"properties": {
"service": "jeton flex token",
"severity": "critical"
}
},
"destination": {
"address": "5.6.7.8",
"ip": "5.6.7.8",
"port": 2080
},
"fortiweb": {
"attack": {
"id": "100663402",
"name": "tcp_src_session"
},
"policy": {
"id": "1",
"type": "DoS-policy"
}
},
"log": {
"hostname": "HOSTNAME"
},
"network": {
"protocol": "6"
},
"related": {
"ip": [
"1.2.3.4",
"5.6.7.8"
]
},
"source": {
"address": "1.2.3.4",
"geo": {
"name": "France"
},
"ip": "1.2.3.4",
"port": 52330
}
}
{
"message": "time=16:58:13 log_id=30001000 msg_id=000669319381 device_id=FVVM010000207514 vd=\"root\" timezone=\"(GMT+1:00)Brussels,Copenhagen,Madrid,Paris\" timezone_dayst=\"GMTc-2\" type=traffic subtype=\"https\" pri=notice proto=tcp service=https/tls1.2 status=success reason=none policy=extranet original_src=192.168.36.2 src=192.168.36.2 src_port=48152 dst=172.26.8.20 dst_port=80 http_request_time=0 http_response_time=0 http_request_bytes=549 http_response_bytes=11272 http_method=get http_url=\"/apiv1/wan/list?take=12&skip=84&orderBy=ponderationValue&sortDirection=desc&filter[]=monitor,equalsBool,true&filter[]=status,equal,DOWN\" http_agent=\"Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux armv7l) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Raspbian Chromium/72.0.3626.121 Chrome/72.0.3626.121 Safari/537.36\" http_retcode=200 msg=\"HTTPS get request from 192.168.36.2:48152 to 172.26.8.20:80\" original_srccountry=\"Reserved\" srccountry=\"Reserved\" content_switch_name=\"none\" server_pool_name=\"extranet.sns-security.fr\" http_host=\"api.sns-security.fr\" user_name=\"Unknown\" http_refer=\"https://technet.sns-security.fr/\" http_version=\"1.x\" dev_id=none cipher_suite=\"TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384\"",
"event": {
"category": "https",
"kind": "traffic",
"message": "HTTPS get request from 192.168.36.2:48152 to 172.26.8.20:80",
"outcome": "success"
},
"action": {
"outcome": "success",
"outcome_reason": "none",
"properties": {
"device_id": "FVVM010000207514",
"log_id": "30001000",
"service": "https/tls1.2"
}
},
"destination": {
"address": "172.26.8.20",
"ip": "172.26.8.20",
"port": 80
},
"http": {
"request": {
"bytes": 549,
"method": "get",
"referrer": "https://technet.sns-security.fr/"
},
"response": {
"bytes": 11272,
"status_code": 200
},
"version": "1.x"
},
"log": {
"hostname": "tyR4LrYORLPlEIBp",
"level": "notice"
},
"network": {
"protocol": "tcp"
},
"related": {
"hosts": [
"api.sns-security.fr"
],
"ip": [
"172.26.8.20",
"192.168.36.2"
],
"user": [
"Unknown"
]
},
"rule": {
"ruleset": "extranet"
},
"source": {
"address": "192.168.36.2",
"geo": {
"name": "Reserved"
},
"ip": "192.168.36.2",
"port": 48152
},
"tls": {
"cipher": "TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384"
},
"url": {
"domain": "api.sns-security.fr",
"path": "/apiv1/wan/list?take=12&skip=84&orderBy=ponderationValue&sortDirection=desc&filter[]=monitor,equalsBool,true&filter[]=status,equal,DOWN",
"registered_domain": "sns-security.fr",
"subdomain": "api",
"top_level_domain": "fr",
"username": "Unknown"
},
"user": {
"name": "Unknown"
},
"user_agent": {
"device": {
"name": "Other"
},
"name": "Chromium",
"original": "Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux armv7l) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Raspbian Chromium/72.0.3626.121 Chrome/72.0.3626.121 Safari/537.36",
"os": {
"name": "Linux"
},
"version": "72.0.3626"
}
}
{
"message": "time=10:16:29 devname=MYDEVICE device_id=1111111111111111111111 log_id=30001000 type=traffic subtype=slb_http pri=information vd=waf msg_id=123456 duration=39186 ibytes=4723 obytes=220 proto=6 service=\"https\" src=\"1.2.3.4\" src_port=56058 dst=\"5.6.7.8\" dst_port=443 trans_src=\"9.10.11.12\" trans_src_port=45124 trans_dst=\"13.14.15.16\" trans_dst_port=80 policy=\"POLICYNAME\" action=\"none\" http_method=\"get\" http_host=\"example.com\" http_agent=\"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/138.0.0.0 Safari/537.36\" http_url=\"/api/users\" http_qry=\"none\" http_referer=\"https://example.com/index\" http_cookie=\"COOKIE\" http_retcode=\"200\" user=\"none\" usrgrp=\"none\" auth_status=\"none\" srccountry=\"Reserved\" dstcountry=\"Reserved\" real_server=\"PROD_WEB01_13.14.15.16\"",
"event": {
"action": "none",
"category": "slb_http",
"kind": "traffic"
},
"action": {
"properties": {
"device_id": "1111111111111111111111",
"log_id": "30001000",
"service": "https"
}
},
"destination": {
"address": "5.6.7.8",
"ip": "5.6.7.8",
"port": 443
},
"http": {
"request": {
"method": "get",
"referrer": "https://example.com/index"
},
"response": {
"status_code": 200
}
},
"log": {
"hostname": "tyR4LrYORLPlEIBp",
"level": "information"
},
"network": {
"protocol": "6"
},
"related": {
"hosts": [
"example.com"
],
"ip": [
"1.2.3.4",
"5.6.7.8"
],
"user": [
"none"
]
},
"rule": {
"ruleset": "POLICYNAME"
},
"source": {
"address": "1.2.3.4",
"geo": {
"name": "Reserved"
},
"ip": "1.2.3.4",
"port": 56058
},
"url": {
"domain": "example.com",
"path": "/api/users",
"registered_domain": "example.com",
"top_level_domain": "com"
},
"user": {
"name": "none"
},
"user_agent": {
"device": {
"name": "Other"
},
"name": "Chrome",
"original": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/138.0.0.0 Safari/537.36",
"os": {
"name": "Windows",
"version": "10"
},
"version": "138.0.0"
}
}
{
"message": "time=10:48:07 log_id=11005607 msg_id=000669559376 device_id=FVVM010000207514 vd=\"root\" timezone=\"(GMT+1:00)Brussels,Copenhagen,Madrid,Paris\" timezone_dayst=\"GMTc-2\" type=event subtype=\"system\" pri=notice trigger_policy=\"\" user=daemon ui=daemon action=check-resource status=success msg=\"The logdisk usage is too high\" ",
"event": {
"action": "check-resource",
"category": "system",
"kind": "event",
"message": "The logdisk usage is too high",
"outcome": "success"
},
"action": {
"outcome": "success",
"properties": {
"device_id": "FVVM010000207514",
"log_id": "11005607"
}
},
"log": {
"hostname": "vnx1hO5mF0pK4IR1",
"level": "notice"
},
"related": {
"user": [
"daemon"
]
},
"user": {
"name": "daemon"
}
}
Extracted Fields
The following table lists the fields that are extracted, normalized under the ECS format, analyzed and indexed by the parser. It should be noted that infered fields are not listed.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
action.properties.cat |
keyword |
|
action.properties.device_id |
keyword |
|
action.properties.log_id |
keyword |
|
action.properties.service |
keyword |
|
action.properties.severity |
keyword |
|
destination.ip |
ip |
IP address of the destination. |
destination.port |
long |
Port of the destination. |
event.action |
keyword |
The action captured by the event. |
event.category |
keyword |
Event category. The second categorization field in the hierarchy. |
event.kind |
keyword |
The kind of the event. The highest categorization field in the hierarchy. |
event.reason |
keyword |
Reason why this event happened, according to the source |
fortiweb.attack.id |
keyword |
|
fortiweb.attack.name |
keyword |
|
fortiweb.policy.id |
keyword |
|
fortiweb.policy.type |
keyword |
|
http.request.bytes |
long |
Total size in bytes of the request (body and headers). |
http.request.method |
keyword |
HTTP request method. |
http.request.referrer |
keyword |
Referrer for this HTTP request. |
http.response.bytes |
long |
Total size in bytes of the response (body and headers). |
http.response.status_code |
long |
HTTP response status code. |
http.version |
keyword |
HTTP version. |
log.level |
keyword |
Log level of the log event. |
network.protocol |
keyword |
Application protocol name. |
rule.ruleset |
keyword |
Rule ruleset |
source.geo.name |
keyword |
User-defined description of a location. |
source.ip |
ip |
IP address of the source. |
source.port |
long |
Port of the source. |
tls.cipher |
keyword |
String indicating the cipher used during the current connection. |
url.domain |
keyword |
Domain of the url. |
url.path |
wildcard |
Path of the request, such as "/search". |
url.username |
keyword |
Username of the request. |
user.domain |
keyword |
Name of the directory the user is a member of. |
user.email |
keyword |
User email address. |
user.id |
keyword |
Unique identifier of the user. |
user.name |
keyword |
Short name or login of the user. |
user_agent.original |
keyword |
Unparsed user_agent string. |
For more information on the Intake Format, please find the code of the Parser, Smart Descriptions, and Supported Events here.